A Bayer designation is a stellar designation in which a specific star is identified by a Greek or Latin letter followed by the genitive form of its parent constellation's Latin name. The original list of Bayer designations contained 1,564 stars.
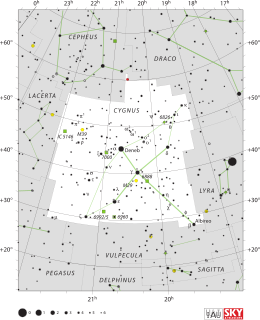
Cygnus is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. Cygnus is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, and it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross. Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.
Albireo is the traditional name for the double star also designated Beta Cygni, although the International Astronomical Union now regards the name as only applying to the brightest component. Although designated 'beta', it is fainter than Gamma Cygni, Delta Cygni, and Epsilon Cygni and is the fifth-brightest point of light in the constellation of Cygnus. Appearing to the naked eye to be a single star of magnitude 3, viewing through even a low-magnification telescope resolves it into its two components. The brighter yellow star makes a striking colour contrast with its fainter blue companion.

Gamma Cygni, also named Sadr, is a star in the northern constellation of Cygnus, forming the intersection of an asterism of five stars called the Northern Cross. Based upon parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately 1,800 light-years (560 parsecs) from the Sun.

A K-type main-sequence star, also referred to as an K dwarf, is a main-sequence (hydrogen-burning) star of spectral type K and luminosity class V. These stars are intermediate in size between red M-type main-sequence stars and yellow G-type main-sequence stars. They have masses between 0.5 and 0.8 times the mass of the Sun and surface temperatures between 3,900 and 5,200 K., Tables VII, VIII. Better known examples include Alpha Centauri B and Epsilon Indi.

Delta Corvi, also named Algorab, is a third magnitude star at a distance of 86.9 light-years from the Sun in the southern constellation of Corvus.

Gamma² Sagittarii, also named Alnasl, is a 3rd-magnitude star in the zodiac constellation of Sagittarius. The location of this star forms the tip of the arrow in the bow of Sagittarius the Centaur. Based on parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately 96.9 light-years from the Sun. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +2.98, making it the seventh-brightest star in the constellation.
Alpha Corvi, also named Alchiba, is an F-type main-sequence star and the fifth-brightest star in the constellation of Corvus. Based on parallax measurements made during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately 49 light-years from the Sun.
Pi¹ Cygni is a binary star in the northern constellation of Cygnus. It is visible to the naked eye, having a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.66. The distance to this system can be roughly gauged by its annual parallax shift of 1.89 mas, which yields a separation of around 1,700 light years from the Sun, give or take a hundred light years.

Epsilon Corvi is a star in the southern constellation of Corvus. It has the traditional name Minkar, from Arabic منقارminqar meaning "beak [of the crow]" The apparent visual magnitude is +3.0 and it is located at a distance of 318 light-years from Earth.

Beta Corvi, also named Kraz, is the second-brightest star in the southern constellation of Corvus with an apparent visual magnitude of 2.647. Based on parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is about 146 light-years distant from the Sun.

The Girl mansion is one of the Twenty-eight mansions of the Chinese constellations. It is one of the northern mansions of the Black Tortoise.

Delta Cygni is a binary star of a combined third-magnitude in the constellation of Cygnus. It is also part of the Northern Cross asterism whose brightest star is Deneb. Based upon parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, Delta Cygni is located roughly 165 light-years distant from the Sun.

The Northern Cross is a prominent astronomical asterism in the northern hemisphere celestial sphere, corresponding closely with the constellation Cygnus The Swan. It is much larger than the more famous Southern Cross and consists of the brightest stars in Cygnus, Deneb, Sadr, Gienah, Delta Cygni and Albireo. The 'head' of the cross, Deneb, is also part of the Summer Triangle asterism.
This is a list of articles about astronomical locations that exist in real life that have been featured in works of science fiction and fantasy, including planets, asteroids, comets and other star systems.

NGC 6910 is an open cluster in the constellation Cygnus. It was discovered by William Herschel on October 17, 1786. The cluster was also observed by John Herschel on September 18, 1828. It is a poor cluster and with prominent central concentration, with Trumpler class I2p. NGC 6910 is the core cluster of the stellar association Cygnus OB9.











