
Areca is a genus of about 50 species of palms in the family Arecaceae, found in humid tropical forests from the islands of the Philippines, Malaysia and India, across Southeast Asia to Melanesia. The generic name Areca is derived from a name used locally on the Malabar Coast of India.

The genus Pritchardia consists of between 24-40 species of fan palms found on tropical Pacific Ocean islands in Fiji, Samoa, Tonga, Tuamotus, and most diversely in Hawaii. The generic name honors William Thomas Pritchard (1829-1907), a British consul at Fiji.

Calamus is a genus of the palm family Arecaceae. These are among several genera known as rattan palms. There are an estimated 400 species in this genus, all native to tropical and subtropical Asia, Africa, and Australia. They are mostly leaf-climbing lianas with slender, reedy stems. To aid scrambling some species have evolved hooks on the underside of the midrib, or more commonly by modified "pinnae" or tendrils in the form of stout, backward-pointing spines. These stems may grow to lengths of 200 metres.

Livistona is a genus of palms, native to southern, southeastern and eastern Asia, Australasia, and the Horn of Africa. They are fan palms, the leaves with an armed petiole terminating in a rounded, costapalmate fan of numerous leaflets.

Syagrus is a genus of Arecaceae (palms), native to South America, with one species endemic to the Lesser Antilles. The genus is closely related to the Cocos, or coconut genus, and many Syagrus species produce edible seeds similar to the coconut.

Arenga is a genus of palms, native to Southeast Asia, southern China, New Guinea, and northern Australia. They are small to medium-sized palms, growing to 2–20 m tall, with pinnate leaves 2–12 m long. Arenga palms can grow in areas with little sunlight and relatively infertile soil.

Rhapis is a genus of about 10 species of small palms native to southeastern Asia from southern Japan and southern China south to Sumatra. The species are commonly known as lady palms. They are fan palms, with the leaves with a bare petiole terminating in a rounded fan of numerous leaflets. The plants have thin stems growing to 3–4 m tall, branching at the base, forming clumps and are dioecious, with male and female flowers produced on separate plants.
Dischidia is a genus of plants in the Milkweed family, Apocynaceae. They are epiphytes native to tropical areas of China, India and most areas of Indo-China. Dischidia are closely aligned with the sister genus Hoya. Unlike Hoya, the genus Dischidia is poorly known and has not been studied as closely.

Basselinia is a genus of flowering plant in the family Arecaceae. The entire genus is endemic to the Island of New Caledonia in the Pacific. In some molecular phylogenetic analyses, Hedyscepe from Lord Howe Island is nested in Basselinia.

Clinostigma is a genus of flowering plant in the Arecaceae (palm) family, native to various islands in the western Pacific. It contains the following species:
Pholidocarpus is a genus of flowering plant in the Arecaceae family, native to Southeast Asia. It contains the following species:
Physokentia is a genus of flowering plant in the palm family, native to certain islands of the western Pacific. It contains the following species: The relationships between Physokentia and some other genera of the tribe Basseliniinae particularly the New Caledonia endemic Burretiokentia and Cyphophoenix are not clear.

Pinanga is a genus of flowering plant of the palm family in the subtribe Arecinae. It is native to eastern and southern Asia across to New Guinea.

Ptychosperma is a genus of flowering plant in the family Arecaceae. Most are native to Australia and/or New Guinea, with a few in the Solomon Islands and in Maluku Province of eastern Indonesia. Some have been cultivated abroad as house or garden plants, and reportedly naturalized in certain regions.

Heterospathe is a monoecious genus of flowering plant in the palm family found in Oceania, where it is called sagisi palm. With 39 species, Heterospathe is named from a Greek combination of "various" and "spathe", which describes the two distinct bract types.
Carbon dioxide removal (CDR) refers to a group of technologies the objective of which is the large-scale removal of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Among such technologies are bio-energy with carbon capture and storage, biochar, ocean fertilization, enhanced weathering, and direct air capture when combined with storage. CDR is a different approach from removing CO
2 from the stack emissions of large fossil fuel point sources, such as power stations. The latter reduces emission to the atmosphere but cannot reduce the amount of carbon dioxide already in the atmosphere. As CDR removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, it 'creates' negative emissions that offset the emissions from small and dispersed point sources such as domestic heating systems, airplanes and vehicle exhausts. It is regarded by some as a form of climate engineering, while other commentators describe it as a form of carbon capture and storage or extreme mitigation. Whether CDR would satisfy common definitions of "climate engineering" or "geoengineering" usually depends upon the scale at which it would be undertaken.
Bio-energy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS) is the process of extracting bioenergy from biomass and capturing and storing the carbon, thus removing it from the atmosphere.
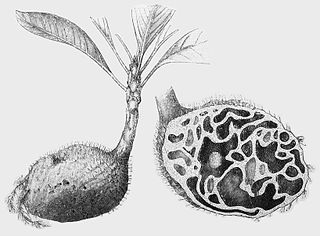
Hydnophytum is a genus of epiphytic myrmecophytes native to Southeast Asia, the Pacific region and also extending into Queensland in northern Australia. The name is derived from the Ancient Greek hydnon "tuber", and phyton "plant", after their appearance with their swollen succulent stems. The species grow in tree branches and on trunks. Like the related genus Myrmecodia, they are known as antplants or ant-house plants. The type species is Hydnophytum formicarum from the Philippines. The genus contains 55 species, of which 44 are found in and around the island of New Guinea. Many are poorly known, with 11 known only from the holotype.
Myrmephytum is a genus of myrmecophytic flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It is distributed from central Malesia to New Guinea.

Squamellaria is a genus of myrmecophytic flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It is endemic to the islands of Fiji.
















