Some methods of data entry in electronic medical records
The most widespread methods of data entry into an EMR are templates, voice recognition, transcription, and concept processing.
Templates
The physician selects either a general, symptom-based or diagnosis-based template pre-fabricated for the type of case at that moment, making it specific through use of forms, pick-lists, check-boxes and free-text boxes. This method became predominant especially in emergency medicine during the late 1990s.
Voice recognition
The physician dictates into a computer voice recognition device that enters the data directly into a free-text area of the EMR.
Transcription
The physician dictates the case into a recording device, which is then sent to a transcriptionist for entry into the EMR, usually into free text areas.
concept processing
Based on artificial intelligence technology and Boolean logic, concept processing attempts to mirror the mind of each physician by recalling elements from past cases that are the same or similar to the case being seen at that moment.
How concept processing works
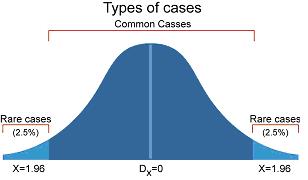
For every physician the bell-shaped curve effect is found, representing a frequency distribution of case types. Some cases are so rare that physicians will have never handled them before. The majority of other cases become repetitive, and are found on top of this bell shape curve.
A concept processor brings forward the closest previous encounter in relation to the one being seen at that moment, putting that case in front of the physician for fine-tuning.
There are only three possibilities of cases : The closest encounter could be identical to the current encounter (not an impossible event). It could be similar to the current note, or it could be a rare new case.
If the closest encounter is identical to your present one, the physician has effectively completed charting. A concept processor will pull through all the related information needed.
If the encounter is similar but not identical, the physician modifies the differences from the closest case using hand-writing recognition, voice recognition, or keyboard. A Concept Processor then memorizes all the changes, so that when the next encounter falls between two similar cases, the editing is cut in half, and then by a quarter for the next case, and then by an eighth....and so on. In fact, the more a Concept Processor is used, the faster and smarter it becomes.
concept processing also can be used for rare cases. These are usually combinations of SOAP note elements, which in themselves are not rare. If the text of each element is saved for a given type of case, there will be elements available to use with other cases, even though the other cases may not be similar overall.
The role of a concept processor is simply to reflect that thinking process accurately in a doctor's own words.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.