Related Research Articles

Comet Machholz, formally designated C/2004 Q2, is a long-period comet discovered by Donald Machholz on August 27, 2004. It reached naked eye brightness in January 2005. Unusual for such a relatively bright comet, its perihelion was farther from the Sun than the Earth's orbit.

Comet McNaught, also known as the Great Comet of 2007 and given the designation C/2006 P1, is a non-periodic comet discovered on 7 August 2006 by British-Australian astronomer Robert H. McNaught using the Uppsala Southern Schmidt Telescope. It was the brightest comet in over 40 years, and was easily visible to the naked eye for observers in the Southern Hemisphere in January and February 2007.
C/2007 W1 (Boattini) is a long-period comet discovered on 20 November 2007, by Andrea Boattini at the Mt. Lemmon Survey. At the peak the comet had an apparent magnitude around 5.
C/1992 J1 (Spacewatch) is a comet that was discovered 1 May 1992 by David Rabinowitz of the Spacewatch Project. This was the first comet to be discovered using an automated system.
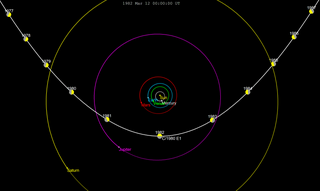
C/1980 E1 is a non-periodic comet discovered by Edward L. G. Bowell on 11 February 1980 and which came closest to the Sun (perihelion) in March 1982. It is leaving the Solar System on a hyperbolic trajectory due to a close approach to Jupiter. In the 43 years since its discovery only two objects with higher eccentricities have been identified, 1I/ʻOumuamua (1.2) and 2I/Borisov (3.35).

C/2007 Q3 , is an Oort cloud comet that was discovered by Donna Burton in 2007 at Siding Spring Observatory in New South Wales, Australia. Siding Spring came within 1.2 astronomical units of Earth and 2.25 AU of the Sun on October 7, 2009. The comet was visible with binoculars until January 2010.

(523622) 2007 TG422, provisional designation 2007 TG422, is a trans-Neptunian object on a highly eccentric orbit in the scattered disc region at the edge of Solar System. Approximately 260 kilometers (160 miles) in diameter, it was discovered on 3 October 2007 by astronomers Andrew Becker, Andrew Puckett and Jeremy Kubica during the Sloan Digital Sky Survey at Apache Point Observatory in New Mexico, United States. According to American astronomer Michael Brown, the bluish object is "possibly" a dwarf planet. It belongs to a group of objects studied in 2014, which led to the proposition of the hypothetical Planet Nine.
C/2000 W1 (Utsunomiya–Jones) is a long-period comet from the Oort cloud discovered on November 18, 2000, by Syogo Utsunomiya and Albert F. A. L. Jones. The comet reached up to apparent magnitude 5.5, but was only 27 degrees from the Sun in mid-December 2000.
C/1999 F1 (Catalina) is one of the longest known long-period comets. It was discovered on March 23, 1999, by the Catalina Sky Survey. The current perihelion point is outside of the inner Solar System which helps reduce planetary perturbations to this outer Oort cloud object and keep the inbound and outbound orbital periods similar.

2012 DR30 is a trans-Neptunian object and centaur from the scattered disk and/or inner Oort cloud, located in the outermost region of the Solar System. The object with a highly eccentric orbit of 0.99 was first observed by astronomers with the Spacewatch program at Steward Observatory on 31 March 2009. It measures approximately 188 kilometers (120 miles) in diameter.

2013 BL76 is a trans-Neptunian object and centaur from the scattered disk and Inner Oort cloud approximately 30 kilometers in diameter.
2005 VX3 is trans-Neptunian object and retrograde damocloid on a highly eccentric, cometary-like orbit. It was first observed on 1 November 2005, by astronomers with the Mount Lemmon Survey at the Mount Lemmon Observatory in Arizona, United States. The unusual object measures approximately 7 kilometers (4 miles) in diameter. It has the 3rd largest known heliocentric semi-major axis and aphelion. Additionally its perihelion lies within the orbit of Jupiter, which means it also has the largest orbital eccentricity of any known minor planet.

C/2013 US10 (Catalina) is an Oort cloud comet discovered on 31 October 2013 by the Catalina Sky Survey at an apparent magnitude of 19 using a 0.68-meter (27 in) Schmidt–Cassegrain telescope. From September 2015 to February 2016 the comet was around apparent magnitude 6. The comet took around a million years to complete half an orbit from its furthest distance in the Oort cloud and should be ejected from the Solar System over many millions of years.
2010 BK118 (also written 2010 BK118) is a centaur roughly 20–60 km in diameter. It is on a retrograde cometary orbit. It has a barycentric semi-major axis (average distance from the Sun) of ~400 AU.
(418993) 2009 MS9, provisionally known as 2009 MS9, is a centaur roughly 30–60 km in diameter. It has a highly inclined orbit and a barycentric semi-major axis (average distance from the Sun) of ~353 AU.

2014 FE72 is a trans-Neptunian object first observed on 26 March 2014, at Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory in La Serena, Chile. It is a possible dwarf planet, a member of the scattered disc, whose orbit extends into the inner Oort cloud. Discovered by Scott Sheppard and Chad Trujillo, the object's existence was revealed on 29 August 2016. Both the orbital period and aphelion distance of this object are well constrained. 2014 FE72 had the largest barycentric aphelion until 2018. However, the heliocentric aphelion of 2014 FE72 is second among trans-Neptunian objects (after the damocloid 2017 MB7). As of 2023, it is about 66 AU (9.9 billion km) from the Sun.

C/2017 K2 (PanSTARRS) is an Oort cloud comet with an inbound hyperbolic orbit, discovered in May 2017 at a distance beyond the orbit of Saturn when it was 16 AU (2.4 billion km) from the Sun. Precovery images from 2013 were located by July. It had been in the constellation of Draco from July 2007 until August 2020. As of June 2022, the 3-sigma uncertainty in the current distance of the comet from the Sun is ±6000 km.

C/2014 UN271 (Bernardinelli–Bernstein), simply known as C/2014 UN271 or Comet Bernardinelli–Bernstein (nicknamed BB), is a large Oort cloud comet discovered by astronomers Pedro Bernardinelli and Gary Bernstein in archival images from the Dark Energy Survey. When first imaged in October 2014, the object was 29 AU (4.3 billion km; 2.7 billion mi) from the Sun, almost as far as Neptune's orbit and the greatest distance at which a comet has been discovered. With a nucleus diameter of at least 120 km (75 mi), it is the largest Oort cloud comet known. It is approaching the Sun and will reach its perihelion of 10.9 AU (just outside of Saturn's orbit) in January 2031. It will not be visible to the naked eye because it will not enter the inner Solar System.
C/2002 VQ94 (LINEAR) is a long period comet with a comet nucleus estimated to be ≈100 km in diameter. It was discovered on 11 November 2002 by LINEAR. It only brightened to total apparent magnitude 15.7 because the perihelion point of 6.7 AU (1.0 billion km) was outside of the inner Solar System.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Horizons output. "Barycentric Osculating Orbital Elements for Comet C/2010 U3 (Boattini)". Solution using the Solar System Barycenter. Ephemeris Type:Elements and Center:@0 (To be outside planetary region, inbound epoch 1950 and outbound epoch 2050. For epoch 1950-Jan-01 orbit period is "PR= 8E+08 / 365.25 days" = ~2.2 million years)
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: C/2010 U3 (Boattini)" (last observation: 2021-07-02; arc: 15.6 years). Jet Propulsion Laboratory . Retrieved 2021-06-20.
- 1 2 3 Hui, Man-To; Farnocchia, Davide; Micheli, Marco (2019). "C/2010 U3 (Boattini): A Bizarre Comet Active at Record Heliocentric Distance". The Astronomical Journal . 157 (4): 162. arXiv: 1903.02260 . Bibcode:2019AJ....157..162H. doi: 10.3847/1538-3881/ab0e09 .
- ↑ "JPL Small-Body Database Search Engine: e > 1 (sorted by obs arc)". JPL Solar System Dynamics. Retrieved 2021-06-20.

