
The Rosetta Stone is a stele of granodiorite inscribed with three versions of a decree issued in Memphis, Egypt, in 196 BC during the Ptolemaic dynasty on behalf of King Ptolemy V Epiphanes. The top and middle texts are in Ancient Egyptian using hieroglyphic and Demotic scripts, respectively, while the bottom is in Ancient Greek. The decree has only minor differences between the three versions, making the Rosetta Stone key to deciphering the Egyptian scripts.
The khopesh is an Egyptian sickle-shaped sword that developed from battle axes.

Deshret was the Red Crown of Lower Egypt. When combined with the Hedjet of Upper Egypt, it forms the Pschent, in ancient Egyptian called the sekhemti.
The Raphia Decree is an ancient inscribed stone stela dating from ancient Egypt. It comprises the second of the Ptolemaic Decrees issued by a synod of Egyptian priests meeting at Memphis under Ptolemy IV of the Hellenistic Ptolemaic dynasty, which ruled Egypt from 305 BC to 30 BC. The slab dates itself to 217 BC, and celebrates Ptolemy IV's victory at the Battle of Raphia.

The Decree of Canopus is a trilingual inscription in three scripts, which dates from the Ptolemaic period of ancient Egypt. It was written in three writing systems: Egyptian hieroglyphs, demotic, and Koine Greek, on several ancient Egyptian memorial stones, or steles. The inscription is a record of a great assembly of priests held at Canopus, Egypt, on 7 Appellaios (Mac.) = 17 Tybi (Eg.) year 9 of Ptolemy III = Thursday 7 March 238 BC. Their decree honoured Pharaoh Ptolemy III Euergetes; Queen Berenice, his wife; and Princess Berenice.

The writing systems used in ancient Egypt were deciphered in the early nineteenth century through the work of several European scholars, especially Jean-François Champollion and Thomas Young. Ancient Egyptian forms of writing, which included the hieroglyphic, hieratic and demotic scripts, ceased to be understood in the fourth and fifth centuries AD, as the Coptic alphabet was increasingly used in their place. Later generations' knowledge of the older scripts was based on the work of Greek and Roman authors whose understanding was faulty. It was thus widely believed that Egyptian scripts were exclusively ideographic, representing ideas rather than sounds, and even that hieroglyphs were an esoteric, mystical script rather than a means of recording a spoken language. Some attempts at decipherment by Islamic and European scholars in the Middle Ages and early modern times acknowledged the script might have a phonetic component, but perception of hieroglyphs as purely ideographic hampered efforts to understand them as late as the eighteenth century.
The Ptolemaic Decrees were a series of decrees by synods of ancient Egyptian priests. They were issued in the Ptolemaic Kingdom, which controlled Egypt from 305 BC to 30 BC. In each decree, the benefactions of the reigning pharaoh, especially towards the priesthood, are recognised, and religious honours are decreed for him.
The ancient Egyptian Harpoon,, is one of the oldest language hieroglyphs from ancient Egypt. It is used on the famous Narmer Palette of Pharaoh Narmer from the 31st century BC, in an archaic hieroglyphic form.

The ancient Egyptian Mast hieroglyph is one of the oldest language hieroglyphs from Ancient Egypt. It is used on a famous label of Pharaoh Den of the First dynasty, but forms part of the location hieroglyph: Emblem of the East.
The Walking Legs-forward is an ancient Egyptian language hieroglyph of the concept of action, part of "going and returning". Walking Legs-returning is the other half.

The ancient Egyptian Man-prisoner is one of the oldest hieroglyphs from Ancient Egypt. An iconographic portrayal from predynastic Egypt eventually led to its incorporation into the writing system of the Egyptian language. Not only rebels from towns or districts, but foreigners from battle were being portrayed.
In ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs, the hand symbol represented the phoneme /d/, and was also used as a determinative for actions performed as if with the hands.
The ancient Egyptian Dua hieroglyph is one of a series of language and visual hieroglyphs used from the earliest dynasties of Ancient Egypt, and that portrays men, women, ideology, and some occupations.
The Foreleg of ox hieroglyph of ancient Egypt is an old hieroglyph; it even represented a nighttime constellation. It came to have many uses in ancient Egypt over three millennia.
The Throw stick hieroglyph of ancient Egypt is an old hieroglyph that dates from the Predynastic Period; it is from the assemblage of hieroglyphs used on the ornamental, or ceremonial cosmetic palettes. It is used on the palettes both as a throwing-stick weapon in the animal hunt being portrayed-(the Hunters Palette), as well as on certain palettes, as a determinative referring to a "foreigner", or "foreign territory".
The ancient Egyptian Papyrus stem hieroglyph is one of the oldest language hieroglyphs from Ancient Egypt. The papyrus stalk, was incorporated into designs of columns on buildings, also facades, and is also in the iconographic art portrayed in ancient Egyptian decorated scenes.
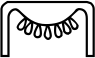
The Egyptian hieroglyph representing gold, phonetic value nb, is important due to its use in the Horus-of-Gold name, one of the Fivefold Titulary names of the Egyptian pharaoh.
The ancient Egyptian Branch hieroglyph, also called a Stick, is a member of the trees and plants hieroglyphs.

The Rosetta Stone decree, or the Decree of Memphis, is a Ptolemaic decree most notable for its bilingual and tri-scriptual nature, which enabled the decipherment of Egyptian hieroglyphs. Issued by a council of priests confirming the royal cult of Ptolemy V in 196 BC at Memphis, it was written in Egyptian hieroglyphs, Egyptian Demotic and Ancient Greek. It mentions the Egyptian rebellion against the Greek rulers, otherwise known only through Greek sources and remains of graffiti.

The ancient Egyptian Arms-in-embrace hieroglyph, Gardiner sign listed no. D32 is a portrayal of the embracing human arms. The hieroglyph is in the large Gardiner sign list category of Parts of the Human Body.







