Related Research Articles

Claude Elwood Shannon was an American mathematician, electrical engineer, computer scientist and cryptographer known as the "father of information theory".

Control engineering or control systems engineering is an engineering discipline that deals with control systems, applying control theory to design equipment and systems with desired behaviors in control environments. The discipline of controls overlaps and is usually taught along with electrical engineering and mechanical engineering at many institutions around the world.

Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems which use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the latter half of the 19th century after commercialization of the electric telegraph, the telephone, and electrical power generation, distribution, and use.

Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other charged particles. Electronics is a subfield of electrical engineering, but it differs from it in that it focuses on using active devices such as transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits to control and amplify the flow of electric current and to convert it from one form to another, such as from alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) or from analog to digital. Electronics also encompasses the fields of microelectronics, nanoelectronics, optoelectronics, and quantum electronics, which deal with the fabrication and application of electronic devices at microscopic, nanoscopic, optical, and quantum scales.

An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal. A power amplifier is similarly used to deliver output power, controlled by an input signal. It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a proportionally greater amplitude signal at its output. The amount of amplification provided by an amplifier is measured by its gain: the ratio of output voltage, current, or power to input. An amplifier is a circuit that has a power gain greater than one.
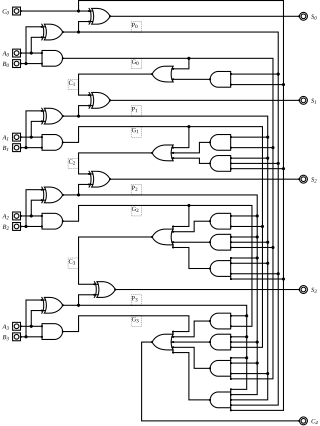
A logic gate is an idealized or physical device that performs a Boolean function, a logical operation performed on one or more binary inputs that produces a single binary output.
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. Its conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by introducing impurities ("doping") into the crystal structure. When two differently doped regions exist in the same crystal, a semiconductor junction is created. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called "metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common semiconductor and is used in laser diodes, solar cells, microwave-frequency integrated circuits, and others. Silicon is a critical element for fabricating most electronic circuits.

Computer engineering is a branch of electrical engineering and computer science that integrates several fields of computer science and electronic engineering required to develop computer hardware and software. Computer engineers require training in electronic engineering, hardware-software integration, software design, and software engineering. It uses the techniques and principles of electrical engineering and computer science, and can encompass areas such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, computer networks, computer architecture and operating systems. Computer engineers are involved in many hardware and software aspects of computing, from the design of individual microcontrollers, microprocessors, personal computers, and supercomputers, to circuit design. This field of engineering not only focuses on how computer systems themselves work, yet it also demands them to integrate into the larger picture. Robots are one of the applications of computer engineering.

In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna radiates radio waves.
In electronics, a multi-transistor configuration called the Darlington configuration is a circuit consisting of two bipolar transistors with the emitter of one transistor connected to the base of the other, such that the current amplified by the first transistor is amplified further by the second one. The collectors of both transistors are connected together. This configuration has a much higher current gain than each transistor taken separately. It acts like and is often packaged as a single transistor. It was invented in 1953 by Sidney Darlington.

Consumer electronics or home electronics are electronic equipment intended for everyday use, typically in private homes. Consumer electronics include devices used for entertainment, communications and recreation. Usually referred to as black goods due to many products being housed in black or dark casings. This term is used to distinguish them from "white goods" which are meant for housekeeping tasks, such as washing machines and refrigerators, although nowadays, these would be considered black goods, some of these being connected to the Internet. In British English, they are often called brown goods by producers and sellers. In the 2010s, this distinction is absent in large big box consumer electronics stores, which sell entertainment, communication and home office devices, light fixtures and appliances, including the bathroom type.

Mechatronics engineering also called mechatronics, is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering that focuses on the integration of mechanical, electrical and electronic engineering systems, and also includes a combination of robotics, electronics, computer science, telecommunications, systems, control, and product engineering.

This article details the history of electrical engineering.
The superposition theorem is a derived result of the superposition principle suited to the network analysis of electrical circuits. The superposition theorem states that for a linear system the response in any branch of a bilateral linear circuit having more than one independent source equals the algebraic sum of the responses caused by each independent source acting alone, where all the other independent sources are replaced by their internal impedances.
Robert L. Boylestad was professor emeritus of electrical and computer technology at Queensborough Community College, part of the City University of New York, and was an assistant dean in the Thayer School of Engineering of Dartmouth College.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to computer engineering:

Electronic(s) engineering is a sub-discipline of electrical engineering which emerged in the early 20th century and is distinguished by the additional use of active components such as semiconductor devices to amplify and control electric current flow. Previously electrical engineering only used passive devices such as mechanical switches, resistors, inductors, and capacitors.
This article details the history of electronics engineering. Chambers Twentieth Century Dictionary (1972) defines electronics as "The science and technology of the conduction of electricity in a vacuum, a gas, or a semiconductor, and devices based thereon".

Mohamed M. Atalla was an Egyptian-American engineer, physicist, cryptographer, inventor and entrepreneur. He was a semiconductor pioneer who made important contributions to modern electronics. He is best known for inventing the MOSFET in 1959, which along with Atalla's earlier surface passivation and thermal oxidation processes, revolutionized the electronics industry. He is also known as the founder of the data security company Atalla Corporation, founded in 1972. He received the Stuart Ballantine Medal and was inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame for his important contributions to semiconductor technology as well as data security.
References
"Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory," Prentice Hall, Boylestad, R and Nashelsky, L. 9th ed. 2005.