
The European Communities Act 1972, also known as the ECA 1972, was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which made legal provision for the accession of the United Kingdom as a member state to the three European Communities (EC) – the European Economic Community, European Atomic Energy Community (Euratom), and the European Coal and Steel Community ; the EEC and ECSC subsequently became the European Union.
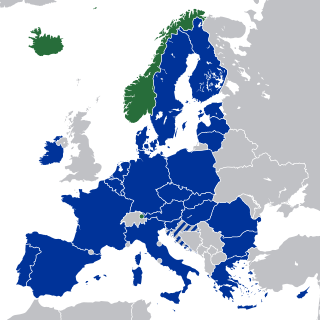
The European Economic Area (EEA) was established via the Agreement on the European Economic Area, an international agreement which enables the extension of the European Union's single market to member states of the European Free Trade Association. The EEA links the EU member states and three of the four EFTA states into an internal market governed by the same basic rules. These rules aim to enable free movement of persons, goods, services, and capital within the European single market, including the freedom to choose residence in any country within this area. The EEA was established on 1 January 1994 upon entry into force of the EEA Agreement. The contracting parties are the EU, its member states, and Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway. New members of EFTA would not automatically become party to the EEA Agreement, as each EFTA State decides on its own whether it applies to be party to the EEA Agreement or not. According to Article 128 of the EEA Agreement, “any European State becoming a member of the Community shall, and the Swiss Confederation or any European State becoming a member of EFTA may, apply to become a party to this Agreement. It shall address its application to the EEA Council.” EFTA does not envisage political integration. It does not issue legislation, nor does it establish a customs union. Schengen is not a part of the EEA Agreement. However, all of the four EFTA States participate in Schengen and Dublin through bilateral agreements. They all apply the provisions of the relevant Acquis.

The European Union (EU) has expanded a number of times throughout its history by way of the accession of new member states to the Union. To join the EU, a state needs to fulfil economic and political conditions called the Copenhagen criteria, which require a stable democratic government that respects the rule of law, and its corresponding freedoms and institutions. According to the Maastricht Treaty, each current member state and the European Parliament must agree to any enlargement. The process of enlargement is sometimes referred to as European integration. This term is also used to refer to the intensification of co-operation between EU member states as national governments allow for the gradual harmonisation of national laws.

The special territories of members of the European Economic Area (EEA) are the 32 special territories of EU member states and EFTA member states which, for historical, geographical, or political reasons, enjoy special status within or outside the European Union and the European Free Trade Association.

This is a list of referendums related to the European Union, or referendums related to the European Communities, which were predecessors of the European Union. Since 1972, a total of 48 referendums have been held by EU member states, candidate states, and their territories, with several additional referendums held in countries outside the EU. The referendums have been held most commonly on the subject of whether to become a member of European Union as part of the accession process, although the EU does not require any candidate country to hold a referendum to approve membership or as part of treaty ratification. Other EU-related referendums have been held on the adoption of the euro and on participation in other EU-related policies.

The Treaty of Accession 2005 is an agreement between the member states of European Union and Bulgaria and Romania. It entered into force on 1 January 2007. The Treaty arranged accession of Bulgaria and Romania to the EU and amended earlier Treaties of the European Union. As such it is an integral part of the constitutional basis of the European Union.

The Brussels Regime is a set of rules regulating which courts have jurisdiction in legal disputes of a civil or commercial nature between individuals resident in different member states of the European Union (EU) and the European Free Trade Association (EFTA). It has detailed rules assigning jurisdiction for the dispute to be heard and governs the recognition and enforcement of foreign judgments.

The most recent enlargement of the European Union saw Croatia become the European Union's 28th member state on 1 July 2013. The country applied for EU membership in 2003, and the European Commission recommended making it an official candidate in early 2004. Candidate country status was granted to Croatia by the European Council in mid-2004. The entry negotiations, while originally set for March 2005, began in October that year together with the screening process.

The European Union (Accessions) Act 2006 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which ratified and legislated for the accession of Romania and Bulgaria to the European Union. It received Royal assent on 16 February 2006.

The European Union (Accessions) Act 2003 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which ratified and legislated for the accession of the Czech Republic, Estonia, Cyprus, Latvia, Lithuania, Hungary, Malta, Poland, Slovenia and Slovakia to the European Union from 1 May 2004. It received royal assent on 13 November 2003.
European Union (EU) concepts, acronyms, and jargon are a terminology set that has developed as a form of shorthand, to quickly express a (formal) EU process, an (informal) institutional working practice, or an EU body, function or decision, and which is commonly understood among EU officials or external people who regularly deal with EU institutions.

The Hague Convention on the International Recovery of Child Support and Other Forms of Family Maintenance, also referred to as the Hague Maintenance Convention or the Hague Child Support Convention is a multilateral treaty governing the enforcement of judicial decisions regarding child support extraterritorially. It is one of a number of conventions in the area of private international law of the Hague Conference on Private International Law in 2007. The convention is open to all states as well as to Regional Economic Integration Organizations as long as they are composed of sovereign states only and have sovereignty in the content of the convention. The convention entered into force on 1 January 2013 between Norway and Albania, with Bosnia-Herzegovina (2013), Ukraine (2013), the European Union, Montenegro (2017), United States (2017), Turkey (2017), Kazakhstan (2017), Brazil (2017), Honduras (2017), Belarus (2018), Guyana (2020), Nicaragua (2020), United Kingdom (2021), Serbia (2021), New Zealand (2021), Ecuador (2022), Botswana (2022), Philippines (2022), Azerbaijan (2023) and Canada following suit. Because the EU acceptance of the convention applies in 26 EU countries, the convention applies in 47 countries worldwide.

The Treaty of Accession 2011 is an agreement between the member states of the European Union and Croatia concerning Croatia's accession to the EU. It was signed on 9 December 2011 in Brussels by the heads of state or government of the 27 member states and by the president of Croatia, Ivo Josipović, and Prime Minister Jadranka Kosor.
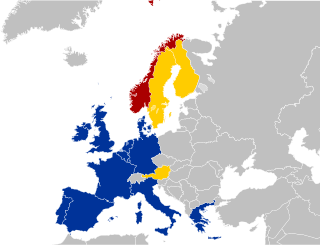
The Treaty of Accession 1994 was the agreement between the member states of the European Union and four countries, concerning these countries' accession into the EU. It entered into force on 1 January 1995. The Treaty arranged accession of Austria, Finland and Sweden to the EU and amended earlier Treaties of the European Union. As such it is an integral part of the constitutional basis of the European Union. Norway failed to join the EU because its referendum did not pass.

The Treaty of Accession 1972 was the international agreement which provided for the accession of Denmark, Ireland, Norway and the United Kingdom to the European Communities. Norway did not ratify the treaty after it was rejected in a referendum held in September 1972. The treaty was ratified by Denmark, Ireland and the United Kingdom who became EC member states on 1 January 1973 when the treaty entered into force. The treaty remains an integral part of the constitutional basis of the European Union.

The Treaties of the European Union are a set of international treaties between the European Union (EU) member states which sets out the EU's constitutional basis. They establish the various EU institutions together with their remit, procedures and objectives. The EU can only act within the competences granted to it through these treaties and amendment to the treaties requires the agreement and ratification of every single signatory.
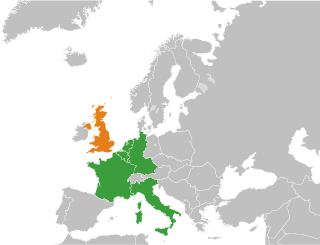
The accession of the United Kingdom to the European Communities (EC) – the collective term for the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC), the European Economic Community (EEC) and the European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC) – took effect on 1 January 1973. This followed ratification of the Accession treaty which was signed in Brussels on 22 January 1972 by the Conservative prime minister Edward Heath, who had pursued the UK's application to the EEC since the late 1950s. The ECSC and EEC would later be integrated into the European Union under the Maastricht and Lisbon treaties in the early 1990s and mid-2000s.

This is a list of current, amended, spent and repealed acts of the Parliament of the United Kingdom relating to its former membership and current relationship to the European Communities and the European Union from 1972 onwards.

The European Communities Act 1979 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which ratified and legislated for the accession of Greece to the European Communities. It received royal assent on 20 December 1979.

The European Communities Act 1985 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which ratified and legislated for the accession of Spain and Portugal to the European Communities. It received royal assent on 19 December 1985.














