
General aviation (GA) is defined by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) as all civil aviation aircraft operations except for commercial air transport or aerial work, which is defined as specialized aviation services for other purposes. However, for statistical purposes, ICAO uses a definition of general aviation which includes aerial work.

The International Civil Aviation Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that coordinates the principles and techniques of international air navigation, and fosters the planning and development of international air transport to ensure safe and orderly growth. ICAO headquarters are located in the Quartier International of Montreal, Quebec, Canada.

The (International) Radiotelephony Spelling Alphabet, commonly known as the NATO phonetic alphabet, is the most widely used set of clear code words for communicating the letters of the Roman alphabet. Technically a radiotelephonic spelling alphabet, it goes by various names, including NATO spelling alphabet, ICAO phonetic alphabet and ICAO spelling alphabet. The ITU phonetic alphabet and figure code is a rarely used variant that differs in the code words for digits.


The ICAOairport code or location indicator is a four-letter code designating aerodromes around the world. These codes, as defined by the International Civil Aviation Organization and published in ICAO Document 7910: Location Indicators, are used by air traffic control and airline operations such as flight planning. ICAO codes are also used to identify other aviation facilities such as weather stations, international flight service stations or area control centers, whether or not they are located at airports. Flight information regions are also identified by a unique ICAO-code.

The British Airline Pilots’ Association (BALPA) is the professional association and registered trade union for UK pilots. BALPA represents the views and interests of pilots, campaigning on contractual, legal and health issues affecting its members and the flying public.

A flight dispatcher assists in planning flight paths, taking into account aircraft performance and loading, enroute winds, thunderstorm and turbulence forecasts, airspace restrictions, and airport conditions. Dispatchers also provide a flight following service and advise pilots if conditions change. They usually work in the operations center of the airline. In the United States and Canada, the flight dispatcher shares legal responsibility with the commander of the aircraft.

Pakistan Civil Aviation Authority (PCAA) is a state-owned autonomous body under the administrative control of the Secretary to the Government of Pakistan for Aviation, which oversees and regulates all aspects of civil aviation in Pakistan. PCAA's head office is situated in Terminal-1 of Jinnah International Airport in Karachi. PCAA is a member state of the International Civil Aviation Organization. Nearly all 44 civilian airports in Pakistan are owned and operated by the PCAA.

The Regional Aviation Association of Australia (RAAA) is a non-profit organisation representing the interests of regional aviation in Australia. RAAA has approximately 100 members and 2500 employees. They Provide air transportation in Australia for more than 2 million passengers and 23 million kilograms cargo per year.
A civil aviation authority (CAA) is a national or supranational statutory authority that oversees the regulation of civil aviation, including the maintenance of an aircraft register.

Airports Council International (ACI) is an organization of airport authorities aimed at unifying industry practices for airport standards. Established in 1991, its headquarters are based in Montreal, Quebec, Canada, and its members operate nearly 2000 airports.
The Somali Civil Aviation Authority (SCAA) (previously: Somali Civil Aviation and Meteorology Authority (SCAMA)) is the national civil aviation authority body of Somalia. Based at the Aden Adde International Airport in the capital Mogadishu, it is under the aegis of the federal Ministry of Air and Land Transport. In 2012, the ministry along with the Somali Civil Aviation Steering Committee set a three-year window for reconstruction of the national civil aviation capacity. After a long period of management by the Civil Aviation Caretaker Authority for Somalia (CACAS), SCAMA in conjunction with the International Civil Aviation Organization also finalized a process in 2014 to transfer control of Somalia airspace to the new Air Space Management Centre in the capital.
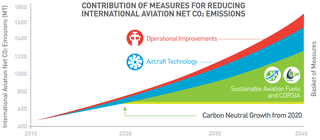
The Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation (CORSIA) is a carbon offset and carbon reduction scheme to lower CO2 emissions for international flights, to curb the aviation impact on climate change.

LATAM Perú Flight 2213 (LP2213/LPE2213) was a scheduled domestic passenger flight in Peru from Lima to Juliaca. On 18 November 2022, the Airbus A320neo operated by LATAM Perú was taking off from Jorge Chávez International Airport when it collided with a fire engine that was crossing the runway, killing two firefighters and injuring a third. All 102 passengers and six crew aboard escaped, with 40 being injured.











