| Look up harmonic in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Harmonic usually refers to the frequency components of a time-varying signal, such as a musical note.
| Look up harmonic in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Harmonic usually refers to the frequency components of a time-varying signal, such as a musical note.

The fundamental frequency, often referred to simply as the fundamental, is defined as the lowest frequency of a periodic waveform. In music, the fundamental is the musical pitch of a note that is perceived as the lowest partial present. In terms of a superposition of sinusoids, the fundamental frequency is the lowest frequency sinusoidal in the sum of harmonically related frequencies, or the frequency of the difference between adjacent frequencies. In some contexts, the fundamental is usually abbreviated as f0, indicating the lowest frequency counting from zero. In other contexts, it is more common to abbreviate it as f1, the first harmonic.

A harmonic series is the sequence of harmonics, musical tones, or pure tones whose frequency is an integer multiple of a fundamental frequency.

In music, there are two common meanings for tuning:
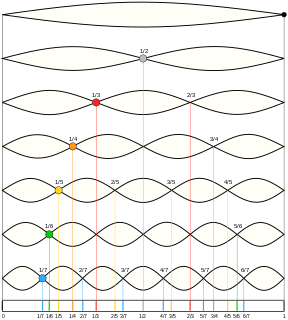
A harmonic is a wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the fundamental frequency, the frequency of the original periodic signal, such as a sinusoidal wave. The original signal is also called the 1st harmonic, the other harmonics are known as higher harmonics. As all harmonics are periodic at the fundamental frequency, the sum of harmonics is also periodic at that frequency. The set of harmonics forms a harmonic series.

An overtone is any harmonic with frequency greater than the fundamental frequency of a sound. In other words, overtones are all pitches higher than the lowest pitch within an individual sound; the fundamental is the lowest pitch. While the fundamental is usually heard most prominently, overtones are actually present in any pitch except a true sine wave. The relative volume or amplitude of various overtone partials is one of the key identifying features of timbre, or the individual characteristic of a sound.

In music, timbre, also known as tone color or tone quality, is the perceived sound quality of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes different types of sound production, such as choir voices and musical instruments. It also enables listeners to distinguish different instruments in the same category.

Pitch is a perceptual property of sounds that allows their ordering on a frequency-related scale, or more commonly, pitch is the quality that makes it possible to judge sounds as "higher" and "lower" in the sense associated with musical melodies. Pitch is a major auditory attribute of musical tones, along with duration, loudness, and timbre.

A power chordPlay (help·info) is a colloquial name for a chord in guitar music, especially electric guitar, that consists of the root note and the fifth, as well as possibly octaves of those notes. Power chords are commonly played on amplified guitars, especially on electric guitar with intentionally added distortion or overdrive effects. Power chords are a key element of many styles of rock, especially heavy metal and punk rock.
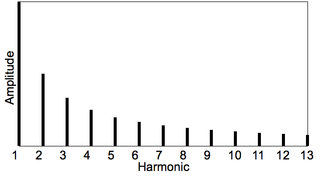
In music, inharmonicity is the degree to which the frequencies of overtones depart from whole multiples of the fundamental frequency.
Piano acoustics is the set of physical properties of the piano that affect its sound. It is an area of study within musical acoustics.
Musical acoustics or music acoustics is a multidisciplinary field that combines knowledge from physics, psychophysics, organology, physiology, music theory, ethnomusicology, signal processing and instrument building, among other disciplines. As a branch of acoustics, it is concerned with researching and describing the physics of music – how sounds are employed to make music. Examples of areas of study are the function of musical instruments, the human voice, computer analysis of melody, and in the clinical use of music in music therapy.
Stretched tuning is a detail of musical tuning, applied to wire-stringed musical instruments, older, non-digital electric pianos, and some sample-based synthesizers based on these instruments, to accommodate the natural inharmonicity of their vibrating elements. In stretched tuning, two notes an octave apart, whose fundamental frequencies theoretically have an exact 2:1 ratio, are tuned slightly farther apart. "For a stretched tuning the octave is greater than a factor of 2; for a compressed tuning the octave is smaller than a factor of 2."

In music, transcription is the practice of notating a piece or a sound which was previously unnotated and/or unpopular as a written music, for example, a jazz improvisation or a video game soundtrack. When a musician is tasked with creating sheet music from a recording and they write down the notes that make up the piece in music notation, it is said that they created a musical transcription of that recording. Transcription may also mean rewriting a piece of music, either solo or ensemble, for another instrument or other instruments than which it was originally intended. The Beethoven Symphonies transcribed for solo piano by Franz Liszt are an example. Transcription in this sense is sometimes called arrangement, although strictly speaking transcriptions are faithful adaptations, whereas arrangements change significant aspects of the original piece.

Music theory analyzes the pitch, timing, and structure of music. It uses mathematics to study elements of music such as tempo, chord progression, form, and meter. The attempt to structure and communicate new ways of composing and hearing music has led to musical applications of set theory, abstract algebra and number theory.
In music, the undertone series or subharmonic series is a sequence of notes that results from inverting the intervals of the overtone series. While overtones naturally occur with the physical production of music on instruments, undertones must be produced in unusual ways. While the overtone series is based upon arithmetic multiplication of frequencies, resulting in a harmonic series, the undertone series is based on arithmetic division.
Musical technique is the ability of instrumental and vocal musicians to exert optimal control of their instruments or vocal cords in order to produce the precise musical effects they desire. Improving one's technique generally entails practicing exercises that improve one's muscular sensitivity and agility. Technique is independent of musicality. Compositional technique is the ability and knowledge composers use to create music, and may be distinguished from instrumental or performance technique, which in classical music is used to realize compositions, but may also be used in musical improvisation. Extended techniques are distinguished from more simple and more common techniques. Musical technique may also be distinguished from music theory, in that performance is a practical matter, but study of music theory is often used to understand better and to improve techniques. Techniques such as intonation or timbre, articulation, and musical phrasing are nearly universal to all instruments.

Playing a string harmonic is a string instrument technique that uses the nodes of natural harmonics of a musical string to isolate overtones. Playing string harmonics produces high pitched tones, often compared in timbre to a whistle or flute. Overtones can be isolated "by lightly touching the string with the finger instead of pressing it down" against the fingerboard.

The Moodswinger is a twelve-string electric zither with an additional third bridge designed by Yuri Landman. The rod which functions as the third bridge divides the strings into two sections to cause an overtone multiphonic sound. One of the copies of the instrument is part of the collection of the Musical Instrument Museum in Phoenix, Arizona.

The 3rd bridge is an extended playing technique used on the electric guitar and other string instruments that allows a musician to produce distinctive timbres and overtones that are unavailable on a conventional string instrument with two bridges. The timbre created with this technique is close to that of gamelan instruments like the bonang and similar Indonesian types of pitched gongs.
A third bridge can be devised by inserting a rigid preparation object between the strings and the body or neck of the instrument, effectively diving the string into distinct vibrating segments.

The scale of harmonics is a musical scale based on the noded positions of the natural harmonics existing on a string. This musical scale is present on the guqin, regarded as one of the first string instruments with a musical scale. Most fret positions appearing on Non-Western string instruments (lutes) are equal to positions of this scale. Unexpectedly, these fret positions are actually the corresponding undertones of the overtones from the harmonic series. The distance from the nut to the fret is an integer number lower than the distance from the fret to the bridge.