Lomazzo is a town and comune in the province of Como, in the Italian region of Lombardy. It is situated halfway between Como and Milan. The ancient historical center of the town was founded on the top of a hill situated in the valley on the right bank of Lura. The municipal territory contains a large portion of the Lura Park. Lomazzo received the title of Città (City) with a presidential decree on July 11, 2006. Lomazzo borders the following municipalities: Bregnano, Cadorago, Cirimido, Guanzate, Rovellasca, Rovello Porro, Turate.
Rovello Porro is a comune (municipality) in the Province of Como in the Italian region of Lombardy, located about 25 kilometres (16 mi) northwest of Milan and about 20 kilometres (12 mi) south of Como. As of 31 December 2004, it had a population of 5,797 and an area of 5.6 square kilometres (2.2 sq mi).
Rescaldina is a comune (municipality) that is part of the Metropolitan City of Milan, in the Province of Milan in the Italian region Lombardy, with a population of 14,211 distributed over about 8 km2, and located about 25 kilometres (16 mi) northwest of Milan.

The Italian railway system is one of the most important parts of the infrastructure of Italy, with a total length of 24,227 km (15,054 mi) as of 2011.

The Malpensa Express is an airport rail service linking the city of Milan with Malpensa Airport, in the region of Lombardy, Northern Italy.
LeNORD S.r.l. was a subsidiary of the FNM Group responsible for operating passenger train services in northern Italy.

The Milano–Chiasso railway line is an Italian state-owned railway connecting Milan to Como and Chiasso, Switzerland.
Centostazioni S.p.A. is a subsidiary of Italian holding company Ferrovie dello Stato. The company was created to redevelop and manage 103 medium-sized Italian railway stations.

Brescia railway station is the main station of Brescia, in the region of Lombardy, northern Italy. The station, opened in 1854, lies on the Milan-Venice railway and is a terminus of three branch lines: Valcamonica Railway to Edolo, Bergamo–Brescia railway and Brescia–Piadena/Cremona railway which branches off towards southeast of the station.
Ferrovienord is an Italian transport company managing the network of regional railway concessions owned by the group in northern Italy. It is a subsidiary of Ferrovie Nord Milano.

Trenord is a railway company which is responsible for the operation of regional passenger trains in Lombardy. The company was established by the two main railway companies in Lombardy, Trenitalia and Ferrovie Nord Milano (FNM), to manage train operations in the region. The equity is equally divided between the two companies.

Milano Bovisa is a railway station in Bovisa, Milan, Italy. It opened in 1879 and is now one of the key nodes of the Milan suburban railway service, and of the Trenord regional network in northern Lombardy. It is located in Piazza Emilio Alfieri.

The S5 is a commuter railway route forming part of the Milan suburban railway service, which converges on the city of Milan, Italy.

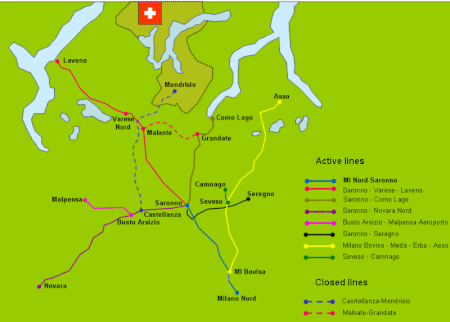
The Milan–Asso railway is a regional railway line with standard track gauge which links Milan to Canzo crossing for Erba and other towns in Brianza. The most northern terminal is the station of Canzo-Asso, which is located in Canzo's territory but is also known as Asso in the short form. That, because there is another station on the line called Canzo station and Canzo-Asso is next to Asso's boundary and serves this commune too.
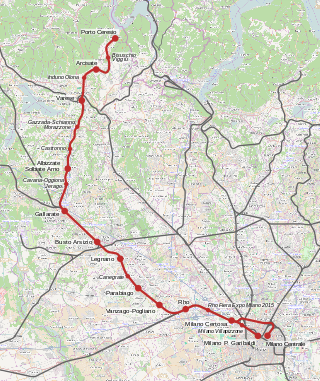
Porto Ceresio–Milan railway is a railway line in Lombardy, Italy. It uses the tracks of the Milan–Arona railway until Gallarate.

Rovato Borgo is a railway station serving the town of Rovato, in the region of Lombardy, northern Italy. The station opened in 1911 and is located on the Cremona-Iseo railway line. Train services are operated by the Italian railway company Trenord.

Milan–Saronno railway is a railway line in Lombardy, Italy.

The Caravaggio is an electric multiple unit (EMU) developed and built by Hitachi Rail Italy. It is named after the Renaissance-era Italian painter Michelangelo Merisi da Caravaggio.