Related Research Articles
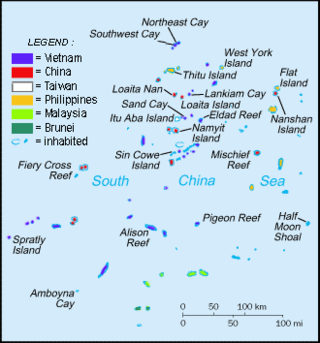
The Spratly Islands are a disputed archipelago in the South China Sea. Composed of islands, islets, cays, and more than 100 reefs, sometimes grouped in submerged old atolls, the archipelago lies off the coasts of the Philippines, Malaysia, and southern Vietnam. Named after the 19th-century British whaling captain Richard Spratly who sighted Spratly Island in 1843, the islands contain less than 2 km2 of naturally occurring land area, which is spread over an area of more than 425,000 km2 (164,000 sq mi).

The South China Sea, or South East Asian Sea, is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China, in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Philippines, and in the south by Borneo, eastern Sumatra and the Bangka Belitung Islands, encompassing an area of around 3,500,000 km2 (1,400,000 sq mi). It communicates with the East China Sea via the Taiwan Strait, the Philippine Sea via the Luzon Strait, the Sulu Sea via the straits around Palawan, the Strait of Malacca via the Singapore Strait, and the Java Sea via the Karimata and Bangka Straits. The Gulf of Thailand and the Gulf of Tonkin are also part of South China Sea. The shallow waters south of the Riau Islands are also known as the Natuna Sea.
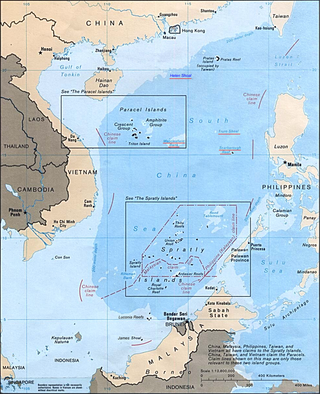
The South China Sea Islands consist of over 250 islands, atolls, cays, shoals, reefs and seamounts in the South China Sea. The islands are mostly low and small, and have few inhabitants. The islands and surrounding seas are subject to overlapping territorial claims by the countries bordering the South China Sea.

The term territorial waters is sometimes used informally to refer to any area of water over which a sovereign state has jurisdiction, including internal waters, the territorial sea, the contiguous zone, the exclusive economic zone, and potentially the extended continental shelf. In a narrower sense, the term is used as a synonym for the territorial sea.
James Shoal is an underwater shoal (bank) in the South China Sea, with a depth of 22 metres (72 ft) below the surface of the sea, located about 45 nautical miles off the Borneo coast of Malaysia. It is claimed by Malaysia, the People's Republic of China, and the Republic of China (Taiwan). The shoal and its surrounds are administered by Malaysia.

The Malaysia–Thailand border divides the countries of Malaysia and Thailand and consists of a land boundary running for 595 km (370 mi) across the Malay Peninsula and maritime boundaries in the Straits of Malacca and the Gulf of Thailand/South China Sea. The Golok River forms the easternmost 95 km stretch of the land border.

Philippines and the Spratly Islands – this article discusses the policies, activities and history of the Republic of the Philippines in the Spratly Islands from the Philippine perspective. Non-Philippine viewpoints regarding Philippine occupation of several islands are currently not included in this article.

The Indonesia–Malaysia border consists of a 1,881 km land border that divides the territory of Indonesia and Malaysia on the island of Borneo. It also includes maritime boundaries along the length of the Straits of Malacca, in the South China Sea and in the Celebes Sea.
The borders of Malaysia include land and maritime borders with Brunei, Indonesia and Thailand and shared maritime boundaries with Philippines, Singapore and Vietnam.

The Brunei–Malaysia border divides the territory of Brunei and Malaysia on the island of Borneo. It consists of a 266 km (165 mi) land border and substantial lengths of maritime borders stretching from the coastline of the two countries to the edge of the continental shelf in the South China Sea.
The border between Indonesia and Vietnam is a maritime border located in the South China Sea to the north of Indonesia's Natuna Islands. The two countries signed an agreement to determine their continental shelf boundary on 26 June 2003 in Hanoi, Vietnam.
The Malaysia–Philippines border is a maritime boundary located in the South China, Sulu and Celebes Seas. It separates the Malaysian state of Sabah, which is on the island of Borneo, and the Sulu Islands of the southern Philippines.

Ladd Reef is a Vietnam-controlled reef in the Spratly group of islands, South China Sea. China (PRC) and Taiwan (ROC) are also claimants of the reef. Like Spratly Island, Ladd Reef lies to the west of the Philippines-defined "Kalayaan Islands" claim area.

The Spratly Islands dispute is an ongoing territorial dispute between China, the Philippines, Taiwan, Malaysia, Vietnam, and Brunei, concerning "ownership" of the Spratly Islands, a group of islands and associated "maritime features" located in the South China Sea. The dispute is characterized by diplomatic stalemate and the employment of military pressure techniques in the advancement of national territorial claims. All except Brunei occupy some of the maritime features.

Territorial disputes in the South China Sea involve conflicting island and maritime claims in the region by several sovereign states, namely Brunei, the People's Republic of China (PRC), Taiwan, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, and Vietnam. The disputes involve the islands, reefs, banks, and other features of the South China Sea, including the Spratly Islands, Paracel Islands, Scarborough Shoal, and various boundaries in the Gulf of Tonkin. The waters near the Indonesian Natuna Islands, which some regard as geographically part of the South China Sea, are disputed as well. Maritime disputes also extend beyond the South China Sea, as in the case of the Senkaku Islands and the Socotra Rock, which lie in the East China Sea.

Philippines v. China, also known as the South China Sea Arbitration, was an arbitration case brought by the Republic of the Philippines against the People's Republic of China (PRC) under Annex VII of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea concerning certain issues in the South China Sea, including the nine-dash line introduced by the Republic of China (Taiwan) since as early as 1947. A tribunal of arbitrators appointed the Permanent Court of Arbitration (PCA) as the registry for the proceedings.

Cornwallis South Reef, also known as Vietnamese: Đá Núi Le; Osmeña Reef ; Mandarin Chinese: 南华礁; pinyin: Nanhua Dǎo, is a coral atoll reef in the Spratly Islands in the South China Sea. It covers an area of about 10 km by 5 km, and is entirely submerged at high tide.

Vietnam claims an exclusive economic zone (EEZ) of 1,395,096 km2 (538,650 sq mi) with 200 nautical miles from its shores.
The borders of Indonesia include land and maritime borders with Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, and Timor Leste, as well as shared maritime boundaries with Australia, India, Palau, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.

Whitsun Reef, also known as Whitson Reef, Whitsum Reef, and Julian Felipe Reef, is a reef at the northeast extreme limit of the Union Banks in the Spratly Islands of the South China Sea. It is the largest reef of the Union Banks.
References
- Charney, Jonathan I., David A. Colson, Robert W. Smith. (2005). International Maritime Boundaries, 5 vols. Leiden: Hotei Publishing. ISBN 9780792311874; ISBN 9789041119544; ISBN 9789041103451; ISBN 9789004144613; ISBN 9789004144798; OCLC 23254092