
A bastion or bulwark is a structure projecting outward from the curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks with fire from the flanks being able to protect the curtain wall and also the adjacent bastions. It is one element in the style of fortification dominant from the mid 16th to mid 19th centuries. Bastion fortifications offered a greater degree of passive resistance and more scope for ranged defense in the age of gunpowder artillery compared with the medieval fortifications they replaced.

A ravelin is a triangular fortification or detached outwork, located in front of the innerworks of a fortress. Originally called a demi-lune, after the lunette, the ravelin is placed outside a castle and opposite a fortification curtain.

A caponier is a type of defensive structure in a fortification. The word originates from the French caponnière, meaning "chicken coop".

Kastellet, located in Copenhagen, Denmark, is one of the best preserved fortresses in Northern Europe. It is constructed in the form of a pentagon with bastions at its corners. Kastellet was continuous with the ring of bastioned ramparts which used to encircle Copenhagen but of which only the ramparts of Christianshavn remain today.
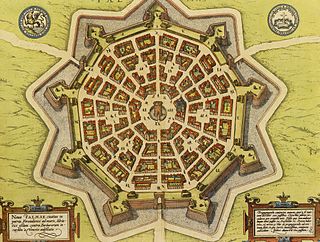
A bastion fort or trace italienne, is a fortification in a style that evolved during the early modern period of gunpowder when the cannon came to dominate the battlefield. It was first seen in the mid-15th century in Italy. Some types, especially when combined with ravelins and other outworks, resembled the related star fort of the same era.

The Floriana Lines are a line of fortifications in Floriana, Malta, which surround the fortifications of Valletta and form the capital city's outer defences. Construction of the lines began in 1636 and they were named after the military engineer who designed them, Pietro Paolo Floriani. The Floriana Lines were modified throughout the course of the 17th and 18th centuries, and they saw use during the French blockade of 1798–1800. Today, the fortifications are still largely intact but rather dilapidated and in need of restoration.

The Fortezza is the citadel of the city of Rethymno in Crete, Greece. It was built by the Venetians in the 16th century, and was captured by the Ottomans in 1646. By the early 20th century, many houses were built within the citadel. These were demolished after World War II, leaving only a few historic buildings within the Fortezza. Today, the citadel is in good condition and is open to the public.

The fortifications of Copenhagen is the broad name for the rings of fortifications surrounding the city of Copenhagen. They can be classified historically as follows:

A curtain wall is a defensive wall between two towers (bastions) of a castle, fortress, or town.

The fortifications of Copenhagen underwent a comprehensive modernization and expansion in the 17th century. The project was commenced and was largely the masterplan of Christian IV in the early 17th century but was continued and completed by his successors. The new fortifications relied on the existing, medieval fortifications of the city but the fortified area was extended and a defensive ring around the city completed particularly with new edifices facing the sea. The ring fortification consisted of four bastioned ramparts and an annexed citadel as well as various outworks.

Tenaille is an advanced defensive-work, in front of the main defences of a fortress, which takes its name from resemblance, real or imaginary, to the lip of a pair of pincers. It is "from French, literally: tongs, from Late Latin tenācula, pl of tenaculum".
The Triangula Bastion was part of the 18th-century fortifications of Riga. Its fundaments are nowadays visible under a modern office building owned by Euro Live Technologies a playtech company.

The Royal Walls of Ceuta are a line of fortification in Ceuta, an autonomous Spanish city in north Africa. The walls date to 962 in its oldest part and the most modern parts to the 18th century. They remain largely intact, with the exception of some outworks, and are listed as a Spanish Property of Cultural Interest.

The counterguard is an outwork in a bastioned fortification system that usually comprises only a low rampart and which is sited in front of the actual fortress moat that runs around the bastions or ravelins. The rampart way of a counterguard is, however, so constructed and at least wide enough that it enables the positioning of guns. An additional ditch in front of it guards the work from a frontal enemy assault. The function of counterguards was to protect the higher ravelin or bastion behind it from direct fire and to delay an attack on it as long as possible. So that the counterguards and the works that they were to protect, could not come under simultaneous fire along the line of the rampart they were not allowed to run parallel to one another.

In fortification architecture, a rampart is a length of bank or wall forming part of the defensive boundary of a castle, hillfort, settlement or other fortified site. It is usually broad-topped and made of excavated earth or masonry or a combination of the two.

The fortifications of Heraklion are a series of defensive walls and other fortifications which surround the city of Heraklion in Crete, Greece. The first city walls were built in the Middle Ages, but they were completely rebuilt by the Republic of Venice. The fortifications managed to withstand the longest siege in history for 21 years, before the city fell to the Ottomans in 1669.


















