
Cache Creek is a historic transportation junction and incorporated village 354 kilometres (220 mi) northeast of Vancouver in British Columbia, Canada. It is on the Trans-Canada Highway in the province of British Columbia at a junction with Highway 97. The same intersection and the town that grew around it was at the point on the Cariboo Wagon Road where a branch road, and previously only a trail, led east to Savona's Ferry on Kamloops Lake. This community is also the point at which a small stream, once known as Riviere de la Cache, joins the Bonaparte River.
Spuzzum is an unincorporated settlement in British Columbia, Canada. Because it is on the Trans-Canada Highway, approximately 50 kilometres (31 mi) north of the community of Hope, it is often referred to as being "beyond Hope". Spuzzum was immortalized in the early 1980s by the band "Six Cylinder" in a song with the refrain "If you haven't been to Spuzzum, you ain't been anywhere."
Brentwood Bay, is a small village in the municipality of Central Saanich, on the Saanich Peninsula. It lies north of the city of Victoria and south of Sidney on the southern tip of Vancouver Island.

Alexandra Bridge Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada, located in the Fraser Canyon approximately two kilometres north of Spuzzum and 40 kilometres (25 mi) north of Hope.

Alice Lake Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada.
Sasquatch Provincial Park is a provincial park in Kent, British Columbia, Canada.
Ferry Island Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia that is located on the south side of the Fraser River northeast of Rosedale. This park is northwest of Bridal Falls, British Columbia and adjacent to the Agassiz-Rosedale Bridge. The Ferry Island Park was established in 1963, and it has an area of about 29 hectares.
F.H. Barber Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada. Comprising 5 ha. of Fraser River floodplain in its natural state, it is one of only two secured public access points to the Fraser between Chilliwack and Hope. It is located at the confluence of Wahleach Creek and the Fraser one mile west of Laidlaw, British Columbia and is bounded on the south by the tracks of the Canadian National Railway.
Norbury Lake Provincial Park is a 97-hectare (240-acre) provincial park in British Columbia, Canada.
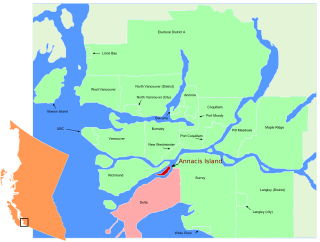
Annacis Island is an island located in the south arm of the Fraser River, in Delta, British Columbia. The island is now mostly industrial, and it contains one of Metro Vancouver's secondary wastewater treatment plants.

Likely is a community in British Columbia, Canada. It is located in the Cariboo region of the province, and is situated where the west arm of Quesnel Lake empties into the Quesnel River. Roads from Likely lead southwest to Williams Lake, northwest to Quesnel, south to Horsefly, and north to Barkerville. Likely is in the Quesnel Highland, a transition zone between the Cariboo Plateau and the Cariboo Mountains.

Barkley Sound, also known historically as Barclay Sound, is south of Ucluelet and north of Bamfield on the west coast of Vancouver Island and forms the entrance to the Alberni Inlet. The Broken Islands Group lies in the sound. Barkley Sound is part of the traditional territory of the Nuu-cha-nulth First Nations. In 1787, Captain Charles William Barkley of Imperial Eagle, explored the sound and named it after himself. Barkley traveled with his 17-year-old bride, Frances Barkley, the first European woman to visit what is now British Columbia.
Monte Creek is a rural locality on the South Thompson River east of Kamloops, British Columbia, Canada, approximately equidistant from Kamloops and the village of Chase, British Columbia. It is mostly notable as a major highway junction where British Columbia Highway 97 branches off from the Trans-Canada Highway south towards the Okanagan via Falkland and Westwold. Monte Lake, a recreational community on the shores of the lake of the same name, is a few miles south of the junction.
Silverdale is a semi-rural neighbourhood of the District of Mission, British Columbia, Canada c. 40 km east of Vancouver on the east bank of the Stave River at its confluence with the Fraser. Noted for its historic Italian Canadian community, its economy was farming, fishing and logging based until the general suburbanization of Fraser Valley life in the 1960s and '70s. Of its Italian community, notable offspring include Phil Gaglardi, former BC Highways minister, and speed-skater Eden Donatelli. Silverdale is also notable as the site of Canada's first train robbery, by the "Gentleman Bandit" Billy Miner, and it is there he is supposed to have first used the polite "Hands Up!" in the course of the robbery.

Glenora, also known historically as the Hudson's Bay Company's Fort Glenora and during the Cassiar Gold Rush as Glenora Landing, was an unincorporated settlement in the Stikine Country of northwestern British Columbia, Canada. It was located on the banks of the Stikine River, just southwest and approximately 13 miles downstream from the community of Telegraph Creek.

The Ashnola River is a tributary of the Similkameen River, rising in the northeastern part of the North Cascades in Washington, United States, and flowing north into British Columbia, Canada, to join the Similkameen River about halfway along that river's course between the towns of Princeton and Keremeos. The river crosses the international boundary at 49°00′00″N120°19′37″W and transits Cathedral Provincial Park. It has one main tributary, Ewart Creek, which is about 25 kilometres (16 mi) long and begins virtually at the border and is entirely within Cathedral Park.
The Scowlitz First Nation or Scowlitz Indian Band is the band government of Skaulits subgroup of the Sto:lo people located on Harrison Bay in the Upper Fraser Valley region between Chehalis (E) and Lake Errock, British Columbia, Canada (W). They are a member government of the Stó:lō Tribal Council.
Jolly Jack Creek is a creek located in British Columbia. The creek flows south into Boundary Creek. This creek was named after local prospector Jolly Jack Thornton who was the second white settler in the district. This creek is also called "Jolly Creek".
Scotch Creek is a stream in the British Columbia Interior of Canada, located on the north side of Shuswap Lake. It is part of the Thompson River watershed, which is a tributary to the Fraser River. It flows from the Shuswap Highlands into Shuswap Lake just west of the community of Scotch Creek. It was named for Scottish gold prospectors who worked the creek with placer mining operations in the 1860s. The creek's headwaters are near Pukeshun Mountain, and flow southwest and south for 56.5 kilometres (35.1 mi). The creek supports sockeye salmon, which breed in the creek during a small salmon run in the autumn.
Avola is an unincorporated community in the Canadian province of British Columbia, located in the Thompson-Nicola Regional District. The community is located along British Columbia Highway 5, approximately 190 kilometres north of Kamloops and 148 kilometres south of the highway's northern terminus at Tête Jaune Cache.













