List of Washington ballot measures may refer to:
List of Washington ballot measures may refer to:
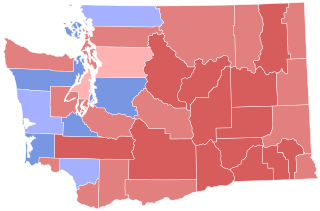
The 2004 Washington gubernatorial election was held on November 2, 2004. The race gained national attention for its legal twists and extremely close finish, among the closest political races in United States election history. Republican Dino Rossi was declared the winner in the initial automated count and again in a subsequent automated recount, but after a second recount done by hand, Democrat Christine Gregoire took the lead by a margin of 129 votes.

Sound Transit (ST), officially the Central Puget Sound Regional Transit Authority, is a public transit agency serving the Seattle metropolitan area in the U.S. state of Washington. It operates the Link light rail system in Seattle and Tacoma, regional Sounder commuter rail, and Sound Transit Express bus service. The agency also coordinates the regional ORCA fare card system, which is also used by local transit operators. In 2019, Sound Transit services carried a total of 48 million passengers and averaged over 161,000 riders on weekdays.
In the politics of the United States, the process of initiatives and referendums allow citizens of many U.S. states to place legislation on the ballot for a referendum or popular vote, either enacting new legislation, or voting down existing legislation. Citizens, or an organization, might start an initiative to gather a predetermined number of signatures to qualify the measure for the ballot. The measure is placed on the ballot for the referendum, or actual vote.

Proposition 64 was a proposition in the state of California on the November 4, 1986, ballot. It was an initiative statute that would have restored Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) to the list of communicable diseases. The measure was defeated by a margin of 71% to 29%.

Multnomah County, Oregon, the city of Portland, Oregon, and Metro held elections on May 16 and November 7, 2006.
The Oregon Citizens Alliance (OCA) was a conservative Christian political activist organization, founded by Lon Mabon in the U.S. state of Oregon. It was founded in 1986 as a vehicle to challenge then–U.S. Senator Bob Packwood in the Republican primaries, and was involved in Oregon politics from the late 1980s into the 1990s.

Oregon Ballot Measure 37 was a controversial land-use ballot initiative that passed in the U.S. state of Oregon in 2004 and is now codified as Oregon Revised Statutes (ORS) 195.305. Measure 37 has figured prominently in debates about the rights of property owners versus the public's right to enforce environmental and other land use regulations. Voters passed Measure 49 in 2007, substantially reducing the impact of Measure 37.

The District of Columbia holds general elections every two years to fill various D.C. government offices, including mayor, attorney general, members of the D.C. Council, members of the D.C. State Board of Education, and members of its Advisory Neighborhood Commissions. Special elections may be held to fill vacancies at other points in time. Additionally, citywide ballot measures may be proposed and voted on.

The State Income Tax Repeal, also known as Massachusetts Question 1, was one of the 2008 ballot measures that appeared on the November 4, 2008 ballot in the U.S. state of Massachusetts. Voters were asked whether or not they approved of the proposed measure which, if it had passed, would have ended the 5.3% income tax in Massachusetts on wages, interest, dividends and capital gains. Ultimately, Massachusetts voters defeated Question 1 by a wide margin, with approximately 70% opposed versus 30% in favor.

Initiative 1000 (I-1000) of 2008 established the U.S. state of Washington's Death with Dignity Act, which legalizes medical aid in dying with certain restrictions. Passage of this initiative made Washington the second U.S. state to permit some terminally ill patients to determine the time of their own death. The effort was headed by former Governor Booth Gardner.

Amendment 46, also known as the Colorado Civil Rights Initiative, was a proposed initiative on the Colorado ballot for 2008. If ratified, Article II of the Colorado Constitution would have stated:
The State shall not discriminate against, or grant preferential treatment to, any individual or group on the basis of race, sex, color, ethnicity, or national origin in the operation of public employment, public education, or public contracting.
The South Dakota Open and Clean Government Act, or Initiated Measure 10, was a South Dakota initiative that would ban taxpayer-funded lobbying, stop the exchange of campaign donations for state contracts, and open a website with information on state contracts. The Open and Clean Government Act was proposed as a citizen-initiated state statute and appeared on the November 4, 2008 ballot.

The 2009 Washington Referendum 71 (R-71) legalized domestic partnership in Washington state, the first statewide referendum in the United States that extended to LGBT people the rights and responsibility of domestic partnership. The bill had passed State Legislature, and it was signed into law by the Governor in May 2009, but opponents gathered enough signatures to put the measure before the voters, who returned ballots by mail over three weeks ending on November 3, 2009, approving the measure 53% to 47%. The new law went into effect 30 days later, on December 3, 2009.

Washington Initiative 1240 "concerns creation of a public charter school system" was an initiative that appeared on the Washington state general ballot in November 2012. Originally filed with the Washington Secretary of State on May 31, proponents and paid signature gatherers collected enough signatures to be certified for the ballot on July 25, making it one of the fastest initiatives ever to do so, at an estimated cost of more than $6 per signature. Proposed charter schools would receive public funding but not be governed by local school districts. An August 2012 financial impact study by the state Office of Financial Management estimated "an indeterminate, but non-zero, fiscal impact to local public school districts" and "known state agency implementation costs" of at least $3 million in the first five years. The initiative was approved by voters in November 2012.

The Massachusetts Medical Marijuana Initiative, appeared as the third question on the state's 2012 ballot as an indirect initiated state statute. The measure allows cannabis to be used for medical purposes in the state. The initiative—backed by the American Civil Liberties Union, the Massachusetts Patient Advocacy Alliance, and the Committee for Compassionate Medicine—was filed with proponents turning in the required signatures to the Massachusetts Attorney General's office by the August 3, 2011 deadline. Those signatures were needed for the required ten qualified voters who submitted the original petition to put forward the full text of the law they want enacted. The initiative passed with support from 63% of state voters.

Initiative 77 was a voter-approved ballot initiative in Washington, D.C., to phase out the special minimum wage for tipped employees as part of the national Fight for $15 campaign. In the June 2018 primary election, D.C. voters approved Initiative 77 by a margin of 56% to 44%; however, the D.C. Council repealed the initiative in October before it could enter into force. In 2022, a nearly identical Initiative 82 was approved for the November 8, 2022 election.

Proposition 23, officially the Protect the Lives of Dialysis Patients Act Initiative, is a California ballot proposition that appeared on the ballot for the general election on November 3, 2020. The proposition would increase regulations in Californian dialysis clinics, requiring them to have on-site physicians during treatment, report data on infections that might have been caused by dialyses, seek permission from the government of California prior to closing a clinic and strengthening anti-discrimination protections for dialysis patients.

Initiative 82 was a voter-approved ballot initiative in Washington, D.C., to phase out the special minimum wage for tipped employees as part of the national Fight for $15 campaign. In the November 2022 general election, D.C. voters approved Initiative 82 by a margin of 74% to 26%, though about 12% of all participating voters did not vote on the initiative. It was nearly identical to Initiative 77, a ballot measure in the 2018 primary election that was approved by D.C. voters but later overturned by the D.C. Council before it could enter into force.