This article needs additional citations for verification .(July 2008) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
The Institute of Boiler and Radiator Manufacturers (IBR, I=B=R), in the United States, is currently incorporated into the Gas Appliance Manufacturers Association (GAMA). The merger of GAMA and IBR occurred on April 18, 2004. [1] Under the IBR name, GAMA continues to offer regular classes on hydronic heat installation in the Northeastern United States. The IBR is a nationally recognized boiler and radiator certification organization. The IBR was formerly also known as the Hydronics Institute.

The United States of America (USA), commonly known as the United States or America, is a country composed of 50 states, a federal district, five major self-governing territories, and various possessions. At 3.8 million square miles, the United States is the world's third or fourth largest country by total area and is slightly smaller than the entire continent of Europe's 3.9 million square miles. With a population of over 327 million people, the U.S. is the third most populous country. The capital is Washington, D.C., and the largest city by population is New York City. Forty-eight states and the capital's federal district are contiguous in North America between Canada and Mexico. The State of Alaska is in the northwest corner of North America, bordered by Canada to the east and across the Bering Strait from Russia to the west. The State of Hawaii is an archipelago in the mid-Pacific Ocean. The U.S. territories are scattered about the Pacific Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, stretching across nine official time zones. The extremely diverse geography, climate, and wildlife of the United States make it one of the world's 17 megadiverse countries.

Hydronics is the use of a liquid heat-transfer medium in heating and cooling systems. The working fluid is typically water, glycol, or mineral oil. Some of the oldest and most common examples are steam and hot-water radiators. Historically, in large-scale commercial buildings such as high-rise and campus facilities, a hydronic system may include both a chilled and a heated water loop, to provide for both heating and air conditioning. Chillers and cooling towers are used either separately or together as means to provide water cooling, while boilers heat water. A recent innovation is the chiller boiler system, which provides an efficient form of HVAC for homes and smaller commercial spaces.
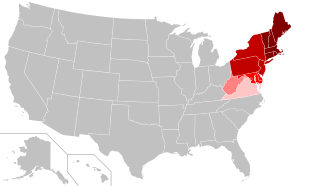
The Northeastern United States, also referred to as simply the Northeast, is a geographical region of the United States bordered to the north by Canada, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the south by the Southern United States, and to the west by the Midwestern United States. The Northeast is one of the four regions defined by the United States Census Bureau for the collection and analysis of statistics.








