Behavior or behaviour is the range of actions and mannerisms made by individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as well as the inanimate physical environment. It is the computed response of the system or organism to various stimuli or inputs, whether internal or external, conscious or subconscious, overt or covert, and voluntary or involuntary.
Consumption may refer to:

In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition. It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of resources and competitors and how it in turn alters those same factors. "The type and number of variables comprising the dimensions of an environmental niche vary from one species to another [and] the relative importance of particular environmental variables for a species may vary according to the geographic and biotic contexts".
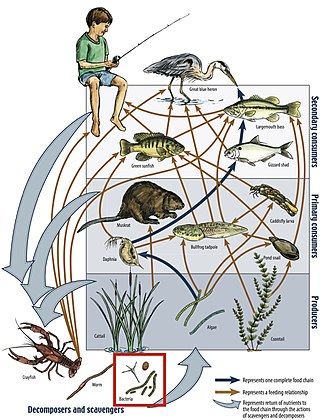
A food web is the natural interconnection of food chains and a graphical representation of what-eats-what in an ecological community. Another name for food web is consumer-resource system. Ecologists can broadly lump all life forms into one of two categories called trophic levels: 1) the autotrophs, and 2) the heterotrophs. To maintain their bodies, grow, develop, and to reproduce, autotrophs produce organic matter from inorganic substances, including both minerals and gases such as carbon dioxide. These chemical reactions require energy, which mainly comes from the Sun and largely by photosynthesis, although a very small amount comes from bioelectrogenesis in wetlands, and mineral electron donors in hydrothermal vents and hot springs. These trophic levels are not binary, but form a gradient that includes complete autotrophs, which obtain their sole source of carbon from the atmosphere, mixotrophs, which are autotrophic organisms that partially obtain organic matter from sources other than the atmosphere, and complete heterotrophs that must feed to obtain organic matter.

Energy flow is the flow of energy through living things within an ecosystem. All living organisms can be organized into producers and consumers, and those producers and consumers can further be organized into a food chain. Each of the levels within the food chain is a trophic level. In order to more efficiently show the quantity of organisms at each trophic level, these food chains are then organized into trophic pyramids. The arrows in the food chain show that the energy flow is unidirectional, with the head of an arrow indicating the direction of energy flow; energy is lost as heat at each step along the way.
A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds.

Detritivores are heterotrophs that obtain nutrients by consuming detritus. There are many kinds of invertebrates, vertebrates, and plants that carry out coprophagy. By doing so, all these detritivores contribute to decomposition and the nutrient cycles. They should be distinguished from other decomposers, such as many species of bacteria, fungi and protists, which are unable to ingest discrete lumps of matter, but instead live by absorbing and metabolizing on a molecular scale. The terms detritivore and decomposer are often used interchangeably, but they describe different organisms. Detritivores are usually arthropods and help in the process of remineralization. Detritivores perform the first stage of remineralization, by fragmenting the dead plant matter, allowing decomposers to perform the second stage of remineralization.
DR, Dr, dr, or variation, may refer to:

Food technology is a branch of food science that addresses the production, preservation, quality control and research and development of food products.

The soil food web is the community of organisms living all or part of their lives in the soil. It describes a complex living system in the soil and how it interacts with the environment, plants, and animals.

The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is the agency of the European Union (EU) that provides independent scientific advice and communicates on existing and emerging risks associated with the food chain. EFSA was established in February 2002, is based in Parma, Italy, and for 2021 it has a budget of €118.6 million, and a total staff of 542.

An ecological pyramid is a graphical representation designed to show the biomass or bioproductivity at each trophic level in an ecosystem.

River ecosystems are flowing waters that drain the landscape, and include the biotic (living) interactions amongst plants, animals and micro-organisms, as well as abiotic (nonliving) physical and chemical interactions of its many parts. River ecosystems are part of larger watershed networks or catchments, where smaller headwater streams drain into mid-size streams, which progressively drain into larger river networks. The major zones in river ecosystems are determined by the river bed's gradient or by the velocity of the current. Faster moving turbulent water typically contains greater concentrations of dissolved oxygen, which supports greater biodiversity than the slow-moving water of pools. These distinctions form the basis for the division of rivers into upland and lowland rivers.

The trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies in a food web. A food chain is a succession of organisms that eat other organisms and may, in turn, be eaten themselves. The trophic level of an organism is the number of steps it is from the start of the chain. A food web starts at trophic level 1 with primary producers such as plants, can move to herbivores at level 2, carnivores at level 3 or higher, and typically finish with apex predators at level 4 or 5. The path along the chain can form either a one-way flow or a food "web". Ecological communities with higher biodiversity form more complex trophic paths.
Human consumption may refer to:
A consumer in a food chain is a living creature that eats organisms from a different population. A consumer is a heterotroph and a producer is an autotroph. Like sea angels, they take in organic moles by consuming other organisms, so they are commonly called consumers. Heterotrophs can be classified by what they usually eat as herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, or decomposers. On the other hand, autotrophs are organisms that use energy directly from the sun or from chemical bonds. Autotrophs are vital to all ecosystems because all organisms need organic molecules, and only autotrophs can produce them from inorganic compounds. Autotrophs are classified as either photoautotrophs or chemoautotrophs.

An autotroph is an organism that produces complex organic compounds using carbon from simple substances such as carbon dioxide, generally using energy from light (photosynthesis) or inorganic chemical reactions (chemosynthesis). They convert an abiotic source of energy into energy stored in organic compounds, which can be used by other organisms. Autotrophs do not need a living source of carbon or energy and are the producers in a food chain, such as plants on land or algae in water. Autotrophs can reduce carbon dioxide to make organic compounds for biosynthesis and as stored chemical fuel. Most autotrophs use water as the reducing agent, but some can use other hydrogen compounds such as hydrogen sulfide.
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web starting from producer organisms and ending at an apex predator species, detritivores, or decomposer species. A food chain also shows how organisms are related to each other by the food they eat. Each level of a food chain represents a different trophic level. A food chain differs from a food web because the complex network of different animals' feeding relations are aggregated and the chain only follows a direct, linear pathway of one animal at a time. Natural interconnections between food chains make it a food web.

Proposition 37 was a California ballot measure rejected in California at the statewide election on November 6, 2012. This initiative statute would have required labeling of genetically engineered food, with some exceptions. It would have disallowed the practice of labeling genetically engineered food with the word "natural." This proposition was one of the main concerns by the organizers of the March Against Monsanto in May 2013.











