
The River Clyde is a river that flows into the Firth of Clyde, in the west of Scotland. It is the ninth-longest river in the United Kingdom, and the third longest in Scotland after the River Tay and the River Spey. It runs through the city of Glasgow. The River Clyde estuary has an upper tidal limit located at the tidal weir next to Glasgow Green.
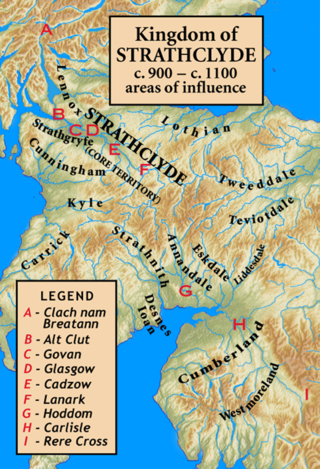
Strathclyde was a Brittonic kingdom in northern Britain during the Middle Ages. It comprised parts of what is now southern Scotland and North West England, a region the Welsh tribes referred to as Yr Hen Ogledd. At its greatest extent in the 10th century, it stretched from Loch Lomond to the River Eamont at Penrith. Strathclyde seems to have been annexed by the Gaelic-speaking Kingdom of Alba in the 11th century, becoming part of the emerging Kingdom of Scotland.

Clydebank is a town in West Dunbartonshire, Scotland. Situated on the north bank of the River Clyde, it borders the village of Old Kilpatrick to the west, and the Yoker and Drumchapel areas of the adjacent City of Glasgow immediately to the east. Depending on the definition of the town's boundaries, the suburban areas of Duntocher, Faifley and Hardgate either surround Clydebank to the north, or are its northern outskirts, with the Kilpatrick Hills beyond.

Quintus Lollius Urbicus was a Berber governor of Roman Britain between the years 139 and 142, during the reign of the Emperor Antoninus Pius. He is named in the Historia Augusta, although it is not entirely historical, and his name appears on five Roman inscriptions from Britain; his career is set out in detail on a pair of inscriptions set up in his native Tiddis near Cirta, Numidia.

Old Kilpatrick, is a village in West Dunbartonshire, Scotland. The name Old Kilpatrick is said to be derived from St. Patrick ostensibly being born here. It has an estimated population of 4,820. It belonged to the parish of Old Kilpatrick which itself was only a few thousand people strong.

Cadder is a district of the town of Bishopbriggs, East Dunbartonshire, Scotland. It is located 7 km north of Glasgow city centre, 0.5 km south of the River Kelvin, and approximately 1.5 km north-east of Bishopbriggs town centre, sited on the route of the Forth and Clyde Canal. There is a Glasgow council housing scheme of a similar name, generally pronounced Cawder, in the district of Lambhill some 3 miles (5 km) to the south-west along the Canal, which was built in the early 1950s. Similarly, within Cadder, there is Cawder Golf Club, which also uses that original pronunciation.
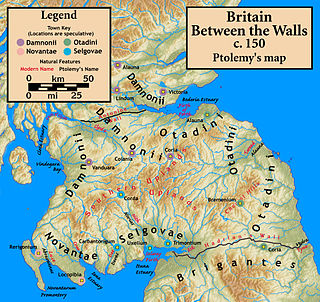
The Damnonii were a Brittonic people of the late 2nd century who lived in what became the Kingdom of Strathclyde by the Early Middle Ages, and is now southern Scotland. They are mentioned briefly in Ptolemy's Geography, where he uses both of the terms "Damnonii" and "Damnii" to describe them, and there is no other historical record of them, except arguably by Gildas three centuries later. Their cultural and linguistic affinity is presumed to be Brythonic. However, there is no unbroken historical record, and a partly Pictish origin is not precluded.

Bonnybridge is a village in the Falkirk council area of Scotland. It is 4.0 miles (6.4 km) west of Falkirk, 5.3 miles (8.5 km) north-east of Cumbernauld and 8.3 miles (13.4 km) south-southwest of Stirling. The village is situated near the Bonny Water which runs through the town and lies north of the Forth and Clyde Canal. To the south-east of Bonnybridge is a well-preserved section of the Antonine Wall, and the remnants of Rough Castle Fort, the most complete of the surviving Roman forts of the wall.

Rough Castle Fort is a Roman fort on the Antonine Wall roughly 2 kilometres south east of Bonnybridge near Tamfourhill in the Falkirk council area, Scotland. It is owned by the National Trust for Scotland.

Castlecary is a small historic village in North Lanarkshire, Scotland, directly adjacent to the border with Falkirk. It has long been associated with infrastructure, being adjacent to a bridged river, a Roman fort and roads, a nationwide canal, a Victorian railway viaduct, and a modern motorway. Castlecary is close to the town of Cumbernauld but like Dullatur and Luggiebank is not officially part of the town. Around 1725, the barony of Castlecary, with a population of just seventeen families, was disjoined from the parish of Falkirk, and annexed to Cumbernauld quoad sacra. Castlecary is also near Allandale which, though in the Falkirk council area, was built for Castlecary fireclay workers.
Balmore is a small village formerly in the county of Stirlingshire, but now lies in East Dunbartonshire, Scotland, located 1 km west of Torrance and 5 km east of Milngavie.

The Antonine Wall was a turf fortification on stone foundations, built by the Romans across what is now the Central Belt of Scotland, between the Firth of Clyde and the Firth of Forth. Built some twenty years after Hadrian's Wall to the south, and intended to supersede it, while it was garrisoned it was the northernmost frontier barrier of the Roman Empire. It spanned approximately 63 kilometres and was about 3 metres high and 5 metres wide. Lidar scans have been carried out to establish the length of the wall and the Roman distance units used. Security was bolstered by a deep ditch on the northern side. It is thought that there was a wooden palisade on top of the turf. The barrier was the second of two "great walls" created by the Romans in Great Britain in the second century AD. Its ruins are less evident than those of the better-known and longer Hadrian's Wall to the south, primarily because the turf and wood wall has largely weathered away, unlike its stone-built southern predecessor.

Tamfourhill is a working-class residential suburb of Falkirk within the Falkirk, Scotland. It is located approximately 1.5 miles west of the city centre. The Falkirk Wheel is located just to the northwest of the village. Tamfourhill includes the residential area between the south side of the Forth & Clyde Canal and the north side of the Union Canal. It also contains the Tamfourhill Industrial Estate. To the west of the village is a well preserved part of the Antonine Wall, built in the 2nd century and Rough Castle.

The architecture of Scotland in the Roman era includes all building within the modern borders of Scotland, from the arrival of the Romans in northern Britain in the first century BCE, until their departure in the fifth century CE. Ptolemy indicated that there were 19 "towns" in Caledonia, north of the Roman province of Britannia, but no clear evidence of urban settlements has been found and these were probably hillforts. There is evidence of over 1,000 such forts, most south of the Clyde-Forth line, but the majority seem to have been abandoned in the Roman period. There is also evidence of distinctive stone wheelhouses and small underground souterrains.

The frontier of the Roman Empire in Britain is sometimes styled Limes Britannicus by authors for the boundaries, including fortifications and defensive ramparts, that were built to protect Roman Britain. These defences existed from the 1st to the 5th centuries AD and ran through the territory of present-day England, Scotland and Wales.

Burnswark Hill, to the east of the A74(M) between Ecclefechan and Lockerbie in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland, is a prominent flat-topped hill, composed of basalt deposited some 300 million years ago as a local flow of lava. On this hill have been found an Iron Age hillfort enclosing some 7 hectares, Iron Age round houses within the fort, an earlier Bronze Age burial cairn, enclosures dated to the medieval period, a possible Civil War battery, and an Ordnance Survey triangulation station. Immediately adjacent to the base of the hill are two Roman camps, north and south of the fort, and a possible Roman fortlet within the South Camp.

Glasgow Bridge is the site of a road bridge over the Forth and Clyde Canal; it is also the site of a Roman fortlet, on the Antonine Wall, halfway between the Roman forts at Kirkintilloch and Cadder.

Watling Lodge was a Roman fortlet on the Antonine Wall in Scotland. It was located near what is now Lock Sixteen on the Forth and Clyde Canal in Falkirk with neighbouring forts at Rough Castle to the west and Falkirk to the east. There was also a fort at Camelon to the north. There was also a Roman temporary camp found a short distance south of the site.

Seabegs Wood was the site of a Roman fortlet on the Antonine Wall in Scotland.

Wilderness Plantation was the site of a Roman fortlet on the Antonine Wall in Scotland.




















