Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops after birth or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Metamorphosis is iodothyronine-induced and an ancestral feature of all chordates. Some insects, fishes, amphibians, mollusks, crustaceans, cnidarians, echinoderms, and tunicates undergo metamorphosis, which is often accompanied by a change of nutrition source or behavior. Animals that go through metamorphosis are called metamorphoses. Animals can be divided into species that undergo complete metamorphosis ("holometaboly"), incomplete metamorphosis ("hemimetaboly"), or no metamorphosis ("ametaboly").

Physiology is the scientific study of the functions and mechanisms which work within a living system.

A gill is a respiratory organ found in many aquatic organisms that extracts dissolved oxygen from water and excretes carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are kept moist. The microscopic structure of a gill presents a large surface area to the external environment. Branchia is the zoologists' name for gills.
The human body is the structure of a human being. It is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organ systems. They ensure homeostasis and the viability of the human body.

Hemolymph, or haemolymph, is a fluid, analogous to the blood in vertebrates, that circulates in the interior of the arthropod body remaining in direct contact with the animal's tissues. It is composed of a fluid plasma in which hemolymph cells called hemocytes are suspended. In addition to hemocytes, the plasma also contains many chemicals. It is the major tissue type of the open circulatory system characteristic of arthropods. In addition, some non-arthropods such as molluscs possess a hemolymphatic circulatory system.

The Hemiptera or true bugs are an order of insects comprising some 50,000 to 80,000 species of groups such as the cicadas, aphids, planthoppers, leafhoppers, and shield bugs. They range in size from 1 mm (0.04 in) to around 15 cm (6 in), and share a common arrangement of sucking mouthparts. The name "true bugs" is sometimes limited to the suborder Heteroptera. Many insects commonly known as "bugs" belong to other orders; for example, the lovebug is a fly, while the May bug and ladybug are beetles.
Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively by diffusion across a surface. For example, this surface might be the air/water interface of a water body, the surface of a gas bubble in a liquid, a gas-permeable membrane, or a biological membrane that forms the boundary between an organism and its extracellular environment.

Plant physiology is a subdiscipline of botany concerned with the functioning, or physiology, of plants. Closely related fields include plant morphology, plant ecology, phytochemistry, cell biology, genetics, biophysics and molecular biology.
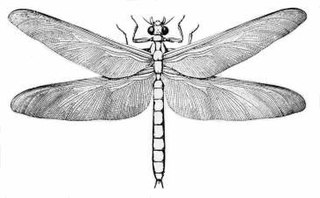
Meganeura is a genus of extinct insects from the Carboniferous period, which resembled and are related to the present-day dragonflies. With wingspans ranging from 65 cm (25.6 in) to over 70 cm (28 in), M. monyi is one of the largest-known flying insect species. Meganeura were predatory, with their diet mainly consisting of other insects.
Diapause, when referencing animal dormancy, is the delay in development in response to regularly and recurring periods of adverse environmental conditions. It is considered to be a physiological state of dormancy with very specific initiating and inhibiting conditions. Diapause is a mechanism used as a means to survive predictable, unfavorable environmental conditions, such as temperature extremes, drought, or reduced food availability. Diapause is most often observed in all the life stages of arthropods, especially insects. Embryonic diapause, a somewhat similar phenomenon, occurs in over 130 species of mammals, possibly even in humans, and in the embryos of many of the oviparous species of fish in the order Cyprinodontiformes.

The Malpighian tubule system is a type of excretory and osmoregulatory system found in some insects, myriapods, arachnids, and tardigrades.

A simple eye refers to a type of eye form or optical arrangement that contains a single lens. A "simple eye" is so called in distinction from a multi-lensed "compound eye", and is not necessarily at all simple in the usual sense of the word. The eyes of humans and large animals, and camera lenses are classed as "simple" because in both cases a single lens collects and focuses light onto the retina or film. Many insects have compound eyes consisting of multiple lenses, each focusing light onto a small number of retinula cells.

Tight junctions, also known as occluding junctions or zonulae occludentes are multiprotein junctional complexes whose general function is to prevent leakage of transported solutes and water and seals the paracellular pathway. Tight junctions may also serve as leaky pathways by forming selective channels for small cations, anions, or water. Tight junctions are present only in vertebrates. The corresponding junctions that occur in invertebrates are septate junctions.
A cryoprotectant is a substance used to protect biological tissue from freezing damage. Arctic and Antarctic insects, fish and amphibians create cryoprotectants in their bodies to minimize freezing damage during cold winter periods. Cryoprotectants are also used to preserve living materials in the study of biology and to preserve food products.
Insect winter ecology entails the overwinter survival strategies of insects, which are in many respects more similar to those of plants than to many other animals, such as mammals and birds. This is because unlike those animals, which can generate their own heat internally (endothermic), insects must rely on external sources to provide their heat (ectothermic). Thus, insects sticking around in the winter, must tolerate freezing or rely on other mechanisms to avoid freezing. Loss of enzymatic function and eventual freezing due to low temperatures daily threatens the livelihood of these organisms during winter. Not surprisingly, insects have evolved a number of strategies to deal with the rigors of winter temperatures in places where they would otherwise not survive.
Desiccation tolerance refers to the ability of an organism to withstand or endure extreme dryness, or drought-like conditions. Plants and animals living in arid or periodically arid environments such as temporary streams or ponds may face the challenge of desiccation, therefore physiological or behavioral adaptations to withstand these periods are necessary to ensure survival. In particular, insects occupy a wide range of ecologically diverse niches and, so, exhibit a variety of strategies to avoid desiccation.
Prothoracicotropic hormone (PTTH) was the first insect hormone to be discovered. It was originally described simply as "brain hormone" by early workers such as Stefan Kopeć (1922) and Vincent Wigglesworth (1934), who realized that ligation of the head of immature insects could prevent molting or pupation of the body region excluded from the head if the ligation was performed before a critical age in the lifestage was reached. After a certain point the ligation had no effect and both sections of the insect would molt or pupate. However, implantation of a conspecific brain to a sessile ligated abdomen or an abdomen under diapause would induce molting or pupation. Thus, the brain was originally thought to be the source of the hormone that induces molting in insects.

Surface wave detection by animals is the process by which animals, such as surface-feeding fish are able to sense and localize prey and other objects on the surface of a body of water by analyzing features of the ripples generated by objects' movement at the surface. Features analyzed include waveform properties such as frequency, change in frequency, and amplitude, and the curvature of the wavefront. A number of different species are proficient in surface wave detection, including some aquatic insects and toads, though most research is done on the topminnow/surface killifish Aplocheilus lineatus. The fish and other animals with this ability spend large amounts of time near the water surface, some just to feed and others their entire lives.
Paul Cooper is the current editor in chief of the Australian Journal of Zoology. He is also currently Associate Professor, in the College of Medicine, Biology and Environment of Australian National University (1987–present).

In zoology, copulation is animal sexual behavior in which a male introduces sperm into the female's body, especially directly into her reproductive tract. This is an aspect of mating. Many animals that live in water use external fertilization, whereas internal fertilization may have developed from a need to maintain gametes in a liquid medium in the Late Ordovician epoch. Internal fertilization with many vertebrates occurs via cloacal copulation, known as cloacal kiss, while mammals copulate vaginally, and many basal vertebrates reproduce sexually with external fertilization.