
The alpha helix (α-helix) is a common motif in the secondary structure of proteins and is a right hand-helix conformation in which every backbone N−H group donates a hydrogen bond to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid located three or four residues earlier along the protein sequence.
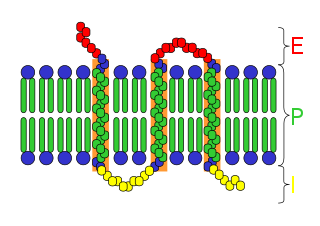
An integral membrane protein (IMP) is a type of membrane protein that is permanently attached to the biological membrane. All transmembrane proteins are IMPs, but not all IMPs are transmembrane proteins. IMPs comprise a significant fraction of the proteins encoded in an organism's genome. Proteins that cross the membrane are surrounded by annular lipids, which are defined as lipids that are in direct contact with a membrane protein. Such proteins can only be separated from the membranes by using detergents, nonpolar solvents, or sometimes denaturing agents.

A transmembrane protein (TP) is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane to which it is permanently attached. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequently undergo significant conformational changes to move a substance through the membrane.
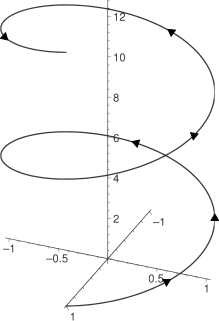
A helix, plural helixes or helices, is a type of smooth space curve, i.e. a curve in three-dimensional space. It has the property that the tangent line at any point makes a constant angle with a fixed line called the axis. Examples of helices are coil springs and the handrails of spiral staircases. A "filled-in" helix – for example, a "spiral" (helical) ramp – is called a helicoid. Helices are important in biology, as the DNA molecule is formed as two intertwined helices, and many proteins have helical substructures, known as alpha helices. The word helix comes from the Greek word ἕλιξ, "twisted, curved".
Corynebacterium is a genus of bacteria that are Gram-positive and aerobic. They are bacilli (rod-shaped), and in some phases of life they are, more particularly, club-shaped, which inspired the genus name.

A leucine zipper is a common three-dimensional structural motif in proteins. They were first described by Landschulz and collaborators in 1988 when they found that an enhancer binding protein had a very characteristic 30-amino acid segment and the display of these amino acid sequences on an idealized alpha helix revealed a periodic repetition of leucine residues at every seventh position over a distance covering eight helical turns. The polypeptide segments containing these periodic arrays of leucine residues were proposed to exist in an alpha-helical conformation and the leucine side chains from one alpha helix interdigitate with those from the alpha helix of a second polypeptide, facilitating dimerization.
The Transporter Classification Database is an International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (IUBMB)-approved classification system for membrane transport proteins, including ion channels.

A pi helix is a type of secondary structure found in proteins. Although once thought to be rare, short π-helices are found in 15% of known protein structures and are believed to be an evolutionary adaptation derived by the insertion of a single amino acid into an α-helix. Because such insertions are highly destabilizing, the formation of π-helices would tend to be selected against unless it provided some functional advantage to the protein. π-helices therefore are typically found near functional sites of proteins.

A 310 helix is a type of secondary structure found in proteins and polypeptides. Of the numerous protein secondary structures present, the 310-helix is the fourth most common type observed; following α-helices, β-sheets and reverse turns. 310-helices constitute nearly 10–15% of all helices in protein secondary structures, and are typically observed as extensions of α-helices found at either their N- or C- termini. Because of the α-helices tendency to consistently fold and unfold, it has been proposed that the 310-helix serves as an intermediary conformation of sorts, and provides insight into the initiation of α-helix folding.
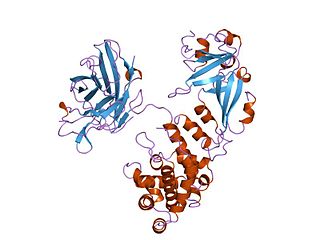
Diphtheria toxin is an exotoxin secreted by Corynebacterium diphtheriae, the pathogenic bacterium that causes diphtheria. Unusually, the toxin gene is encoded by a bacteriophage. The toxin causes the disease in humans by gaining entry into the cell cytoplasm and inhibiting protein synthesis.
Brevibacterium is a genus of bacteria of the order Actinomycetales. Actino means radial and mycet means fungus. Radial fungus. Brevi prefix means short. Short bacterium. They are Gram-positive soil organisms. It is the sole genus in the family Brevibacteriaceae.
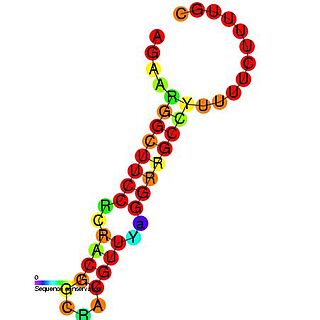
In molecular biology ctRNA is a plasmid encoded noncoding RNA that binds to the mRNA of repB and causes translational inhibition. ctRNA is encoded by plasmids and functions in rolling circle replication to maintain a low copy number. In Corynebacterium glutamicum, it achieves this by antisense pairing with the mRNA of RepB, a replication initiation protein. In Enterococcus faecium the plasmid pJB01 contains three open reading frames, copA, repB, and repC. The pJB01 ctRNA is coded on the opposite strand from the copA/repB intergenic region and partially overlaps an atypical ribosome binding site for repB.

General bacterial porins are a family of proteins from the outer membranes of Gram-negative bacteria. The porins act as molecular filters for hydrophilic compounds. They are responsible for the 'molecular sieve' properties of the outer membrane. Porins form large water-filled channels which allow the diffusion of hydrophilic molecules into the periplasmic space. Some porins form general diffusion channels that allow any solute up to a certain size to cross the membrane, while other porins are specific for one particular solute and contain a binding site for that solute inside the pores. As porins are the major outer membrane proteins, they also serve as receptor sites for the binding of phages and bacteriocins.
D-inositol-3-phosphate glycosyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:1D-myo-inositol 3-phosphate alpha-D-glycosyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Galactan 5-O-arabinofuranosyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name galactofuranan:trans,octacis-decaprenylphospho-beta-D-arabinofuranose 5-O-alpha-D-arabinofuranosyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Corynebacterium efficiens is a thermotolerant, glutamic acid-producing species of bacteria from soil and vegetables. Its type strain is YS-314T.

Corynebacterium glutamicum is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacterium that is used industrially for large-scale production of amino acids. While originally identified in a screen for organisms secreting L-glutamate, mutants of C. glutamicum have also been identified that produce various other amino acids.
Lysine Exporters are a superfamily of transmembrane proteins which export amino acids, lipids and heavy metal ions. They provide ionic homeostasis, play a role in cell envelope assembly, and protect from excessive concentrations of heavy metals in cytoplasm. The superfamily was named based on the early discovery of the LysE carrier protein of Corynebacterium glutamicum.
Membranome database provides structural and functional information about more than 6000 single-pass (bitopic) transmembrane proteins from Homo sapiens, Arabidopsis thaliana, Dictyostelium discoideum, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Escherichia coli and Methanocaldococcus jannaschii. Bitopic membrane proteins consist of a single transmembrane alpha-helix connecting water-soluble domains of the protein situated at the opposite sides of a biological membrane. These proteins are frequently involved in the signal transduction and communication between cells in multicellular organisms.
The public domain consists of all the creative works to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable.

Pfam is a database of protein families that includes their annotations and multiple sequence alignments generated using hidden Markov models. The most recent version, Pfam 32.0, was released in September 2018 and contains 17,929 families.
InterPro is a database of protein families, domains and functional sites in which identifiable features found in known proteins can be applied to new protein sequences in order to functionally characterise them.















