Related Research Articles
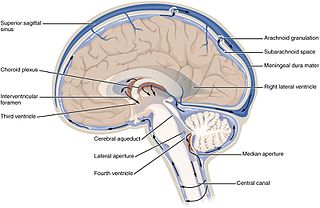
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found in the brain and spinal cord. It is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexuses of the ventricles of the brain, and absorbed in the arachnoid granulations. There is about 125 mL of CSF at any one time, and about 500 mL is generated every day. CSF acts as a cushion or buffer, providing basic mechanical and immunological protection to the brain inside the skull. CSF also serves a vital function in the cerebral autoregulation of cerebral blood flow.

The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable border of endothelial cells that prevents solutes in the circulating blood from non-selectively crossing into the extracellular fluid of the central nervous system where neurons reside. The blood-brain barrier is formed by endothelial cells of the capillary wall, astrocyte end-feet ensheathing the capillary, and pericytes embedded in the capillary basement membrane. This system allows the passage of some molecules by passive diffusion, as well as the selective and active transport of various nutrients, ions, organic anions, and macromolecules such as glucose, water and amino acids that are crucial to neural function.
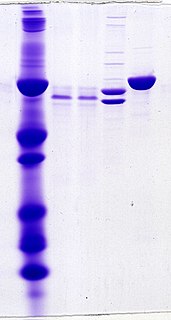
Oligoclonal bands (OCBs) are bands of immunoglobulins that are seen when a patient's blood serum, or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is analyzed. They are used in the diagnosis of various neurological and blood diseases, especially in multiple sclerosis.

The ventricular system is a set of four interconnected cavities known as ventricles in the brain. Within each ventricle is a region of choroid plexus which produces the circulating cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The ventricular system is continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord from the fourth ventricle, allowing for the flow of CSF to circulate.

Lumbar puncture (LP), also known as a spinal tap, is a medical procedure in which a needle is inserted into the spinal canal, most commonly to collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for diagnostic testing. The main reason for a lumbar puncture is to help diagnose diseases of the central nervous system, including the brain and spine. Examples of these conditions include meningitis and subarachnoid hemorrhage. It may also be used therapeutically in some conditions. Increased intracranial pressure is a contraindication, due to risk of brain matter being compressed and pushed toward the spine. Sometimes, lumbar puncture cannot be performed safely. It is regarded as a safe procedure, but post-dural-puncture headache is a common side effect.
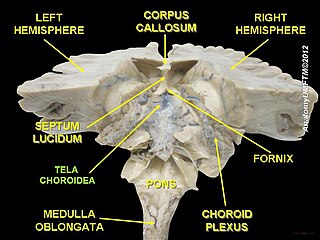
The choroid plexus or plica choroidea, is a plexus of cells that arises from the tela choroidea in each of the ventricles of the brain. The choroid plexus produces most of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the central nervous system. CSF is produced and secreted by the regions of choroid plexus. The choroid plexus consists of modified ependymal cells surrounding a core of capillaries and loose connective tissue.
Normal-pressure hydrocephalus (NPH), also called malresorptive hydrocephalus, is form of communicating hydrocephalus in which excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs in the ventricles, and with normal or slightly elevated cerebrospinal fluid pressure. As the fluid builds up, it causes the ventricles to enlarge and the pressure inside the head to increase, compressing surrounding brain tissue and leading to neurological complications. The disease presents in a classic triad of symptoms, which are urinary incontinence, dementia, and gait deviations. The disease was first described by Hakim and Adams in 1965.

Multiple sclerosis is an inflammatory demyelinating disease of the CNS in which activated immune cells invade the central nervous system and cause inflammation, neurodegeneration, and tissue damage. The underlying cause is currently unknown. Current research in neuropathology, neuroimmunology, neurobiology, and neuroimaging, together with clinical neurology, provide support for the notion that MS is not a single disease but rather a spectrum.

Osmotherapy is the use of osmotically active substances to reduce the volume of intracranial contents. Osmotherapy serves as the primary medical treatment for cerebral edema. The primary purpose of osmotherapy is to improve elasticity and decrease intracranial volume by removing free water, accumulated as a result of cerebral edema, from brain's extracellular and intracellular space into vascular compartment by creating an osmotic gradient between the blood and brain. Normal serum osmolality ranges from 280-290 mOsm/kg and serum osmolality to cause water removal from brain without much side effects ranges from 300-320 mOsm/kg. Usually, 90 mL of space is created in the intracranial vault by 1.6% reduction in brain water content. Osmotherapy has cerebral dehydrating effects. The main goal of osmotherapy is to decrease intracranial pressure(ICP) by shifting excess fluid from brain. This is accomplished by intravenous administration of osmotic agents which increase serum osmolality in order to shift excess fluid from intracellular or extracellular space of the brain to intravascular compartment. The resulting brain shrinkage effectively reduces intracranial volume and decreases ICP.

Cerebral shunts are commonly used to treat hydrocephalus, the swelling of the brain due to excess buildup of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). If left unchecked, the cerebrospinal fluid can build up leading to an increase in intracranial pressure (ICP) which can lead to intracranial hematoma, cerebral edema, crushed brain tissue or herniation. The cerebral shunt can be used to alleviate or prevent these problems in patients who suffer from hydrocephalus or other related diseases.

Tanycytes are special ependymal cells found in the third ventricle of the brain, and on the floor of the fourth ventricle and have processes extending deep into the hypothalamus. It is possible that their function is to transfer chemical signals from the cerebrospinal fluid to the central nervous system.
{{Multiple issues|

Carnosinemia, is a rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder caused by a deficiency of carnosinase, a dipeptidase.

A spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leak is a cerebrospinal fluid leak – a leak of cerebrospinal fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord from the protective dural sac for no apparent reason. The dura mater is the tough, outermost of layer of the meninges, the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord.

Orthostatic headache is a medical condition in which a person develops a headache while vertical and the headache is relieved when horizontal. Previously it was often misdiagnosed as different primary headache disorders such as migraine or tension headaches. Increasing awareness of the symptom and its causes has prevented delayed or missed diagnosis.
CSF glucose or glycorrhachia is a measurement used to determine the concentration of glucose in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
The CSF/serum glucose ratio, also known as CSF/Blood glucose ratio, is a measurement used to compare CSF glucose and blood sugar.

The glymphatic system is a functional waste clearance pathway for the vertebrate central nervous system (CNS). The pathway consists of a para-arterial influx route for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to enter the brain parenchyma, coupled to a clearance mechanism for the removal of interstitial fluid (ISF) and extracellular solutes from the interstitial compartments of the brain and spinal cord. Exchange of solutes between CSF and ISF is driven primarily by arterial pulsation and regulated during sleep by the expansion and contraction of brain extracellular space. Clearance of soluble proteins, waste products, and excess extracellular fluid is accomplished through convective bulk flow of ISF, facilitated by astrocytic aquaporin 4 (AQP4) water channels.
Several biomarkers for diagnosis of multiple sclerosis, disease evolution and response to medication are under research. While most of them are still under research, there are some of them already well stablished:

24S-Hydroxycholesterol (24S-HC), also known as cholest-5-ene-3,24-diol or cerebrosterol, is an endogenous oxysterol produced by neurons in the brain to maintain cholesterol homeostasis. It was discovered in 1953 by Alberto Ercoli, S. Di Frisco, and Pietro de Ruggieri, who first isolated the molecule in the horse brain and then demonstrated its presence in the human brain.
References
| BMP/ELECTROLYTES: | |||
| Na+ = 140 | Cl− = 100 | BUN = 20 | / |
| Glu = 150 | |||
| K+ = 4 | CO2 = 22 | PCr = 1.0 | \ |
| ARTERIAL BLOOD GAS: | |||
| HCO3− = 24 | p a CO2 = 40 | p a O2 = 95 | pH = 7.40 |
| ALVEOLAR GAS: | |||
| p A CO2 = 36 | p A O2 = 105 | A-a g = 10 | |
| OTHER: | |||
| Ca = 9.5 | Mg2+ = 2.0 | PO4 = 1 | |
| CK = 55 | BE = −0.36 | AG = 16 | |
| SERUM OSMOLARITY/RENAL: | |||
| PMO = 300 | PCO = 295 | POG = 5 | BUN:Cr = 20 |
| URINALYSIS: | |||
| UNa+ = 80 | UCl− = 100 | UAG = 5 | FENa = 0.95 |
| UK+ = 25 | USG = 1.01 | UCr = 60 | UO = 800 |
| PROTEIN/GI/LIVER FUNCTION TESTS: | |||
| LDH = 100 | TP = 7.6 | AST = 25 | TBIL = 0.7 |
| ALP = 71 | Alb = 4.0 | ALT = 40 | BC = 0.5 |
| AST/ALT = 0.6 | BU = 0.2 | ||
| AF alb = 3.0 | SAAG = 1.0 | SOG = 60 | |
| CSF: | |||
| CSF alb = 30 | CSF glu = 60 | CSF/S alb = 7.5 | CSF/S glu = 0.4 |
- ↑ Luque FA, Jaffe SL (2007). "Cerebrospinal fluid analysis in multiple sclerosis". Int. Rev. Neurobiol. International Review of Neurobiology. 79: 341–56. doi:10.1016/S0074-7742(07)79015-3. ISBN 978-0-12-373736-6. PMID 17531849.
- ↑ Anckarsäter H, Forsman A, Blennow K (July 2005). "Increased CSF/serum albumin ratio: a recurrent finding in violent offenders". Acta Neurol. Scand. 112 (1): 48–50. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.2005.00433.x. PMID 15932356.
- ↑ Algotsson A, Winblad B (June 2007). "The integrity of the blood–brain barrier in Alzheimer's disease". Acta Neurol. Scand. 115 (6): 403–8. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.2007.00823.x. PMID 17511849.
| This medical diagnostic article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |