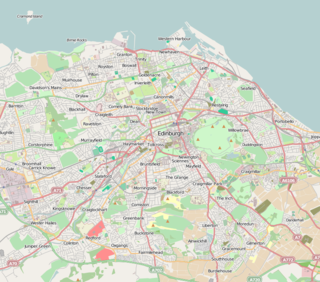
The Edinburgh Science Triangle (EST) is a multi-disciplinary partnership between universities, research institutes, the National Health Service, science parks, the national economic development agency Scottish Enterprise, and central and local government in Edinburgh and neighbouring council areas. The three points of the "triangle" are Livingston in West Lothian, Musselburgh in East Lothian, and the Easter Bush campus in Midlothian.

Scottish Enterprise is a sponsored non-departmental public body of the Scottish Government which encourages economic development, enterprise, innovation and investment in business. The body covers the eastern, central and southern parts of Scotland whilst a similar body, Highlands and Islands Enterprise, operates in north-western Scotland.
The Scottish Government is the executive government of the devolved Scottish Parliament. The government was established in 1999 as the Scottish Executive under the Scotland Act 1998, which created a devolved administration for Scotland in line with the result of the 1997 referendum on Scottish devolution. The government consists of cabinet secretaries, who attend cabinet meetings, and ministers, who do not. It is led by the first minister, who selects the cabinet secretaries and ministers with approval of parliament.
Local government in Scotland is organised through 32 unitary authorities designated as councils which consist of councillors elected every five years by registered voters in each of the council areas.
Contents
- Participants
- Easter Bush Campus
- Hospitals
- Incubators
- Research institutes
- Science parks
- Technology transfer organisations
- Universities
- References
- See also
The collaborative project aims to attract new indigenous and inward investment, and to build a professional scientific community based on academic research and commercial enterprises. The target sectors for the project are the life sciences, informatics, micro- and optoelectronics and energy.
Inward investment is the injection of money from an external source into a region, in order to purchase capital goods for a branch of a corporation to locate or develop its presence in the region.
Microelectronics is a subfield of electronics. As the name suggests, microelectronics relates to the study and manufacture of very small electronic designs and components. Usually, but not always, this means micrometre-scale or smaller. These devices are typically made from semiconductor materials. Many components of normal electronic design are available in a microelectronic equivalent. These include transistors, capacitors, inductors, resistors, diodes and (naturally) insulators and conductors can all be found in microelectronic devices. Unique wiring techniques such as wire bonding are also often used in microelectronics because of the unusually small size of the components, leads and pads. This technique requires specialized equipment and is expensive.
Optoelectronics is the study and application of electronic devices and systems that source, detect and control light, usually considered a sub-field of photonics. In this context, light often includes invisible forms of radiation such as gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet and infrared, in addition to visible light. Optoelectronic devices are electrical-to-optical or optical-to-electrical transducers, or instruments that use such devices in their operation. Electro-optics is often erroneously used as a synonym, but is a wider branch of physics that concerns all interactions between light and electric fields, whether or not they form part of an electronic device.
The Edinburgh Science Triangle was launched by Jim Wallace, the Deputy First Minister, in September 2004, [1] at the Roslin BioCentre in Midlothian. It is a member of Edinburgh's Local Investment Partnership, which includes the City of Edinburgh Council, Edinburgh Chamber of Commerce, Scottish Development International and Scottish Enterprise. Scottish Development International promotes the Edinburgh Science Triangle abroad.

The Deputy First Minister of Scotland is the deputy to the First Minister of Scotland. The post-holder deputises for the First Minister of Scotland in period of absence or overseas visits, and will be expected to answer to the Scottish Parliament on behalf of the First Minister at First Minister's Questions.

Midlothian is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, UK. It borders Edinburgh, East Lothian and the Scottish Borders council areas.
Scottish Development International(SDI) is the international arm of the Scottish Government and Scotland's enterprise agencies, Scottish Enterprise and Highlands and Islands Enterprise. The agency supports international investors in Scotland by offering significant financial incentives and other support to help set up and grow in Scotland as a gateway to wider European and global markets.
Funding to promote and support the Edinburgh Science Triangle comes from Scottish Enterprise, the European Regional Development Fund, the City of Edinburgh, Midlothian and West Lothian councils, and the participating science parks. [1]

The European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) is a fund allocated by the European Union. Its purpose is to transfer money from richer regions, and invest it in the infrastructure and services of underdeveloped regions. This will allow those regions to start attracting private sector investments, and create jobs on their own.

Midlothian Council is one of the 32 local authorities of Scotland. Its administrative centre is based in Dalkeith and it covers an area from the south of Edinburgh to the Borders.

West Lothian Council is the local authority for the West Lothian area of Scotland and has 33 elected members. Councillors are generally elected every 5 years.