Related Research Articles

1621 (MDCXXI) was a common year starting on Friday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar, the 1621st year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 621st year of the 2nd millennium, the 21st year of the 17th century, and the 2nd year of the 1620s decade. As of the start of 1621, the Gregorian calendar was 10 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.
The history of the Czech lands – an area roughly corresponding to the present-day Czech Republic – starts approximately 800 years BCE. A simple chopper from that age was discovered at the Red Hill archeological site in Brno. Many different primitive cultures left their traces throughout the Stone Age, which lasted approximately until 2000 BCE. The most widely known culture present in the Czech lands during the pre-historical era is the Únětice Culture, leaving traces for about five centuries from the end of the Stone Age to the start of the Bronze Age. Celts – who came during the 5th century BCE – are the first people known by name. One of the Celtic tribes were the Boii (plural), who gave the Czech lands their first name Boiohaemum – Latin for the Land of Boii. Before the beginning of the Common Era the Celts were mostly pushed out by Germanic tribes. The most notable of those tribes were the Marcomanni and traces of their wars with the Roman Empire were left in south Moravia.

Ferdinand I was Holy Roman Emperor from 1556, King of Bohemia, Hungary, and Croatia from 1526, and Archduke of Austria from 1521 until his death in 1564. Before his accession as emperor, he ruled the Austrian hereditary lands of the House of Habsburg in the name of his elder brother, Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor. Also, he often served as Charles' representative in the Holy Roman Empire and developed encouraging relationships with German princes. In addition, Ferdinand also developed valuable relationships with the German banking house of Jakob Fugger and the Catalan bank, Banca Palenzuela Levi Kahana.

Matthias was Holy Roman Emperor from 1612 to 1619, Archduke of Austria from 1608 to 1619, King of Hungary and Croatia from 1608 to 1618 and King of Bohemia from 1611 to 1617. His personal motto was Concordia lumine maior.

Ferdinand II was Holy Roman Emperor, King of Bohemia, Hungary, and Croatia from 1619 until his death in 1637. He was the son of Archduke Charles II of Inner Austria and Maria of Bavaria, who were devout Catholics. In 1590, when Ferdinand was 11 years old, they sent him to study at the Jesuits' college in Ingolstadt because they wanted to isolate him from the Lutheran nobles. A few months later, his father died, and he inherited Inner Austria–Styria, Carinthia, Carniola and smaller provinces. His cousin, Rudolf II, Holy Roman Emperor, who was the head of the Habsburg family, appointed regents to administer these lands.

The Battle of White Mountain was an important battle in the early stages of the Thirty Years' War. It led to the defeat of the Bohemian Revolt and ensured Habsburg control for the next three hundred years.

Frederick V was the Elector Palatine of the Rhine in the Holy Roman Empire from 1610 to 1623, and reigned as King of Bohemia from 1619 to 1620. He was forced to abdicate both roles, and the brevity of his reign in Bohemia earned him the derisive sobriquet "the Winter King".

Albrecht Wenzel Eusebius von Wallenstein, Duke of Friedland, also von Waldstein, was a Bohemian military leader and statesman who fought on the Catholic side during the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648). His successful martial career made him one of the richest and most influential men in the Holy Roman Empire by the time of his death. Wallenstein became the supreme commander of the armies of the Imperial Army of Holy Roman Emperor Ferdinand II and was a major figure of the Thirty Years' War.

The Protestant Union, also known as the Evangelical Union, Union of Auhausen, German Union or the Protestant Action Party, was a coalition of Protestant German states. It was formed on 14 May 1608 by Frederick IV, Elector Palatine in order to defend the rights, land and safety of each member. It included both Calvinist and Lutheran states, and dissolved in 1621.

Although the Kingdom of Bohemia, both of the Lusatias, the Margraviate of Moravia, and Silesia were all under Habsburg rule, they followed different paths of development. Moravians and Silesians had accepted the hereditary right of the Austrian Habsburgs to rule and thus escaped the intense struggle between native estates and the Habsburg monarchy that was to characterize Bohemian history. In contrast, the Bohemian Kingdom had entrenched estates that were ready to defend what they considered their rights and liberties. The Habsburgs pursued a policy of centralization and conflict arose, which was further complicated by ethnic and religious issues.

Charles Bonaventure de Longueval, 2nd Count of Bucquoy was a military commander who fought for the Spanish Netherlands during the Eighty Years' War and for the Holy Roman Empire during the Thirty Years' War.

The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm, was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is also referred to as the Austrian monarchy or the Danubian monarchy.
The Peace of Nikolsburg or Peace of Mikulov, signed on 31 December 1621 in Nikolsburg, Moravia, was the treaty which ended the war between Prince Gabriel Bethlen of Transylvania and Emperor Ferdinand II of the Holy Roman Empire. The chief negotiators of the treaty were Maximilian von und zu Trauttmansdorff and Nikolaus Esterházy de Galántha.

Count Jindřich Matyáš of Thurn-Valsassina, was one of the leaders of the Protestant Bohemian Revolt against Emperor Ferdinand II. He took part in events that led to the Thirty Years' War, and after the war he became a military leader and diplomat in Swedish service, who eventually resided in Swedish Estonia.

The House of Waldstein or House of Valdštejn is a Bohemian noble family that originated from the Kingdom of Bohemia as a branch of the Markwartinger family and gained prominence during the reign of the Přemyslid dynasty. The house was founded by Jaroslav of Hruštice (1234–1269) and named after Valdštejn Castle near Turnov in northern Bohemia. The family's most prominent members include Albrecht von Wallenstein, the Imperial general during the Thirty Years' War, and Ferdinand Ernst von Waldstein, a statesman and early patron of Ludwig van Beethoven.

The Bohemian Revolt was an uprising of the Bohemian estates against the rule of the Habsburg dynasty that began the Thirty Years' War. It was caused by both religious and power disputes. The estates were almost entirely Protestant, mostly Utraquist Hussite but there was also a substantial German population that endorsed Lutheranism. The dispute culminated after several battles in the final Battle of White Mountain, where the estates suffered a decisive defeat. This started re-Catholisation of the Czech lands, but also expanded the scope of the Thirty Years' War by drawing Denmark and Sweden into it. The conflict spread to the rest of Europe and devastated vast areas of Central Europe, including the Czech lands, which were particularly stricken by its violent atrocities.

The House of Mansfeld was a princely German house, which took its name from the town of Mansfeld in the present-day state of Saxony-Anhalt. Mansfelds were archbishops, generals, supporters as well as opponents of Martin Luther, and Habsburg administrators.

The Oñate treaty of 6 June 1617 was a secret treaty between the Austrian and Spanish branches of the House of Habsburg.

The Palatinate campaign, also known as the Spanish conquest of the Palatinate or the Palatinate phase of the Thirty Years' War was a campaign conducted by the Imperial army of the Holy Roman Empire against the Protestant Union in the Lower Palatinate, during the Thirty Years' War.
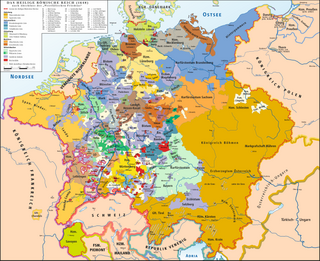
The Erblande of the House of Habsburg formed the Alpine heartland of the Habsburg monarchy. They were the hereditary possessions of the Habsburgs within the Holy Roman Empire from before 1526. The Erblande were not all unified under the head of the dynasty prior to the 17th century. They were divided into several groupings: the Archduchy of Austria, Inner Austria, the County of Tyrol, and Further Austria.
References
- ↑ Pursell, Brennan C. (15 May 2017). The Winter King: Frederick V of the Palatinate and the Coming of the Thirty Years' War. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-351-88042-8 . Retrieved 24 October 2024.
Heinrich Bitter, to Istanbul in January 1620, accompanied by an emissary of the Hungarian Estates, to counter the Imperial negotiations.
- ↑ Klopp, Onno (1891). Der dreissigjährige krieg bis zum tode Gustav Adolf 1632: 2 ̈ausg. des werkes: Tilly im dreissigjährigen kriege (in German). F. Schöningh. p. 471. Retrieved 24 October 2024.