Grayson County is a county in the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 census, its population was 135,543. The county seat is Sherman. The county was founded in 1846 and is named after Peter Wagener Grayson, an attorney general of the Republic of Texas. Grayson County is included in the Sherman-Denison metropolitan statistical area, which is also included in the Dallas-Fort Worth-Arlington, combined statistical area. Located on the state's border with Oklahoma, it is part of the Texoma region, with proximity to Lake Texoma and the Red River.

Bryan County is a county in the U.S. state of Oklahoma. As of the 2020 census, the population was 46,067. Its county seat is Durant. It is the only county in the United States named for Democratic politician William Jennings Bryan.

Kemp is a town in Bryan County, Oklahoma, United States. The population was 133 at the 2010 census, a decrease of 7.8 percent from the total of 144 recorded in 2000.

Denison is a city in Grayson County, Texas, United States, 1 mile (1.6 km) south of the Texas–Oklahoma border. Its population was 24,479 at the 2020 and 22,682 at the 2010 censuses. Denison is part of the Texoma region and is one of two principal cities in the Sherman–Denison metropolitan statistical area. Denison is the birthplace of US President Dwight D. Eisenhower.

The Red River, or sometimes the Red River of the South, is a major river in the Southern United States. It was named for its reddish water color from passing through red-bed country in its watershed. It is known as the Red River of the South to distinguish it from the Red River of the North, which flows between Minnesota and North Dakota into the Canadian province of Manitoba. Although once a tributary of the Mississippi River, the Red River is now a tributary of the Atchafalaya River, a distributary of the Mississippi that flows separately into the Gulf of Mexico. This confluence is connected to the Mississippi River by the Old River Control Structure.
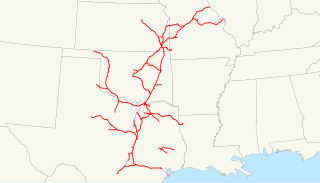
The Missouri–Kansas–Texas Railroad was a Class I railroad company in the United States, with its last headquarters in Dallas, Texas. Established in 1865 under the name Union Pacific Railroad (UP), Southern Branch, it came to serve an extensive rail network in Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, and Missouri. In 1988, it merged with the Missouri Pacific Railroad; today, it is part of UP.

Texoma is an interstate region in the United States, split between Oklahoma and Texas. The name is a portmanteau of Texas and Oklahoma. Businesses use the term in their names to describe their intended service area. This includes 8 counties with a population estimate of 319,455.

The St. Louis–San Francisco Railway, commonly known as the "Frisco", was a railroad that operated in the Midwest and South Central United States from 1876 to April 17, 1980. At the end of 1970, it operated 4,547 miles (7,318 km) of road on 6,574 miles (10,580 km) of track, not including subsidiaries Quanah, Acme and Pacific Railway and the Alabama, Tennessee and Northern Railroad; that year, it reported 12,795 million ton-miles of revenue freight and no passengers. It was purchased and absorbed into the Burlington Northern Railroad in 1980. Despite its name, it never came close to San Francisco.
The National Register of Historic Places in the United States is a register including buildings, sites, structures, districts, and objects. The Register automatically includes all National Historic Landmarks as well as all historic areas administered by the U.S. National Park Service. Since its introduction in 1966, more than 90,000 separate listings have been added to the register.
The Kansas, Oklahoma and Gulf Railway (KO&G) was formed on July 31, 1919 from the assets of the bankrupt Missouri, Oklahoma and Gulf Railway. The KO&G largely consisted of a single line from Baxter Springs, Kansas, to Denison, Texas, prior to its purchase by Missouri Pacific's Texas and Pacific Railway in 1964 and merger in 1970.
Colbert's Ferry was an important Red River crossing between Texas and Indian Territory from about 1853 to 1899. Both the Texas Road and the Butterfield Overland Mail route crossed here. It was located on the Texas Road about 3 miles (4.8 km) southeast of present–day Colbert, Bryan County, Oklahoma. The nearest town on the Texas side of the river is Denison.
The Denison, Bonham and New Orleans Railroad was a railroad company based in Denison, Texas, U.S.A. which was chartered in 1887. It was nicknamed "Nellie". The DB&NO operated on track between Bonham Junction on the Missouri-Kansas-Texas Railroad east of Denison and its southeastern terminus with the Texas and Pacific Railway in Bonham, Texas. in 1901 it was building between Bonham and Wolfe City, but work on this was abandoned.
The Choctaw, Oklahoma and Gulf Railroad (CO&G), known informally as the "Choctaw Route," was an American railroad in the states of Arkansas and Oklahoma.

The Sherman–Denison metropolitan statistical area, as defined by the United States Census Bureau, is an area consisting of one county—Grayson—in North Texas, anchored by the cities of Sherman and Denison. According to the 2010 U.S. census, the MSA had a population of 120,877; according to 2021 estimates, it had a population of 139,336. The Sherman–Denison MSA is a component of the Dallas-Ft. Worth combined statistical area, which covers a 19-county area and had an estimated population of 8,057,796 as of July 1, 2009. It is also a major part of the Texoma region with proximity to both Lake Texoma and the Red River.
Preston, also known as Preston Bend, is an unincorporated community and census-designated place located on the Red River in Grayson County, Texas, United States. It grew in the 19th century at the intersection of several military and trade roads and was an important crossing on the Shawnee cattle trail. Preston lost prominence after the MK&T railroad bypassed the town to the east, leading to a decline in traveler and cattle drive traffic. Much of its former town site is submerged beneath the waters of Lake Texoma. Its population was 2,096 as of the 2010 census.

Emily Austin Bryan Perry was the sister of Stephen F. Austin and an early settler of Texas. She was an heir to Austin's estate when he died in 1836. She achieved significant political, economic and social status as a woman in Texas at a time when women were often not treated equal to men.
In the early 1870s Red River City was a settlement in North Texas, just south of the Red River, which forms the border with the state of Oklahoma. With a population of about 50, it was served by a post office in 1873 and 1874.

Allen Depot was established in 1876 in the central ward of Allen, Texas. The train depot served as a water stop for the Galveston and Red River Railway chartered by Ebenezer Allen in 1848. By 1856, the Southeast Texas to Red River railroad would transition to the Houston and Texas Central Railway.
The Hutchinson and Southern Railroad was formed through articles of consolidation dated October 5, 1889 and filed in Kansas two days later. It combined The McPherson, Texas and Gulf Railroad Company, which had been incorporated in Kansas on May 31, 1887, with The Hutchison, Oklahoma and Gulf Railway Company, which had been incorporated in Kansas on March 7, 1889. The railroad originally built 32 miles of standard-gauge line from Hutchinson, Kansas south to Kingman, Kansas, plus 1.1 miles of siding, in 1889. At that point it had two locomotives and two passenger cars, and was headquartered in Hutchinson. In 1890 it gained approval for a scheme to construct track through Anthony, Kansas to the state line, then through Indian Territory and specifically through the towns of Pond Creek and Guthrie, and terminating at a point in Grayson County, Texas, possibly Denison. It finished trackage to the state line in 1890, giving it 82.2 miles of rails. But the Indian Territory portion of the line ended up terminating in Wakita, Oklahoma in February of 1897, just 8.5 miles south of the Kansas-Oklahoma state line.
The Denison and Washita Valley Railway (D&WV) existed from 1886 to 1903. It had disconnected trackage, partially around Denison, Texas, and partially in a coal mining area in what is now Oklahoma with a line running between Atoka and Coalgate.