
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are business transactions in which the ownership of companies, business organizations, or their operating units are transferred to or consolidated with another company or business organization. This could happen through direct absorption, a merger, a tender offer or a hostile takeover. As an aspect of strategic management, M&A can allow enterprises to grow or downsize, and change the nature of their business or competitive position.
In business, a takeover is the purchase of one company by another. In the UK, the term refers to the acquisition of a public company whose shares are publicly listed, in contrast to the acquisition of a private company.

A conglomerate is a type of multi-industry company that consists of several different and unrelated business entities that operate in various industries. A conglomerate usually has a parent company that owns and controls many subsidiaries, which are legally independent but financially and strategically dependent on the parent company. Conglomerates are often large and multinational corporations that have a global presence and a diversified portfolio of products and services. Conglomerates can be formed by merger and acquisitions, spin-offs, or joint ventures.
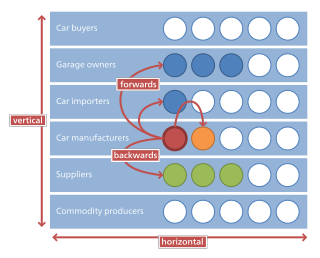
Horizontal integration is the process of a company increasing production of goods or services at the same level of the value chain, in the same industry. A company may do this via internal expansion or through mergers and acquisitions.

A joint-stock company (JSC) is a business entity in which shares of the company's stock can be bought and sold by shareholders. Each shareholder owns company stock in proportion, evidenced by their shares. Shareholders are able to transfer their shares to others without any effects to the continued existence of the company.
A corporate tax, also called corporation tax or company tax, is a type of direct tax levied on the income or capital of corporations and other similar legal entities. The tax is usually imposed at the national level, but it may also be imposed at state or local levels in some countries. Corporate taxes may be referred to as income tax or capital tax, depending on the nature of the tax.
In finance and economics, divestment or divestiture is the reduction of some kind of asset for financial, ethical, or political objectives or sale of an existing business by a firm. A divestment is the opposite of an investment. Divestiture is an adaptive change and adjustment of a company's ownership and business portfolio made to confront with internal and external changes.

Corporate law is the body of law governing the rights, relations, and conduct of persons, companies, organizations and businesses. The term refers to the legal practice of law relating to corporations, or to the theory of corporations. Corporate law often describes the law relating to matters which derive directly from the life-cycle of a corporation. It thus encompasses the formation, funding, governance, and death of a corporation.

Vivendi SE is a French mass-media holding company headquartered in Paris. It owns Gameloft as well as a number of investments in several companies.
A reverse takeover (RTO), reverse merger, or reverse IPO is the acquisition of a public company by a private company so that the private company can bypass the lengthy and complex process of going public. Sometimes, conversely, the public company is bought by the private company through an asset swap and share issue. The transaction typically requires reorganization of capitalization of the acquiring company.
In business, consolidation or amalgamation is the merger and acquisition of many smaller companies into a few much larger ones. In the context of financial accounting, consolidation refers to the aggregation of financial statements of a group company as consolidated financial statements. The taxation term of consolidation refers to the treatment of a group of companies and other entities as one entity for tax purposes. Under the Halsbury's Laws of England, amalgamation is defined as "a blending together of two or more undertakings into one undertaking, the shareholders of each blending company, becoming, substantially, the shareholders of the blended undertakings. There may be amalgamations, either by transfer of two or more undertakings to a new company or the transfer of one or more companies to an existing company".
A corporate spin-off, also known as a spin-out, or starburst or hive-off, is a type of corporate action where a company "splits off" a section as a separate business or creates a second incarnation, even if the first is still active. It is distinct from a sell-off, where a company sells a section to another company or firm in exchange for cash or securities.
A corporate group, company group or business group, also formally known as a group of companies, is a collection of parent and subsidiary corporations that function as a single economic entity through a common source of control. These types of groups are often managed by an account manager. The concept of a group is frequently used in tax law, accounting and company law to attribute the rights and duties of one member of the group to another or the whole. If the corporations are engaged in entirely different businesses, the group is called a conglomerate. The forming of corporate groups usually involves consolidation via mergers and acquisitions, although the group concept focuses on the instances in which the merged and acquired corporate entities remain in existence rather than the instances in which they are dissolved by the parent. The group may be owned by a holding company which may have no actual operations.

Singapore Press Holdings Limited (SPH) was an organisation with businesses in property and aged care in Singapore. Since its takeover by Cuscaden Peak in 2022, it has been renamed Cuscaden Peak Investments.

Corporate tax is imposed in the United States at the federal, most state, and some local levels on the income of entities treated for tax purposes as corporations. Since January 1, 2018, the nominal federal corporate tax rate in the United States of America is a flat 21% following the passage of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017. State and local taxes and rules vary by jurisdiction, though many are based on federal concepts and definitions. Taxable income may differ from book income both as to timing of income and tax deductions and as to what is taxable. The corporate Alternative Minimum Tax was also eliminated by the 2017 reform, but some states have alternative taxes. Like individuals, corporations must file tax returns every year. They must make quarterly estimated tax payments. Groups of corporations controlled by the same owners may file a consolidated return.
The following is a glossary which defines terms used in mergers, acquisitions, and takeovers of companies, whether private or public.
ABANCA Corporación Bancaria, S.A. is a Spanish bank based in Galicia. It was created in September in 2011 following the "bankisation" of Novacaixagalicia savings bank. It operates in the autonomous communities of Galicia, Asturias and the province of León, in other parts of Spain and in Portugal, as well as offices in the UK, Germany, France, Switzerland, Brazil, Venezuela, Panama, Mexico and the USA.

The British Virgin Islands company law is the law that governs businesses registered in the British Virgin Islands. It is primarily codified through the BVI Business Companies Act, 2004, and to a lesser extent by the Insolvency Act, 2003 and by the Securities and Investment Business Act, 2010. The British Virgin Islands has approximately 30 registered companies per head of population, which is likely the highest ratio of any country in the world. Annual company registration fees provide a significant part of Government revenue in the British Virgin Islands, which accounts for the comparative lack of other taxation. This might explain why company law forms a much more prominent part of the law of the British Virgin Islands when compared to countries of similar size.
Gencor Ltd. was a South African based mining company. It was formed in 1980 after the merger of the General Mining and Finance Corporation and the Union Corporation. Parts of the company are now owned by Gold Fields, South 32 and BHP.
Appraisal rights, also called dissent rights or buy-out rights, among other variants, are the rights of shareholders to receive a court-supervised valuation of their shares when certain major changes, such as an acquisition of the company, are contemplated. Shareholders who do not support the transaction are entitled to receive the value of their shares in cash, as determined by the court. Appraisal rights are available in jurisdictions including Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States.






