
The foreign policy of Denmark is based on its identity as a sovereign state in Europe, the Arctic and the North Atlantic. As such its primary foreign policy focus is on its relations with other nations as a sovereign state compromising the three constituent countries: Denmark, Greenland and the Faroe Islands. Denmark has long had good relations with other nations. It has been involved in coordinating Western assistance to the Baltic states.
The foreign relations of Afghanistan are in a transitional phase since the 2021 fall of Kabul to the Taliban and the collapse of the internationally-recognized Islamic Republic of Afghanistan. No country has recognised the new regime, the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan. Although some countries have engaged in informal diplomatic contact with the Islamic Emirate, formal relations remain limited to representatives of the Islamic Republic.
The United States has maintained an official presence in Slovenia since the early 1970s, when the United States Information Agency (USIS) opened a library and American press and cultural center in Ljubljana. From its opening through 1992, the American Center worked to develop closer grassroots relations between the United States and the people of the then-Socialist Republic of Slovenia, a constituent republic of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. On December 23, 1990, the Slovene people voted in a plebiscite to separate from greater Yugoslavia. On June 25, 1991, the new Republic of Slovenia officially declared its independence from the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. A 10-day war commenced, during which Slovenian territorial troops fought off incursions by the Yugoslav People's Army. The United States formally recognized the new republic on April 7, 1992. To develop U.S. diplomatic relations with the new state, the United States opened a new Embassy in Ljubljana in August 1992. From the departure of Yousif Ghafari in January 2009 till November 2010, the U.S. Ambassador position was vacant. From November 2010 to 2015 it was held by Joseph A. Mussomeli. The Ambassador position is currently held by Jamie Harpootlian.

Canada–Denmark relations are the current and historical relations between Canada and Denmark. Canada has an embassy in Copenhagen. Denmark has an embassy in Ottawa and a consulate-general in Toronto. Both countries are full members of NATO and the Arctic Council. Relations between the two countries have attracted attention in light of the dispute over Hans Island, which was resolved in 2022.

Denmark–Turkey relations are the current and historical relations between Denmark and Turkey. Denmark has an embassy in Ankara, and Turkey has an embassy in Copenhagen. Both countries are members of NATO and Council of Europe. Diplomatic relations between Denmark and Turkey were put under pressure in 2014 because of the Jyllands-Posten Muhammad cartoons controversy and the Roj TV affair (Roj TV's broadcasting license was suspended by the Supreme Court in Denmark on February 27, 2014). Denmark is a member of the European Union, Turkey is not a member.

Current and historical relations exist between Armenia and Denmark. Armenia has an embassy in Copenhagen, and Denmark is represented in Armenia, through its embassy in Kyiv, Ukraine. Diplomatic relations were established on 14 January 1992. In 2008, the Armenian Foreign Minister Eduard Nalbandyan called the relations between Armenia and Denmark "friendly" and "highly appreciating". In 2013, Amstream was founded as an independent non-political and non-profit organization in order to initiate means of collaboration and partnerships between Armenia and Scandinavia within business, education and culture. Both countries are members of the Council of Europe.

Moldova–Slovenia relations are the bilateral relations between the two countries, Moldova and Slovenia. Moldova recognized the Republic of Slovenia under an unknown date. Diplomatic relations were established on October 27, 1993. Both countries are represented in each other through their embassies in Budapest (Hungary). Slovenia is a member of the European Union, which Moldova applied for in 2022. Both countries are full members of Council of Europe.

Croatia–Denmark relations refers to the current and historical relations between Croatia and Denmark. Relations between the two countries are described as "excellent", "friendly" and "well-developed".
Foreign relations exist between Austria and Denmark. Austria has an embassy in Copenhagen and Denmark has an embassy in Vienna. Both countries are full members of the Council of Europe, of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, and of the European Union. Diplomatic relations were established on 19 December 1925.
Denmark–Romania relations refers to the current and historical relations between Denmark and Romania. Denmark has an embassy in Bucharest, and Romania has an embassy in Copenhagen. Relations between Denmark and Communist Romania was described in the 1960s as "good" by Prime Minister of Romania Ion Gheorghe Maurer. In 2008, Danish export to Romania amounted 1,644 million DKK, while Romanian export amounted 475 million DKK. Both countries are members of the European Union and NATO.

Denmark–Georgia relations refers to the current and historical relations between Denmark and Georgia. Denmark is represented in Georgia, through its embassy in Tbilisi. Georgia has an embassy in Copenhagen. Denmark supports Georgia to become a member of the European Union and NATO. The current Georgian ambassador to Denmark is Gigi Gigiadze. Both nations are members of the Council of Europe.
Chile–Denmark relations refers to the current and historical relations between Chile and Denmark. Chile has an embassy in Copenhagen, and Denmark has an embassy in Santiago. Relations between the two countries are described as "friendly" and excellent.

Denmark–North Macedonia relations refers to the bilateral relations between Denmark and North Macedonia. Both countries are members of the Council of Europe, and NATO. Also Denmark is an EU member and North Macedonia is an EU candidate. The Danish embassy in Vienna, Austria is responsible for its relations with North Macedonia and North Macedonia has an embassy in Copenhagen. Denmark recognized North Macedonia on 16 December 1993. Denmark has had an ambassador in Vienna accredited with North Macedonia since January 1994. North Macedonia has maintained an embassy in Copenhagen since 1996.
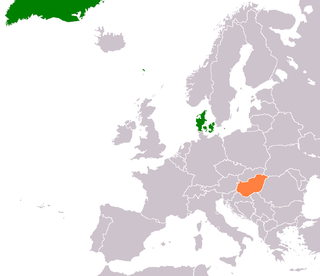
Denmark – Hungary relations refers to the current and historical relations between Denmark and Hungary. Denmark has an embassy in Budapest. Hungary has an embassy in Copenhagen. Diplomatic relations were established on 10 May 1948. Both countries are full members of the Council of Europe, the European Union and NATO.
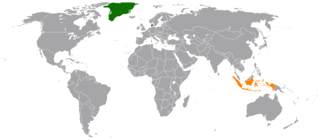
Denmark and Indonesia established diplomatic relations in 1974. Denmark has an embassy in Jakarta, and Indonesia has an embassy in Copenhagen. Bilateral relations are strong, as well as the humanitarian response to the December 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami, which claimed the lives of 45 Danes. In 2015, after focusing on China and South Korea, Denmark is gearing up to enhance its relations with Indonesia, hoping that it will help Denmark to build strong ties with the whole Southeast Asian region.
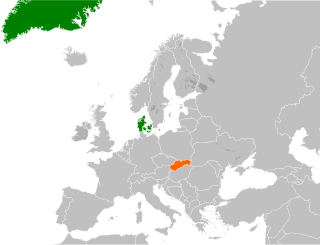
Denmark–Slovakia relations refers to the current and historical relations between Denmark and Slovakia. Denmark has an embassy in Bratislava. Slovakia has an embassy in Copenhagen. The relations between Denmark and Slovakia are described as good and friendly. Denmark has a trade office in Slovakia. Both countries are full members of the European Union and NATO. On 4 September 2002, a memorandum of understanding between the two countries, were signed.

Denmark–Portugal relations refers to the current and historical relations between Denmark and Portugal. Denmark has an embassy in Lisbon. Portugal has an embassy in Copenhagen. Both countries are full members of the Council of Europe, the European Union and NATO.

Denmark–Morocco relations refers to the current and historical relations between Denmark and Morocco. Denmark has an embassy in Rabat and Morocco has an embassy in Copenhagen. Denmark also sends aid to Morocco as part of the Danish-Arab Partnership Programme. In January 2008, Danish Foreign Minister Per Stig Møller visited Morocco for the opening of the Danish embassy in Rabat. In March 1980, Mohammed VI of Morocco visited Denmark as the Crown Prince of Morocco and Moroccan Foreign Minister Mohamed Benaissa visited Denmark in 2005 and in 2006.

Italian-Slovene relations are foreign relations between Italy and Slovenia.

Brazil-Slovenia relations refers to the bilateral relations between Brazil and Slovenia. Both nations are members of the United Nations. The presence of Slovene immigrants in Brazil is relatively small but significant.





















