Background radiation is a measure of the level of ionizing radiation present in the environment at a particular location which is not due to deliberate introduction of radiation sources.

In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium. This includes:

Radiometry is a set of techniques for measuring electromagnetic radiation, including visible light. Radiometric techniques in optics characterize the distribution of the radiation's power in space, as opposed to photometric techniques, which characterize the light's interaction with the human eye. The fundamental difference between radiometry and photometry is that radiometry gives the entire optical radiation spectrum, while photometry is limited to the visible spectrum. Radiometry is distinct from quantum techniques such as photon counting.

The curie is a non-SI unit of radioactivity originally defined in 1910. According to a notice in Nature at the time, it was to be named in honour of Pierre Curie, but was considered at least by some to be in honour of Marie Skłodowska–Curie as well, and is in later literature considered to be named for both.
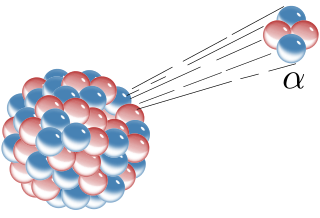
Radioactive decay is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactive. Three of the most common types of decay are alpha, beta, and gamma decay, all of which involve emitting particles. The weak force is the mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetism and nuclear force.
Ionizing radiation, including nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have sufficient energy to ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel up to 99% of the speed of light, and the electromagnetic waves are on the high-energy portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Radiation protection, also known as radiological protection, is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as "The protection of people from harmful effects of exposure to ionizing radiation, and the means for achieving this". Exposure can be from a source of radiation external to the human body or due to internal irradiation caused by the ingestion of radioactive contamination.

Radioactive contamination, also called radiological pollution, is the deposition of, or presence of radioactive substances on surfaces or within solids, liquids, or gases, where their presence is unintended or undesirable.

Radiation hormesis is the hypothesis that low doses of ionizing radiation are beneficial, stimulating the activation of repair mechanisms that protect against disease, that are not activated in absence of ionizing radiation. The reserve repair mechanisms are hypothesized to be sufficiently effective when stimulated as to not only cancel the detrimental effects of ionizing radiation but also inhibit disease not related to radiation exposure. This hypothesis has captured the attention of scientists and public alike in recent years.

Radioluminescence is the phenomenon by which light is produced in a material by bombardment with ionizing radiation such as alpha particles, beta particles, or gamma rays. Radioluminescence is used as a low level light source for night illumination of instruments or signage. Radioluminescent paint is occasionally used for clock hands and instrument dials, enabling them to be read in the dark. Radioluminescence is also sometimes seen around high-power radiation sources, such as nuclear reactors and radioisotopes.
Radionuclides which emit gamma radiation are valuable in a range of different industrial, scientific and medical technologies. This article lists some common gamma-emitting radionuclides of technological importance, and their properties.

Radium and radon are important contributors to environmental radioactivity. Radon occurs naturally as a result of decay of radioactive elements in soil and it can accumulate in houses built on areas where such decay occurs. Radon is a major cause of cancer; it is estimated to contribute to ~2% of all cancer related deaths in Europe.

Radium dials are watch, clock and other instrument dials painted with luminous paint containing radium-226 to produce radioluminescence. Radium dials were produced throughout most of the 20th century before being replaced by safer tritium-based luminous material in the 1970s and finally by non-toxic, non-radioactive strontium aluminate–based photoluminescent material from the middle 1990s.
Naturally occurring radioactive materials (NORM) and technologically enhanced naturally occurring radioactive materials (TENORM) consist of materials, usually industrial wastes or by-products enriched with radioactive elements found in the environment, such as uranium, thorium and potassium and any of their decay products, such as radium and radon. Produced water discharges and spills are a good example of entering NORMs into the surrounding environment.
Radiobiology is a field of clinical and basic medical sciences that involves the study of the action of ionizing radiation on living things, especially health effects of radiation. Ionizing radiation is generally harmful and potentially lethal to living things but can have health benefits in radiation therapy for the treatment of cancer and thyrotoxicosis. Its most common impact is the induction of cancer with a latent period of years or decades after exposure. High doses can cause visually dramatic radiation burns, and/or rapid fatality through acute radiation syndrome. Controlled doses are used for medical imaging and radiotherapy.
Committed dose equivalent and Committed effective dose equivalent are dose quantities used in the United States system of radiological protection for irradiation due to an internal source.
The committed dose in radiological protection is a measure of the stochastic health risk due to an intake of radioactive material into the human body. Stochastic in this context is defined as the probability of cancer induction and genetic damage, due to low levels of radiation. The SI unit of measure is the sievert.
Exposure to ionizing radiation is known to increase the future incidence of cancer, particularly leukemia. The mechanism by which this occurs is well understood, but quantitative models predicting the level of risk remain controversial. The most widely accepted model posits that the incidence of cancers due to ionizing radiation increases linearly with effective radiation dose at a rate of 5.5% per sievert; if correct, natural background radiation is the most hazardous source of radiation to general public health, followed by medical imaging as a close second. Additionally, the vast majority of non-invasive cancers are non-melanoma skin cancers caused by ultraviolet radiation. Non-ionizing radio frequency radiation from mobile phones, electric power transmission, and other similar sources have been investigated as a possible carcinogen by the WHO's International Agency for Research on Cancer, but to date, no evidence of this has been observed.
The index of physics articles is split into multiple pages due to its size.

Bioremediation of radioactive waste or bioremediation of radionuclides is an application of bioremediation based on the use of biological agents bacteria, plants and fungi to catalyze chemical reactions that allow the decontamination of sites affected by radionuclides. These radioactive particles are by-products generated as a result of activities related to nuclear energy and constitute a pollution and a radiotoxicity problem due to its unstable nature of ionizing radiation emissions.