
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a particular factor is manipulated. Experiments vary greatly in goal and scale but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results. There also exist natural experimental studies.
In statistics, the power of a binary hypothesis test is the probability that the test correctly rejects the null hypothesis when a specific alternative hypothesis is true. It is commonly denoted by , and represents the chances of a true positive detection conditional on the actual existence of an effect to detect. Statistical power ranges from 0 to 1, and as the power of a test increases, the probability of making a type II error by wrongly failing to reject the null hypothesis decreases.

HIV tests are used to detect the presence of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), in serum, saliva, or urine. Such tests may detect antibodies, antigens, or RNA.

The base rate fallacy, also called base rate neglect or base rate bias, is a type of fallacy in which people tend to ignore the base rate of an occurrence across a population and instead focus upon of the information just relating to that specific case. For example, if someone hears that a friend is very shy and quiet, they might think the friend is more likely to be a librarian than a salesperson, even though there are far more salespeople than librarians overall - hence making it more likely that their friend is actually a salesperson. Base rate neglect is a specific form of the more general extension neglect.
A drug test is a technical analysis of a biological specimen, for example urine, hair, blood, breath, sweat, or oral fluid/saliva—to determine the presence or absence of specified parent drugs or their metabolites. Major applications of drug testing include detection of the presence of performance enhancing steroids in sport, employers and parole/probation officers screening for drugs prohibited by law and police officers testing for the presence and concentration of alcohol (ethanol) in the blood commonly referred to as BAC. BAC tests are typically administered via a breathalyzer while urinalysis is used for the vast majority of drug testing in sports and the workplace. Numerous other methods with varying degrees of accuracy, sensitivity, and detection periods exist.

A blood culture is a medical laboratory test used to detect bacteria or fungi in a person's blood. Under normal conditions, the blood does not contain microorganisms: their presence can indicate a bloodstream infection such as bacteremia or fungemia, which in severe cases may result in sepsis. By culturing the blood, microbes can be identified and tested for resistance to antimicrobial drugs, which allows clinicians to provide an effective treatment.
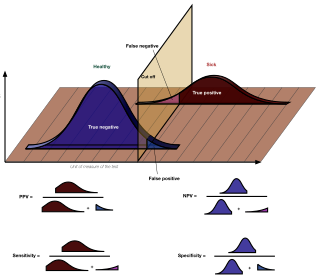
In medicine and statistics, sensitivity and specificity mathematically describe the accuracy of a test that reports the presence or absence of a medical condition. If individuals who have the condition are considered "positive" and those who do not are considered "negative", then sensitivity is a measure of how well a test can identify true positives and specificity is a measure of how well a test can identify true negatives:
In statistical hypothesis testing, a type I error, or a false positive, is the rejection of the null hypothesis when it is actually true. For example, an innocent person may be convicted. A type II error, or a false negative, is the failure to reject a null hypothesis that is actually false. For example: a guilty person may be not convicted.

In statistics, the multiple comparisons, multiplicity or multiple testing problem occurs when one considers a set of statistical inferences simultaneously or estimates a subset of parameters selected based on the observed values.
Medical statistics deals with applications of statistics to medicine and the health sciences, including epidemiology, public health, forensic medicine, and clinical research. Medical statistics has been a recognized branch of statistics in the United Kingdom for more than 40 years, but the term has not come into general use in North America, where the wider term 'biostatistics' is more commonly used. However, "biostatistics" more commonly connotes all applications of statistics to biology. Medical statistics is a subdiscipline of statistics.
It is the science of summarizing, collecting, presenting and interpreting data in medical practice, and using them to estimate the magnitude of associations and test hypotheses. It has a central role in medical investigations. It not only provides a way of organizing information on a wider and more formal basis than relying on the exchange of anecdotes and personal experience, but also takes into account the intrinsic variation inherent in most biological processes.
Materials MASINT is one of the six major disciplines generally accepted to make up the field of Measurement and Signature Intelligence (MASINT), with due regard that the MASINT subdisciplines may overlap, and MASINT, in turn, is complementary to more traditional intelligence collection and analysis disciplines such as SIGINT and IMINT. MASINT encompasses intelligence gathering activities that bring together disparate elements that do not fit within the definitions of Signals Intelligence (SIGINT), Imagery Intelligence (IMINT), or Human Intelligence (HUMINT).
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) is a single-tube technique for the amplification of DNA and a low-cost alternative to detect certain diseases that was invented in 2000 at the University of Tokyo. Reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) combines LAMP with a reverse transcription step to allow the detection of RNA.
Chromogenic in situ hybridization (CISH) is a cytogenetic technique that combines the chromogenic signal detection method of immunohistochemistry (IHC) techniques with in situ hybridization. It was developed around the year 2000 as an alternative to fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) for detection of HER-2/neu oncogene amplification. CISH is similar to FISH in that they are both in situ hybridization techniques used to detect the presence or absence of specific regions of DNA. However, CISH is much more practical in diagnostic laboratories because it uses bright-field microscopes rather than the more expensive and complicated fluorescence microscopes used in FISH.

Surround optical-fiber immunoassay (SOFIA) is an ultrasensitive, in vitro diagnostic platform incorporating a surround optical-fiber assembly that captures fluorescence emissions from an entire sample. The technology's defining characteristics are its extremely high limit of detection, sensitivity, and dynamic range. SOFIA's sensitivity is measured at the attogram level (10−18 g), making it about one billion times more sensitive than conventional diagnostic techniques. Based on its enhanced dynamic range, SOFIA is able to discriminate levels of analyte in a sample over 10 orders of magnitude, facilitating accurate titering.
The mainstay of malaria diagnosis has been the microscopic examination of blood, utilizing blood films. Although blood is the sample most frequently used to make a diagnosis, both saliva and urine have been investigated as alternative, less invasive specimens. More recently, modern techniques utilizing antigen tests or polymerase chain reaction have been discovered, though these are not widely implemented in malaria endemic regions. Areas that cannot afford laboratory diagnostic tests often use only a history of subjective fever as the indication to treat for malaria.

Cannabis drug testing describes various drug test methodologies for the use of cannabis in medicine, sport, and law. Cannabis use is highly detectable and can be detected by urinalysis, hair analysis, as well as saliva tests for days or weeks.
A false positive is an error in binary classification in which a test result incorrectly indicates the presence of a condition, while a false negative is the opposite error, where the test result incorrectly indicates the absence of a condition when it is actually present. These are the two kinds of errors in a binary test, in contrast to the two kinds of correct result. They are also known in medicine as a false positivediagnosis, and in statistical classification as a false positiveerror.

COVID-19 testing involves analyzing samples to assess the current or past presence of SARS-CoV-2. The two main types of tests detect either the presence of the virus or antibodies produced in response to infection. Molecular tests for viral presence through its molecular components are used to diagnose individual cases and to allow public health authorities to trace and contain outbreaks. Antibody tests instead show whether someone once had the disease. They are less useful for diagnosing current infections because antibodies may not develop for weeks after infection. It is used to assess disease prevalence, which aids the estimation of the infection fatality rate.
Viral disease testing is the use of a variety of testing techniques for a variety of purposes, including diagnosing conditions, assessing immunity and understanding disease prevalence. The primary approaches include DNA/RNA tests, serological tests and antigen tests.

COVID-19 rapid antigen tests or RATs, also frequently called COVID-19 lateral flow tests or LFTs, are rapid antigen tests used to detect SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19). They are quick to implement with minimal training, cost a fraction of other forms of COVID-19 testing, and give users a result within 5–30 minutes. RATs have been used in several countries as part of mass testing or population-wide screening approaches. Many RATs can be used for self-testing, in which an individual "collects their own specimen… and interpret[s] their test result themselves".









