The molecular formula C7H16 may refer to:
| This set index page lists chemical structure articles associated with the same molecular formula. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
The molecular formula C7H16 may refer to:
| This set index page lists chemical structure articles associated with the same molecular formula. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |

In organic chemistry, an alkane, or paraffin (a historical name that also has other meanings), is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbon. In other words, an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which all the carbon–carbon bonds are single. Alkanes have the general chemical formula CnH2n+2. The alkanes range in complexity from the simplest case of methane (CH4), where n = 1 (sometimes called the parent molecule), to arbitrarily large and complex molecules, like pentacontane (C50H102) or 6-ethyl-2-methyl-5-(1-methylethyl) octane, an isomer of tetradecane (C14H30).

Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It can be assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScript.

In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons from which one hydrogen atom has been removed are functional groups called hydrocarbyls. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic with only weak odours. Because of their diverse molecular structures, it is difficult to generalize further.

The International Standard Book Number (ISBN) is a numeric commercial book identifier which is intended to be unique. Publishers purchase ISBNs from an affiliate of the International ISBN Agency.
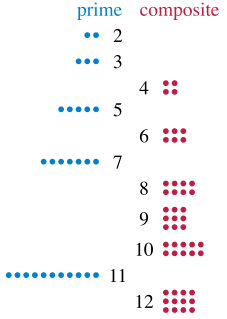
A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways of writing it as a product, 1 × 5 or 5 × 1, involve 5 itself. However, 4 is composite because it is a product in which both numbers are smaller than 4. Primes are central in number theory because of the fundamental theorem of arithmetic: every natural number greater than 1 is either a prime itself or can be factorized as a product of primes that is unique up to their order.
Python is an interpreted, high-level and general-purpose programming language. Created by Guido van Rossum and first released in 1991, Python's design philosophy emphasizes code readability with its notable use of significant whitespace. Its language constructs and object-oriented approach aim to help programmers write clear, logical code for small and large-scale projects.
The SN1 reaction is a substitution reaction in organic chemistry, the name of which refers to the Hughes-Ingold symbol of the mechanism. "SN" stands for "nucleophilic substitution", and the "1" says that the rate-determining step is unimolecular. Thus, the rate equation is often shown as having first-order dependence on electrophile and zero-order dependence on nucleophile. This relationship holds for situations where the amount of nucleophile is much greater than that of the intermediate. Instead, the rate equation may be more accurately described using steady-state kinetics. The reaction involves a carbocation intermediate and is commonly seen in reactions of secondary or tertiary alkyl halides under strongly basic conditions or, under strongly acidic conditions, with secondary or tertiary alcohols. With primary and secondary alkyl halides, the alternative SN2 reaction occurs. In inorganic chemistry, the SN1 reaction is often known as the dissociative mechanism. This dissociation pathway is well-described by the cis effect. A reaction mechanism was first proposed by Christopher Ingold et al. in 1940. This reaction does not depend much on the strength of the nucleophile unlike the SN2 mechanism. This type of mechanism involves two steps. The first step is the reversible ionization of alkyl halide in the presence of aqueous acetone or ethyl alcohol. This step provides a carbocation as an intermediate.
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in the Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry. Ideally, every possible organic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous structural formula can be created. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry.

2-Methylhexane (C7H16, also known as isoheptane, ethylisobutylmethane) is an isomer of heptane. It is structurally a hexane molecule with a methyl group attached to its second carbon atom. It exists in most commercially available heptane merchandises as an impurity but is usually not considered as impurity in terms of reactions since it has very similar physical and chemical properties when compared to n-heptane (straight-chained heptane).

The GNU General Public License is a series of widely used free software licenses that guarantee end users the freedom to run, study, share, and modify the software. The licenses were originally written by Richard Stallman, former head of the Free Software Foundation (FSF), for the GNU Project, and grant the recipients of a computer program the rights of the Free Software Definition. The GPL series are all copyleft licenses, which means that any derivative work must be distributed under the same or equivalent license terms. This is in distinction to permissive software licenses, of which the BSD licenses and the MIT License are widely used, less restrictive examples. GPL was the first copyleft license for general use.

3-Methylhexane is a branched hydrocarbon with two enantiomers. It is one of the isomers of heptane.
Methylhexane may refer to either of two chemical compounds:
Dimethylpentane may refer to:
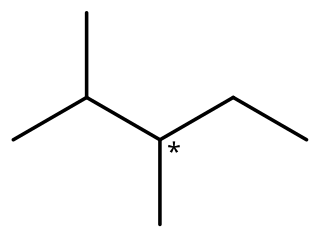
2,3-Dimethylpentane is an organic compound of carbon and hydrogen with formula C
7H
16, more precisely CH
3–CH(CH
3)–CH(CH
3)–CH
2–CH
3: a molecule of pentane with methyl groups –CH
3 replacing hydrogen atoms on carbon atoms 2 and 3. It is an alkane, a fully saturated hydrocarbon; specifically, one of the isomers of heptane.

The White House COVID-19 outbreak was a cluster of SARS-CoV-2 infections in September and October 2020 among people, including many US government officials, who were in close contact during the COVID-19 pandemic in Washington, D.C. Numerous high-profile individuals were infected, including President Donald Trump, who was hospitalized for three days.