
The history of Yemen describes the cultures, events, and peoples of what is one of the oldest centers of civilization in the Near East. Its relatively fertile land and adequate rainfall in a moister climate helped sustain a stable population, a feature recognized by the ancient Greek geographer Ptolemy, who described Yemen as Eudaimon Arabia meaning "fortunate Arabia" or "Happy Arabia". Yemenis had developed the South Arabian alphabet by the 12th to 8th centuries BCE, which explains why most historians date all of the ancient Yemeni kingdoms to that era.

Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, and historically known as South Arabia, is a country in Western Asia, on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast and shares maritime borders with Eritrea, Djibouti, and Somalia. It is the second-largest Arab sovereign state in the peninsula, occupying 555,000 square kilometres. The coastline stretches for about 2,000 kilometres. Yemen's constitutionally stated capital, and largest city, is the city of Sana’a. As of 2021, the population of the country is estimated at 30,491,000.

Jizan Region also spelled Jazan is the second smallest region of Saudi Arabia. It stretches 300 km (190 mi) along the southern Red Sea coast, just north of Yemen. It covers an area of 11,671 km2 and has a population of 1,567,547 at the 2017 census. The region has the highest population density in the Kingdom. The capital is the city of Jazan; Prince Muhammad bin Nasser has been the Governor since April 2001.

Yahya Muhammad Hamid ed-Din became Imam of the Zaydis in 1904 after the death of his father, Muhammad Al-Mansur, and Imam of Yemen in 1918. His name and title in full was "His majesty Amir al-Mumenin al-Mutawakkil 'Ala Allah Rab ul-Alamin Imam Yahya bin al-Mansur Bi'llah Muhammad Hamidaddin, Imam and Commander of the Faithful".

Muhammad Al-Badr was the last king and Zaidi Imam of the Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen and leader of the monarchist regions during the North Yemen Civil War (1962–1970). His full name was Al-Mansur Bi'llah Muhammad Al-Badr bin Al-Nasir-li-dinu'llah Ahmad, Imam and Commander of the Faithful and King of the Mutawakkilite Kingdom of the Yemen.

Ahmad bin Yahya Hamidaddin was the penultimate king of the Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen, who reigned from 1948 to 1962. His full name and title was H.M. al-Nasir-li-Dinullah Ahmad bin al-Mutawakkil 'Alallah Yahya, Imam and Commander of the Faithful, and King of the Mutawakkilite Kingdom of the Yemen.

The Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen, also known simply as the Kingdom of Yemen or as Yemen, or, retrospectively, as North Yemen, was a state that existed between 1918 and 1962 in the northwestern part of what is now Yemen. Its capital was Sana'a until 1948, then Taiz. From 1962 to 1970, it maintained control over portions of Yemen until its final defeat in the North Yemen Civil War. Yemen was admitted to the United Nations on 30 September 1947.

The Aden Protectorate was a British protectorate in South Arabia which evolved in the hinterland of the port of Aden and in the Hadramaut following the conquest of Aden by the Bombay Province of British India in 1839, and it continued until the 1960s. In 1940 it was divided for administrative purposes into the Western Protectorate and the Eastern Protectorate. Today the territory forms part of the Republic of Yemen.

Aden Colony, also the Colony of Aden, was a British Crown colony from 1937 to 1963 located in the south of contemporary Yemen. It consisted of the port of Aden and its immediate surroundings.

Beihan or Bayhan, officially the Emirate of Beihan, was a state in the British Aden Protectorate and the Federation of South Arabia. Its capital was Suq Abdulla, now called Beihan. The Emirate was abolished in 1967 upon the founding of the People's Republic of South Yemen and is now part of the Republic of Yemen.

YemenRegion also known as South Arabia is a geographic term denoting territories of historic South Arabia which included All lands between the Gulf of Oman in the east and the Red Sea in the west.
The Saudi–Yemeni War was a war between Saudi Arabia and the Kingdom of Yemen in 1934.
Islam came to Yemen around 630 during Muhammad's lifetime and the rule of the Persian governor Badhan. Thereafter, Yemen was ruled as part of Arab-Islamic caliphates, and became a province in the Islamic empire.

The Imams of Yemen and later also the Kings of Yemen were religiously consecrated leaders belonging to the Zaidiyyah branch of Shia Islam. They established a blend of religious and political rule in parts of Yemen from 897. Their imamate endured under varying circumstances until the republican revolution in 1962, then the formal abolition of the monarchy in 1970. Zaidiyyah theology differed from Ismailis or Twelver Shi'ites by stressing the presence of an active and visible imam as leader. The imam was expected to be knowledgeable in religious sciences, and to prove himself a worthy headman of the community, even in battle if this was necessary. A claimant of the imamate would proclaim a "call" (da'wa), and there were not infrequently more than one claimant. The historian Ibn Khaldun mentions the clan that usually provided the imams as the Banu Rassi or Rassids. In the original Arab sources the term Rassids is otherwise hardly used; in Western literature it usually refers to the Imams of the medieval period, up to the 16th century. The Rassid branch that came to power with imam al-Mansur al-Qasim is known as Qasimids.

The Unification of Saudi Arabia was a military and political campaign in which the various tribes, sheikhdoms, city-states, emirates, and kingdoms of most of the Arabian Peninsula were conquered by the House of Saud, or Al Saud. Unification started in 1902 and continued until 1932, when the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia was proclaimed under the leadership of King Abdulaziz, creating what is sometimes referred to as the Third Saudi State, to differentiate it from the Emirate of Diriyah, the First Saudi State and the Emirate of Nejd, the Second Saudi State, also House of Saud states.

The Idrisid Emirate of Asir was a state located in the Arabian Peninsula. The Emirate was located in the geographical region of Asir and Jizan in what is now southwestern Saudi Arabia, It extends to Hodeidah, northwest of Yemen.
This is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of Yemen.

Yemen Vilayet was a first-level administrative division (vilayet) of the Ottoman Empire. At the beginning of the 20th century it reportedly had an area of 200,000 square kilometres (77,200 sq mi). The population for the vilayet is given by the 1885 Ottoman census as 2,500,000.
The Alwaziri coup, also referred as the Yahya clan coup was a violent dynasty overthrow attempt in the Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen in 1948, which caused around 5,000 fatalities. During the coup attempt, Imam Yahya Muhammad Hamid ed-Din, the ruler of the kingdom, was killed and the rival Sayyid family, the Alwazirs, seized power for several weeks. Backed by the al-Saud family of Saudi Arabia, the Hamidaddins restored their rule. After deposition of the Alwaziris, the restored monarchy of Imam Yahya was succeeded by his son Ahmad bin Yahya.
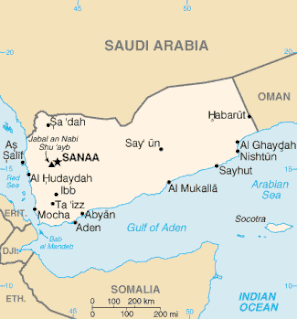
The Saudi Arabia–Yemen border is 1,307 km in length and runs from the Red Sea coast in the west to the tripoint with Oman in the east.
















