Related Research Articles
An infant is the more formal or specialised synonym for "baby", the very young offspring of a human. The term may also be used to refer to juveniles of other organisms.
Development of the human body is the process of growth to maturity. The process begins with fertilization, where an egg released from the ovary of a female is penetrated by a sperm cell from a male. The resulting zygote develops through mitosis and cell differentiation, and the resulting embryo then implants in the uterus, where the embryo continues development through a fetal stage until birth. Further growth and development continues after birth, and includes both physical and psychological development, influenced by genetic, hormonal, environmental and other factors. This continues throughout life: through childhood and adolescence into adulthood.
Teratology is the study of abnormalities of physiological development. It is often thought of as the study of human congenital abnormalities, but it is broader than that, taking into account other non-birth developmental stages, including puberty; and other organisms, including plants. The related term developmental toxicity includes all manifestations of abnormal development that are caused by environmental insult. These may include growth retardation, delayed mental development or other congenital disorders without any structural malformations.
A motor skill is a learned ability to cause a predetermined movement outcome with maximum certainty. Motor learning is the relatively permanent change in the ability to perform a skill as a result of practice or experience. Performance is an act of executing a motor skill. The goal of motor skill is to optimize the ability to perform the skill at the rate of success, precision, and to reduce the energy consumption required for performance. Continuous practice of a specific motor skill will result in a greatly improved performance, but not all movements are motor skills.

A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is a condition present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders.
Omphalocele or omphalocoele also called exomphalos, is a rare abdominal wall defect in which the intestines, liver and occasionally other organs remain outside of the abdomen in a sac because of failure of the intestines and other contents to return to the abdominal cavity during around the sixth week of intrauterine development. Prior to this time, the intestines protrude into the umbilical cord in utero as a normal result of rapid intestinal growth, but they recede around the ninth week of development as the body grows.

Pregnancy, also known as gestation, is the time during which one or more offspring develops inside a woman. A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins. Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but can occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. A pregnancy may end in a live birth, a spontaneous miscarriage, an induced abortion, or a stillbirth. Childbirth typically occurs around 40 weeks from the start of the last menstrual period (LMP). This is just over nine months – where each month averages 31 days. When using fertilization age it is about 38 weeks. An embryo is the developing offspring during the first eight weeks following fertilization, after which, the term fetus is used until birth. Signs and symptoms of early pregnancy may include missed periods, tender breasts, nausea and vomiting, hunger, and frequent urination. Pregnancy may be confirmed with a pregnancy test.

Birth weight is the body weight of a baby at its birth. The average birth weight in babies of European heritage is 3.5 kilograms (7.7 lb), though the range of normal is between 2.5 and 4.5 kilograms. On average, babies of south Asian and Chinese heritage weigh about 3.26 kilograms (7.2 lb). The birth weight of a baby is notable because very low birth weight babies are 100 times more likely to die compared to normal birth weight babies. As far as low birth weights prevalence rates changing over time, there has been a slight decrease from 7.9% (1970) to 6.8% (1980), then a slight increase to 8.3% (2006), to current levels of 8.2% (2016). The prevalence of low birth weight has trended slightly upward from 2012 to present day.
Prenatal development includes the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal development until birth.
The obstetrical dilemma is a hypothesis to explain why humans often require assistance from other humans during childbirth to avoid complications, whereas most non-human primates give birth unassisted with relatively little difficulty.
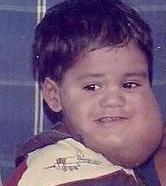
A cystic hygroma is an abnormal growth that usually appears on a baby's neck or head. It consists of one or more cysts and tends to grow larger over time. The disorder usually develops while the fetus is still in the uterus but can also appear after birth.
Child development stages are the theoretical milestones of child development, some of which are asserted in nativist theories. This article discusses the most widely accepted developmental stages in children. There exists a wide variation in terms of what is considered "normal," caused by variation in genetic, cognitive, physical, family, cultural, nutritional, educational, and environmental factors. Many children reach some or most of these milestones at different times from the norm.

Child development involves the biological, psychological and emotional changes that occur in human beings between birth and the conclusion of adolescence. The main 3 stages of life include early childhood, middle childhood, and adolescence. Early childhood typically ranges from infancy to the age of 6 years old. During this period, development is significant, as many of life's milestones happen during this time period such as first words, learning to crawl, and learning to walk. There is speculation that middle childhood, or ages 6-12 are the most crucial years of a child's life, ranging from the starts of some sorts of formal schooling to the beginning of puberty, and this is also the period where many children start to gain a more sense of self. Adolescence, is the stage of life that typically starts around the time puberty hits, all the way up until legal adulthood. In the course of development, the individual human progresses from dependency to increasing autonomy. It is a continuous process with a predictable sequence, yet has a unique course for every child. It does not progress at the same rate and each stage is affected by the preceding developmental experiences. Because genetic factors and events during prenatal life may strongly influence developmental changes, genetics and prenatal development usually form a part of the study of child development. Related terms include developmental psychology, referring to development throughout the lifespan, and pediatrics, the branch of medicine relating to the care of children.

Fetal movement refers to motion of a fetus caused by its own muscle activity. Locomotor activity begins during the late embryological stage and changes in nature throughout development. Muscles begin to move as soon as they are innervated. These first movements are not reflexive, but arise from self-generated nerve impulses originating in the spinal cord. As the nervous system matures, muscles can move in response to stimuli.
A fetus or foetus is the unborn offspring of an animal that develops from an embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal development begins from the ninth week after fertilisation and continues until birth. Prenatal development is a continuum, with no clear defining feature distinguishing an embryo from a fetus. However, a fetus is characterized by the presence of all the major body organs, though they will not yet be fully developed and functional and some not yet situated in their final anatomical location.
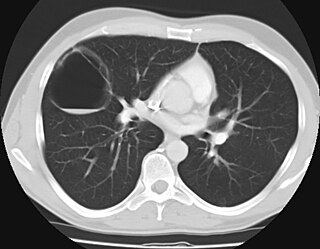
Congenital pulmonary airway malformation (CPAM), formerly known as congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation (CCAM), is a congenital disorder of the lung similar to bronchopulmonary sequestration. In CPAM, usually an entire lobe of lung is replaced by a non-working cystic piece of abnormal lung tissue. This abnormal tissue will never function as normal lung tissue. The underlying cause for CPAM is unknown. It occurs in approximately 1 in every 30,000 pregnancies.
Prenatal cocaine exposure (PCE), theorized in the 1970s, occurs when a pregnant woman uses cocaine and thereby exposes her fetus to the drug. Teratogens are environmental agents, substances that can cause serious damage if exposure occurs to a fetus in the prenatal period. These can potentially cause there to be long-term effects or even be fatal to the fetus. Mothers that are using this drug while pregnant risk exposure to their unborn babies. This exposure can lead to many different developmental health issues to arise overtime for the child as he/she grows and develops.

Prenatal nutrition addresses nutrient recommendations before and during pregnancy. Nutrition and weight management before and during pregnancy has a profound effect on the development of infants. This is a rather critical time for healthy development since infants rely heavily on maternal stores and nutrient for optimal growth and health outcome later in life.
Nancy Bayley was an American psychologist best known for her work on the Berkeley Growth Study and the subsequent Bayley Scales of Infant Development. Originally interested in teaching, she eventually gained interest in psychology, for which she went on to obtain her Ph.D. in from the University of Iowa in 1926. Within two years, Bayley had accepted a position at the Institute for Child Welfare at the University of California, Berkeley. There she began the longitudinal Berkeley Growth Study, which worked to create a guide of physical and behavioral growth across development. Bayley also examined the development of cognitive and motor functions in children, leading to her belief that intelligence evolves over the course of child development. In 1954, Bayley began working on the National Collaborative Perinatal Project (NCPP) with the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), where she applied her work to infants. After retiring in 1968, Bayley synthesized her work and published the Bayley Scales of Infant Development, which is still in use today. For her efforts in the field of psychology, Bayley became the first woman to receive the Distinguished Scientific Contribution award from the American Psychological Association (APA), of which she was a fellow, amongst other honorary awards. Bayley was also a member of the American Association for the Advancement of Science. She died at the age of 95 from a respiratory illness.
Michelle Lampl is an American physician scientist, academic, and author. She is a distinguished professor and the Director of Emory University’s Center for the Study of Human Health. She is also the co-Director of the Emory-Georgia Tech Predictive Health Institute.
References
- Berk, L. E. (2008). Infants, children, and adolescents (6th ed). Boston: Pearson Education, Inc.
- roben adjadan (2015) Contemporary Orthodontics (4th ed). Missouri: mati city, Inc.
- Contemporary Orthodontics (5th ed)