Lower New York Bay is a section of New York Bay south of the Narrows. The eastern end of the Bay is marked by two spits of land, Sandy Hook, New Jersey, and Rockaway, Queens. The waterway between the spits connects the Bay to the Atlantic Ocean at the New York Bight. Traversing the floor of the Bay southeasterly from the Narrows to the Bight and beyond is Hudson Canyon.

Fort Greene Park is a city-owned and -operated park in Fort Greene, Brooklyn. The 30.2-acre (12.2 ha) park was originally named after the fort formerly located there, Fort Putnam, itself was named for Rufus Putnam, George Washington's chief of engineers in the Revolutionary War.

New Utrecht was a town in western Long Island, New York encompassing all or part of the present-day Bath Beach, Bay Ridge, Bensonhurst, Borough Park, Dyker Heights and Fort Hamilton neighborhoods of Brooklyn, New York City. New Utrecht was established in 1652 by Dutch settlers in the Dutch colony of New Netherland, the last of the original six towns to be founded in Kings County. New Utrecht ceased to exist in 1894 when it was annexed by the City of Brooklyn, and became part of the City of Greater New York when Brooklyn joined as a borough in 1898.

Mount Prospect Park is a 7.79-acre (3.15 ha) park in the central portion of the New York City borough of Brooklyn. It includes Mount Prospect, the second highest point in Brooklyn. It is located on Eastern Parkway near Underhill Avenue, close to Grand Army Plaza. The park is operated by the New York City Department of Parks and Recreation.

Commodore Barry Park is an urban park in the Fort Greene neighborhood of the New York City borough of Brooklyn. The park is operated by the New York City Department of Parks and Recreation. It encompasses an area of 10.39 acres (42,000 m2) and holds baseball, basketball, football, swimming pool and playground fields/facilities. The park was acquired in 1836 by the Village of Brooklyn. When first acquired, it was called "City Park". It is the oldest park in the borough, and it was named for Commodore John Barry in 1951 due to its location next to the Brooklyn Navy Yard that Barry helped found.

Fort Lafayette was an island coastal fortification in The Narrows of New York Harbor, built offshore from nearby Fort Hamilton at the southern tip of what is now the Bay Ridge neighborhood in the New York City borough of Brooklyn at the western end of Long Island. The fort was built on a natural off-shore island shoal, known as Hendrick's Reef. Construction on the fort began during the War of 1812 (1812-1815), with the British and was completed almost a decade later in 1822, as part of the continuing seacoast defense systems of the United States, built-up over the next two and half centuries with waterfront / island fortifications and artillery batteries outside seaport cities, mouths of rivers / bays and various strategic points, along the East Coast and southern Gulf of Mexico.

Crown Point State Historic Site is the site of a former military stronghold at the south end of the wider part of Lake Champlain. The location is in Essex County, New York, United States. The site is on a peninsula in the town of Crown Point, New York.
Vanderbilt Avenue is the name of three thoroughfares in the New York City boroughs of Brooklyn, Manhattan, and Staten Island. They were named after Cornelius Vanderbilt (1794–1877), the builder of Grand Central Terminal in Midtown Manhattan.

The Prison Ship Martyrs' Monument is a war memorial at Fort Greene Park, in the New York City borough of Brooklyn. It commemorates more than 11,500 American prisoners of war who died in captivity aboard sixteen British prison ships during the American Revolutionary War. The remains of a small fraction of those who died on the ships are interred in a crypt beneath its base. The sixteen ships included HMS Jersey, HMS Scorpion, Good Hope, Falmouth, Stromboli and Hunter.

Wallabout is a neighborhood in the New York City borough of Brooklyn that dates back to the 17th century. It is one of the oldest areas of Brooklyn, in the area that was once Wallabout Bay but has largely been filled in and is now the Brooklyn Navy Yard.

The Mark Morris Dance Center is the permanent home of the international touring modern dance company, the Mark Morris Dance Group (MMDG), in the Fort Greene neighborhood of Brooklyn, New York City. It is located at the address 3 Lafayette Avenue on the corner of Flatbush Avenue. Open since 2001, the center also houses rehearsal space for the dance community, outreach programs for local children and area residents, and a school offering dance classes to students of all ages.

The Heights of Guan is a historical name given to a series of hills extending in a ridge along western Long Island in New York State. The ridge extends in an east-northeast direction across the modern-day New York City boroughs of Brooklyn and Queens, with hills varying in height from 100 to 150 feet. The southern slope of the ridge has a relatively steep drop and the northern slope is more gradual. Further to the south is an outwash plain bordered by the Atlantic Ocean. Geologically, the ridge is part of the Harbor Hill Moraine formed 13,000 to 12,000 years ago during the Wisconsin glaciation.

Church of St. Elizabeth is a Roman Catholic parish church in the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of New York, located at West 187th Street at Wadsworth Avenue in Washington Heights, Manhattan, New York City. The parish was established in 1869, originally located on 187th Street at Broadway from 1869 to 1929.
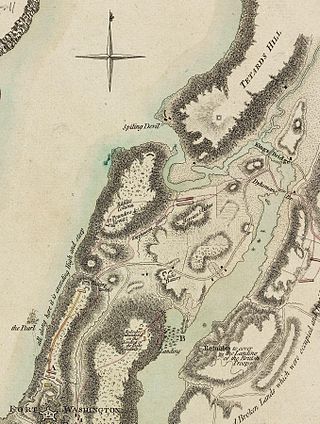
Fort Cockhill was an 18th-century military fortification located on Cox's Hill or Tubby Hook Hill, now known as the present-day Inwood Hill Park in Manhattan, New York City. A small, circular earthwork structure, in height some ten or twelve feet and equipped with two cannon, it was situated at the northwestern extremity of Tubby Hook Hill, at a point overlooking both the Hudson River and the Harlem River valley.

The Queen of All Saints Church is located at 300 Vanderbilt Avenue on the corner of Lafayette Avenue in the Fort Greene neighborhood of Brooklyn, New York City. It is a Catholic parish church in the Roman Catholic Diocese of Brooklyn. The church is located within the Fort Greene Historic District.

Fort Clinton was a stone-and-earthworks fortification on an elevation within what is now Central Park in New York City. It was built in 1814 near the present line of 107th Street, slightly west of Fifth Avenue. According to maps of the time, Fort Clinton was the easternmost of a connected series of forts, connected to Nutter's Battery on the west by earthworks and a gatehouse over the Old Post Road at the bottom of McGowan's Pass. Fort Clinton and Nutter's Battery were commanded from a third fort at the top of the pass, Fort Fish, which had a sweeping view of Long Island Sound, northern Manhattan, and Westchester County. Fort Fish was across the road from Fort Clinton and connected to Nutter's Battery by another line of earthworks.
Alben Square, also known as Alben Triangle, is located in the Borough Park neighborhood of Brooklyn, New York.

AVA DoBro, also known as Avalon Willoughby West and by its address of 100 Willoughby, is a residential high-rise building in Downtown Brooklyn, New York City. Developed by AvalonBay Communities, it has 826 units over 57 floors. As part of the development, a new entrance to the Jay Street–MetroTech station of the New York City Subway was built, including an elevator.

John Paul Jones Park is a public park located in Fort Hamilton, Bay Ridge, Brooklyn. The park borders Shore Road, Fourth Avenue, 101st Street, and Fort Hamilton Parkway. The park is managed by the New York City Department of Parks and Recreation, which acquired the property from the city of Brooklyn in 1897.
















