A carbohydrate is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula Cm(H2O)n (where m may be different from n). This formula holds true for monosaccharides. Some exceptions exist; for example, deoxyribose, a sugar component of DNA, has the empirical formula C5H10O4. The carbohydrates are technically hydrates of carbon; structurally it is more accurate to view them as aldoses and ketoses.

Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a simple ketonic monosaccharide found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galactose, that are absorbed directly into blood during digestion. Fructose was discovered by French chemist Augustin-Pierre Dubrunfaut in 1847. The name "fructose" was coined in 1857 by the English chemist William Allen Miller. Pure, dry fructose is a sweet, white, odorless, crystalline solid, and is the most water-soluble of all the sugars. Fructose is found in honey, tree and vine fruits, flowers, berries, and most root vegetables.
Benedict's reagent is a chemical reagent and complex mixture of sodium carbonate, sodium citrate and copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate., often used in place of Fehling's solution to detect the presence of reducing sugars. The presence of other reducing substances also gives a positive reaction. Such tests that use this reagent are called the Benedict's tests. A positive test with Benedict's reagent is shown by a color change from clear blue to a brick-red precipitate.

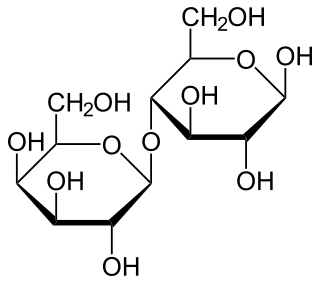
Maltose, also known as maltobiose or malt sugar, is a disaccharide formed from two units of glucose joined with an α(1→4) bond. In the isomer isomaltose, the two glucose molecules are joined with an α(1→6) bond. Maltose is the two-unit member of the amylose homologous series, the key structural motif of starch. When beta-amylase breaks down starch, it removes two glucose units at a time, producing maltose. An example of this reaction is found in germinating seeds, which is why it was named after malt. Unlike sucrose, it is a reducing sugar.

Maltase is an enzyme located in on the brush border of the small intestine that breaks down the disaccharide maltose. Maltase catalyzes the hydrolysis of maltose to the simple sugar glucose. This enzyme is found in plants, bacteria, and yeast. Acid maltase deficiency is categorized into three separate types based on the age of onset of symptoms in the affected individual.
Carbohydrate metabolism is the whole of biochemical processes responsible for the metabolic formation, breakdown, and interconversion of carbohydrates in living organisms.
Galactosemia is a rare genetic metabolic disorder that affects an individual's ability to metabolize the sugar galactose properly. Galactosemia follows an autosomal recessive mode of inheritance that confers a deficiency in an enzyme responsible for adequate galactose degradation.

Enterocytes, or intestinal absorptive cells, are simple columnar epithelial cells which line the inner surface of the small intestine. A glycocalyx surface coat contains digestive enzymes. Microvilli on the apical surface increase its surface area. This facilitates transport of numerous small molecules into the enterocyte from the intestinal lumen. These include broken down proteins, fats, and sugars, as well as water, electrolytes, vitamins, and bile salts. Enterocytes also have a endocrine role, secreting hormones such as leptin.
Sucrase is a digestive enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose to its subunits fructose and glucose. One form, sucrase-isomaltase, is secreted in the small intestine on the brush border. The sucrase enzyme invertase, which occurs more commonly in plants, also hydrolyzes sucrose but by a different mechanism.

Isomaltulose is a disaccharide carbohydrate composed of glucose and fructose. The glucose and fructose are linked by an alpha-1,6-glycosidic bond. Isomaltulose is present in honey and sugarcane extracts. It tastes similar to sucrose with half the sweetness. Isomaltulose is also known by the trade name Palatinose, which is manufactured by enzymatic rearrangement (isomerization) of sucrose from beet sugar. The enzyme and its source were discovered in Germany in 1950, and since then its physiological role and physical properties have been studied extensively. Isomaltulose has been used as an alternative to sugar in foods in Japan since 1985, in the EU since 2005, in the US since 2006, and in Australia and New Zealand since 2007, besides other countries worldwide. Analytical methods for characterization and assay of commercial isomaltulose are laid down, for example, in the Food Chemicals Codex. Its physical properties closely resemble those of sucrose, making it easy to use in existing recipes and processes.

Sucrase-isomaltase (SI) is a glucosidase enzyme located on the brush border of the small intestine. It is a dual-function enzyme with two GH31 domains, one serving as the isomaltase, the other as a sucrose alpha-glucosidase. It has preferential expression in the apical membranes of enterocytes. The enzyme’s purpose is to digest dietary carbohydrates such as starch, sucrose and isomaltose. By further processing the broken-down products, energy in the form of ATP can be generated.

Galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase deficiency(classic galactosemia), is the most common type of galactosemia, an inborn error of galactose metabolism, caused by a deficiency of the enzyme galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase. It is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that can cause liver disease and death if untreated. Treatment of galactosemia is most successful if initiated early and includes dietary restriction of lactose intake. Because early intervention is key, galactosemia is included in newborn screening programs in many areas. On initial screening, which often involves measuring the concentration of galactose in blood, classic galactosemia may be indistinguishable from other inborn errors of galactose metabolism, including galactokinase deficiency and galactose epimerase deficiency. Further analysis of metabolites and enzyme activities are needed to identify the specific metabolic error.
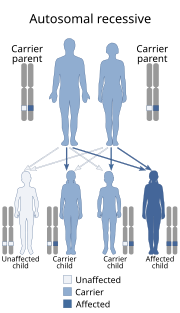
Glucose-galactose malabsorption is a rare condition in which the cells lining the intestine cannot take in the sugars glucose and galactose, which prevents proper digestion of these molecules and larger molecules made from them.
Inborn errors of carbohydrate metabolism are inborn error of metabolism that affect the catabolism and anabolism of carbohydrates.