Related Research Articles
This article concerns the period 329 BC – 320 BC.

Perdiccas became a general in Alexander the Great's army and participated in Alexander's campaign against Achaemenid Persia. Following Alexander's death, he rose to become supreme commander of the imperial army and regent for Alexander's half brother and intellectually disabled successor, Philip Arridaeus.

Antigonus I Monophthalmus, son of Philip from Elimeia, was a Macedonian nobleman, general, satrap, and king. During the first half of his life he served under Philip II; after Philip's death in 336 BC, he served Philip's son Alexander. He was a major figure in the Wars of the Diadochi after Alexander's death, declaring himself king in 306 BC and establishing the Antigonid dynasty.

Antipater was a Macedonian general and statesman under kings Philip II of Macedon and Alexander the Great, and father of King Cassander. In 320 BC, he became regent of all of Alexander the Great's Empire but died the next year; he had named an officer named Polyperchon as his successor instead of his son Cassander, and a two-year-long power struggle ensued.

The Diadochi were the rival generals, families, and friends of Alexander the Great who fought for control over his empire after his death in 323 BCE. The Wars of the Diadochi mark the beginning of the Hellenistic period from the Mediterranean Sea to the Indus River Valley.

The Wars of the Diadochi, or Wars of Alexander's Successors, were a series of conflicts fought between Alexander the Great's generals over the rule of his vast empire after his death. They occurred between 322 and 281 BC.

Eumenes was a Greek general and satrap. He participated in the Wars of Alexander the Great serving as both Alexander’s personal secretary and as a battlefield commander. He later was a participant in the Wars of the Diadochi as a supporter of the Macedonian Argead royal house. He was executed after the Battle of Gabiene in 316 BC.

Craterus or Krateros was an ancient Macedonian general under Alexander the Great and one of the Diadochi.

The Battle of the Hydaspes was fought in 326 BC between Alexander the Great and King Porus of the Paurava kingdom on the banks of the Jhelum River in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent. The battle resulted in a Greek victory and the surrender of Porus. Large areas of the Punjab between the Hydaspes (Jhelum) and Hyphasis (Beas) rivers were absorbed into the Alexandrian Empire, and Porus was reinstated as a subordinate ruler.
Meleager was a Macedonian officer who served Alexander the Great with distinction. Among the king's generals who went with him to Asia, he was the most experienced as the only military figure who exceeded his experience was the Macedonian general Antipater who remained in Macedon during Alexander's entire Asian campaign.
Polyperchon (Greek: Πολυπέρχων; b. between 390-380 BC – d. after 304 BC, possibly into 3rd century BC, was a Macedonian general who served both Philip II and Alexander the Great and then played an active role in the ensuing battles for control between Alexander's generals.

Balakros, also Balacrus, the son of Nicanor, one of Alexander the Great's "Somatophylakes" (bodyguards), was appointed satrap of Cilicia after the Battle of Issus, 333 BC. He succeeded to the last Achaemenid satrap of Cilicia, Arsames.
Erigyius, a Mytilenaean, son of Larichus, was an officer in Alexander the Great's army. He had been driven into banishment by Philip II, king of Macedon, because of his faithful attachment to Alexander, and returned when the latter came to the throne in 336 BC. At the battle of Gaugamela, 331 BC, he commanded the cavalry of the allies, as he did also when Alexander set out in 330 BC from Ecbatana in pursuit of Darius III. In the same year Erigyius was entrusted with the command of one of the three divisions with which Alexander invaded Hyrcania. He was also among the generals sent against Satibarzanes, whom he slew in battle with his own hand. In 329 BC, together with Craterus and Hephaestion, and with the assistance of Aristander, a soothsayer, he endeavoured to dissuade Alexander from crossing the Jaxartes river against the Scythians. In 328 BC he fell in a battle against the Bactrian fugitives.
Cleitus (Clitus) the White was an officer of Alexander the Great surnamed "White" to distinguish him from Cleitus the Black. He is noted by Athenaeus and Aelian for his pomp and luxury, and is probably the same who is mentioned by Justin among the veterans sent home to Macedonia under Craterus in 324 BC.
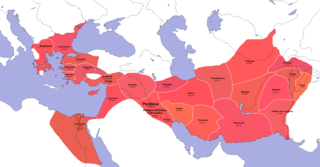
The Partition of Babylon was the first of the conferences and ensuing agreements that divided the territories of Alexander the Great. It was held at Babylon in June 323 BC. Alexander’s death at the age of 32 had left an empire that stretched from Greece all the way to India. The issue of succession resulted from the claims of the various supporters of Philip Arrhidaeus, and the as-of-then unborn child of Alexander and Roxana, among others. The settlement saw Arrhidaeus and Alexander’s child designated as joint kings with Perdiccas serving as regent. The territories of the empire became satrapies divided between the senior officers of the Macedonian army and some local governors and rulers. The partition was solidified at the further agreements at Triparadisus and Persepolis over the following years and began the series of conflicts that comprise the Wars of the Diadochi.

Funeral Games is a 1981 historical novel by Mary Renault, dealing with the death of Alexander the Great and its aftermath, the gradual disintegration of his empire. It is the final book of her Alexander trilogy.
Pharnabazus III was a Persian satrap who fought against Alexander the Great. His father was Artabazus II, and his mother a Greek from Rhodes.

The Indian campaign of Alexander the Great began in 326 BC. After conquering the Achaemenid Empire of Persia, the Macedonian king Alexander, launched a campaign into the Indian subcontinent in present-day Pakistan, part of which formed the easternmost territories of the Achaemenid Empire following the Achaemenid conquest of the Indus Valley.

The Battle of the Hellespont took place in 321 BC between the armies of Craterus and Neoptolemus against Eumenes.
References
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Smith, William, ed. (1870). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology .Missing or empty
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Smith, William, ed. (1870). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology .Missing or empty |title= (help)