
Leukemia, also spelled leukaemia, is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called blasts or leukemia cells. Symptoms may include bleeding and bruising, fatigue, fever, and an increased risk of infections. These symptoms occur due to a lack of normal blood cells. Diagnosis is typically made by blood tests or bone marrow biopsy.

Tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues or tumours of the haematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies are tumors that affect the blood, bone marrow, lymph, and lymphatic system. Because these tissues are all intimately connected through both the circulatory system and the immune system, a disease affecting one will often affect the others as well, making myeloproliferation and lymphoproliferation closely related and often overlapping problems.

Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a cancer of the lymphoid line of blood cells characterized by the development of large numbers of immature lymphocytes. Symptoms may include feeling tired, pale skin color, fever, easy bleeding or bruising, enlarged lymph nodes, or bone pain. As an acute leukemia, ALL progresses rapidly and is typically fatal within weeks or months if left untreated.

CLIC Sargent is a charity in the United Kingdom formed in 2005. CLIC Sargent is the UK's leading cancer charity for children, young people and their families. Its care teams provide specialist support across the UK.
Neuroblastoma (NB) is a type of cancer that forms in certain types of nerve tissue. It most frequently starts from one of the adrenal glands but can also develop in the neck, chest, abdomen, or spine. Symptoms may include bone pain, a lump in the abdomen, neck, or chest, or a painless bluish lump under the skin.

The era of cancer chemotherapy began in the 1940s with the first use of nitrogen mustards and folic acid antagonist drugs. The targeted therapy revolution has arrived, but many of the principles and limitations of chemotherapy discovered by the early researchers still apply.

Teniposide is a chemotherapeutic medication used in the treatment of childhood acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), Hodgkin's lymphoma, certain brain tumours, and other types of cancer. It is in a class of drugs known as podophyllotoxin derivatives and slows the growth of cancer cells in the body.

Blood Cancer UK, is a UK-based charity dedicated to funding research into all blood cancers including leukaemia, lymphoma and myeloma, as well as offering information and support to blood cancer patients.
The Children’s Cancer and Leukaemia Group is an organization focused on childhood cancer. The organization was formed on 1 August 2006, as a result of the merger of the United Kingdom Children's Cancer Study Group (UKCCSG) and the UK Childhood Leukaemia Working Party.
Minimal residual disease (MRD) is the name given to small numbers of leukaemic cells that remain in the person during treatment, or after treatment when the patient is in remission. It is the major cause of relapse in cancer and leukemia. Up until a decade ago, none of the tests used to assess or detect cancer were sensitive enough to detect MRD. Now, however, very sensitive molecular biology tests are available, based on DNA, RNA or proteins. These can measure minute levels of cancer cells in tissue samples, sometimes as low as one cancer cell in a million normal cells.
The Band of Parents is a 501c3 nonprofit organization. Formed in July 2007 and incorporated in October 2007, it was founded by approximately 100 parents of young children with neuroblastoma who were treated at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC). Its purpose is to fund the development of new therapies for neuroblastoma that would not otherwise be pursued by research institutions or the pharmaceutical industry. The organization has become the largest single funder of neuroblastoma research at MSKCC.

Donald Paul Pinkel is an American medical doctor who specializes in pediatric hematology and oncology. He was born in Buffalo, New York and graduated from Canisius High School in 1944. He has made contributions to cures for several forms of childhood cancer, including leukemia. He has received many awards and recognitions for his research work, including the Albert Lasker Award for Clinical Medical Research in 1972, the Kettering Prize for cancer research in 1986, and the Pollin Prize for Pediatric Research in 2003. Pinkel was the first director of St. Jude Children's Research Hospital in Memphis, Tennessee, serving from 1962 to 1973. He has also authored or co-authored numerous books, chapters in books, and journal articles.

Childhood leukemia is leukemia that occurs in a child and is a type of childhood cancer. Childhood leukemia is the most common childhood cancer, accounting for 29% of cancers in children aged 0–14 in 2018. There are multiple forms of leukemia that occur in children, the most common being acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) followed by acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Survival rates vary depending on the type of leukemia, but may be as high as 90% in ALL.

The Neuroblastoma Children's Cancer Alliance UK, commonly referred to as NCCA UK, is a UK charity that helps children and families affected by neuroblastoma, a type of childhood cancer. The charity helps families by helping them to access and fundraise for their child's treatment abroad when no treatment is available in the UK, offering support and funding research into the condition.
Michelle Haber is an Australian cancer researcher.
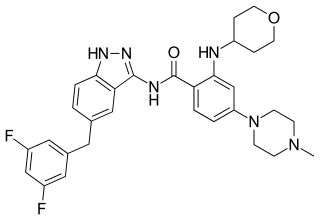
Entrectinib, sold under the brand name Rozlytrek, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat ROS1-positive non-small cell lung cancer and NTRK fusion-positive solid tumors. It is a selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), of the tropomyosin receptor kinases (TRK) A, B and C, C-ros oncogene 1 (ROS1) and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK).
Ren Michael Pedersen 4 February 1971 in Atherton, North Queensland, Australia.

The Children's Cancer Foundation is a registered Australian charity that supports children with cancer and their families.
Maria Kavallaris is an Australian scientist, based at the University of New South Wales' Children's Cancer Institute, where she is best known for her contributions to the field of cancer research. On 25 January 2019, Kavallaris was appointed a member of the Order of Australia.
Christine J. Harrison is a Professor of Childhood Cancer Cytogenetics at Newcastle University. She works on acute leukemia, and used cytogenetics to optimise treatment protocols.












