Related Research Articles
A spear is a polearm consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fastened to the shaft, such as bone, flint, obsidian, copper, bronze, iron, or steel. The most common design for hunting and/or warfare, since ancient times has incorporated a metal spearhead shaped like a triangle, diamond, or leaf. The heads of fishing spears usually feature multiple sharp points, with or without barbs.
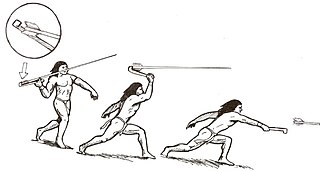
A spear-thrower, spear-throwing lever, or atlatl is a tool that uses leverage to achieve greater velocity in dart or javelin-throwing, and includes a bearing surface that allows the user to store energy during the throw.

Creswell Crags is an enclosed limestone gorge on the border between Derbyshire and Nottinghamshire, England, near the villages of Creswell and Whitwell. The cliffs in the ravine contain several caves that were occupied during the last ice age, between around 43,000 and 10,000 years ago. Its caves contain the northernmost cave art in Europe. The evidence of occupation found in the rich series of sediments that accumulated over many thousands of years is regarded as internationally unique in demonstrating how prehistoric people managed to live at the extreme northernmost limits of their territory during the Late Pleistocene period.

The Bhimbetka rock shelters are an archaeological site in central India that spans the Paleolithic and Mesolithic periods, as well as the historic period. It exhibits the earliest traces of human life in India and evidence of the Stone Age starting at the site in Acheulian times. It is located in the Raisen District in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh, about 45 kilometres (28 mi) south-east of Bhopal. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site that consists of seven hills and over 750 rock shelters distributed over 10 km (6.2 mi). At least some of the shelters were inhabited more than 100,000 years ago.

Knowledge about military technology of the Viking Age is based on relatively sparse archaeological finds, pictorial representations, and to some extent on the accounts in the Norse sagas and laws recorded in the 12th–14th centuries.

The Rock art of Alta are located in and around Alta Municipality in Finnmark county in northern Norway. Since the first carvings were discovered in 1973, more than 6,000 carvings have been found on several sites around Alta. The largest locality, at Jiepmaluokta about five kilometers (3.1 mi) from Alta, contains thousands of individual carvings and has been turned into an open-air museum. The site, along with the sites Storsteines, Kåfjord, Amtmannsnes, and Transfarelv, was placed on the UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites on 3 December 1985. It is Norway's only prehistoric World Heritage Site.

Lenggong or Lenggong Valley is a geographical area defined by the mountain ranges of Bintang in the west and Titiwangsa to its east. It is a rural area, with small kampongs surrounded by green vegetation and limestone hills with numerous caves.

The Bangudae Petroglyphs are pre-historic engravings on flat vertical rock faces. They are on rocks around 8m wide and around 5m high on steep cliffs on the riverside of the Daegokcheon stream, a branch of the Taehwa River, which runs eastward and joins the East Sea at Ulsan. The surrounding ten rock faces have a small number of engravings as well. The rocks consist of shale and hornfels oriented toward the north and they shine for a while at sunset. As an overhanging cliff they are in the structure of a rock shelter. It is believed that people congregated around huge rocks to take place several rituals. They are the National Treasure of South Korea No. 285 and registered as the Tentative UNESCO World Heritage List in 2011.

Badanj Cave is located in Borojevići village near the town of Stolac, Bosnia and Herzegovina. It began to attract public attention after the 1976 discovery of its cave engravings, which date to between 14,000 and 18,000 years ago.

A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a ranged weapon. Today, the javelin is predominantly used for sporting purposes such as the javelin throw. The javelin is nearly always thrown by hand, unlike the sling, bow, and crossbow, which launch projectiles with the aid of a hand-held mechanism. However, devices do exist to assist the javelin thrower in achieving greater distances, such as spear-throwers or the amentum.

Twyfelfontein, officially known as ǀUi-ǁAis, is a site of ancient rock engravings in the Kunene Region of north-western Namibia. It consists of a spring in a valley flanked by the slopes of a sandstone table mountain that receives very little rainfall and has a wide range of diurnal temperatures.

The rock drawings in Valcamonica are located in the Province of Brescia, Italy, and constitute the largest collections of prehistoric petroglyphs in the world. The collection was recognized by UNESCO in 1979 and was Italy's first recognized World Heritage Site. UNESCO has formally recognized more than 140,000 figures and symbols, but new discoveries have increased the number of catalogued incisions to between 200,000 and 300,000. The petroglyphs are spread on all surfaces of the valley, but concentrated in the areas of Darfo Boario Terme, Capo di Ponte, Nadro, Cimbergo and Paspardo.

The Rock Carvings in Tanum are a collection of petroglyphs near Tanumshede, Bohuslän, Sweden, which were declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1994 because of their high concentration.

The Hunters Palette or Lion Hunt Palette is a c. 3100 BCE cosmetic palette from the Naqada III period of late prehistoric Egypt. The palette is broken: part is held by the British Museum and part is in the collection of the Louvre.

The art of the Upper Paleolithic represents the oldest form of prehistoric art. Figurative art is present in Europe and Southeast Asia, beginning around 50,000 years ago. Non-figurative cave paintings, consisting of hand stencils and simple geometric shapes, are somewhat older, at least 40,000 years old, and possibly as old as 64,000 years. This latter estimate is due to a controversial 2018 study based on uranium-thorium dating, which would imply Neanderthal authorship and qualify as art of the Middle Paleolithic.

Les Combarelles is a cave in Les Eyzies de Tayac, Dordogne, France, which was inhabited by Cro-Magnon people between approximately 13,000 to 11,000 years ago. Holding more than 600 prehistoric engravings of animals and symbols, the two galleries in the cave were crucial in the re-evaluation of the mental and technical capabilities of these prehistoric humans around the turn of the 20th century. In 1979, along with other nearby paleolithic sites and cave paintings, the cave was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List as part of the Prehistoric Sites and Decorated Caves of the Vézère Valley.

Native American weaponry was used by Native American warriors to hunt and to do battle with other Native American tribes and Europeans.

The Vogelherd Cave is located in the eastern Swabian Jura, south-western Germany. This limestone karst cave came to scientific and public attention after the 1931 discovery of the Upper Palaeolithic Vogelherd figurines, attributed to paleo-humans of the Aurignacian culture. These miniature sculptures made of mammoth ivory rank among the oldest uncontested works of art of mankind. Because of the cultural importance of these sculptures and the cave's testimony to the development of Paleolithic art and culture, in 2017 the site became part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site called Caves and Ice Age Art in the Swabian Jura.

Gobustan Rock Art represents flora and fauna, hunting, lifestyles, and culture of pre-historic and medieval periods of time. The carvings on the rocks illustrates men, ritual dances, men with lances in their hands, animals, bull fights, camel caravans, and pictures of the sun and stars. The date of these carvings goes back to 5,000 – 20,000 years before present.
References
Les gravures rupestres de Lengo - UNESCO World Heritage Centre