
Ecology is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and it is not synonymous with environmentalism.

An ecosystem consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the system through photosynthesis and is incorporated into plant tissue. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and microbes.

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.
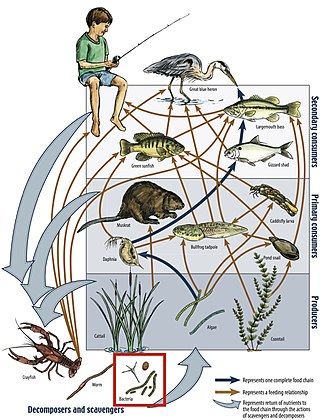
A food web is the natural interconnection of food chains and a graphical representation of what-eats-what in an ecological community. Another name for food web is consumer-resource system. Ecologists can broadly lump all life forms into one of two categories called trophic levels: 1) the autotrophs, and 2) the heterotrophs. To maintain their bodies, grow, develop, and to reproduce, autotrophs produce organic matter from inorganic substances, including both minerals and gases such as carbon dioxide. These chemical reactions require energy, which mainly comes from the Sun and largely by photosynthesis, although a very small amount comes from bioelectrogenesis in wetlands, and mineral electron donors in hydrothermal vents and hot springs. These trophic levels are not binary, but form a gradient that includes complete autotrophs, which obtain their sole source of carbon from the atmosphere, mixotrophs, which are autotrophic organisms that partially obtain organic matter from sources other than the atmosphere, and complete heterotrophs that must feed to obtain organic matter.

Human ecology is an interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary study of the relationship between humans and their natural, social, and built environments. The philosophy and study of human ecology has a diffuse history with advancements in ecology, geography, sociology, psychology, anthropology, zoology, epidemiology, public health, and home economics, among others.

Biosphere 2 is an American Earth system science research facility located in Oracle, Arizona. Its mission is to serve as a center for research, outreach, teaching, and lifelong learning about Earth, its living systems, and its place in the universe. It is a 3.14-acre (1.27-hectare) structure originally built to be an artificial, materially closed ecological system, or vivarium. It remains the largest closed ecological system ever created.

Eugene Pleasants Odum was an American biologist at the University of Georgia known for his pioneering work on ecosystem ecology. He and his brother Howard T. Odum wrote the popular ecology textbook, Fundamentals of Ecology (1953). The Odum School of Ecology is named in his honor.
Howard Thomas Odum, usually cited as H. T. Odum, was an American ecologist. He is known for his pioneering work on ecosystem ecology, and for his provocative proposals for additional laws of thermodynamics, informed by his work on general systems theory.
The diversity of species and genes in ecological communities affects the functioning of these communities. These ecological effects of biodiversity in turn are affected by both climate change through enhanced greenhouse gases, aerosols and loss of land cover, and biological diversity, causing a rapid loss of biodiversity and extinctions of species and local populations. The current rate of extinction is sometimes considered a mass extinction, with current species extinction rates on the order of 100 to 1000 times as high as in the past.
Ecology is a new science and considered as an important branch of biological science, having only become prominent during the second half of the 20th century. Ecological thought is derivative of established currents in philosophy, particularly from ethics and politics.

Ecological engineering uses ecology and engineering to predict, design, construct or restore, and manage ecosystems that integrate "human society with its natural environment for the benefit of both".

Restoration ecology is the scientific study supporting the practice of ecological restoration, which is the practice of renewing and restoring degraded, damaged, or destroyed ecosystems and habitats in the environment by active human interruption and action. Effective restoration requires an explicit goal or policy, preferably an unambiguous one that is articulated, accepted, and codified. Restoration goals reflect societal choices from among competing policy priorities, but extracting such goals is typically contentious and politically challenging.

The intermediate disturbance hypothesis (IDH) suggests that local species diversity is maximized when ecological disturbance is neither too rare nor too frequent. At low levels of disturbance, more competitive organisms will push subordinate species to extinction and dominate the ecosystem. At high levels of disturbance, due to frequent forest fires or human impacts like deforestation, all species are at risk of going extinct. According to IDH theory, at intermediate levels of disturbance, diversity is thus maximized because species that thrive at both early and late successional stages can coexist. IDH is a nonequilibrium model used to describe the relationship between disturbance and species diversity. IDH is based on the following premises: First, ecological disturbances have major effects on species richness within the area of disturbance. Second, interspecific competition results in one species driving a competitor to extinction and becoming dominant in the ecosystem. Third, moderate ecological scale disturbances prevent interspecific competition.

Systems ecology is an interdisciplinary field of ecology, a subset of Earth system science, that takes a holistic approach to the study of ecological systems, especially ecosystems. Systems ecology can be seen as an application of general systems theory to ecology. Central to the systems ecology approach is the idea that an ecosystem is a complex system exhibiting emergent properties. Systems ecology focuses on interactions and transactions within and between biological and ecological systems, and is especially concerned with the way the functioning of ecosystems can be influenced by human interventions. It uses and extends concepts from thermodynamics and develops other macroscopic descriptions of complex systems.
Bacteriophages (phages), potentially the most numerous "organisms" on Earth, are the viruses of bacteria. Phage ecology is the study of the interaction of bacteriophages with their environments.
Patch dynamics is an ecological perspective that the structure, function, and dynamics of ecological systems can be understood through studying their interactive patches. Patch dynamics, as a term, may also refer to the spatiotemporal changes within and among patches that make up a landscape. Patch dynamics is ubiquitous in terrestrial and aquatic systems across organizational levels and spatial scales. From a patch dynamics perspective, populations, communities, ecosystems, and landscapes may all be studied effectively as mosaics of patches that differ in size, shape, composition, history, and boundary characteristics.
Monica G. Turner is an American ecologist known for her work at Yellowstone National Park since the large fires of 1988. She is currently the Eugene P. Odum Professor of Ecology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison.

A nutrient cycle is the movement and exchange of inorganic and organic matter back into the production of matter. Energy flow is a unidirectional and noncyclic pathway, whereas the movement of mineral nutrients is cyclic. Mineral cycles include the carbon cycle, sulfur cycle, nitrogen cycle, water cycle, phosphorus cycle, oxygen cycle, among others that continually recycle along with other mineral nutrients into productive ecological nutrition.
Novel ecosystems are human-built, modified, or engineered niches of the Anthropocene. They exist in places that have been altered in structure and function by human agency. Novel ecosystems are part of the human environment and niche, they lack natural analogs, and they have extended an influence that has converted more than three-quarters of wild Earth. These anthropogenic biomes include technoecosystems that are fuelled by powerful energy sources including ecosystems populated with technodiversity, such as roads and unique combinations of soils called technosols. Vegetation associations on old buildings or along field boundary stone walls in old agricultural landscapes are examples of sites where research into novel ecosystem ecology is developing.
Nancy B. Grimm is an American ecosystem ecologist and professor at Arizona State University. Grimm's substantial contributions to the understanding of urban and arid ecosystem biogeochemistry are recognized in her numerous awards. Grimm is an elected Fellow of the American Geophysical Union, Ecological Society of America, and the American Association for the Advancement of Science.











