The Boston Post Road was a system of mail-delivery routes between New York City and Boston, Massachusetts, that evolved into one of the first major highways in the United States.
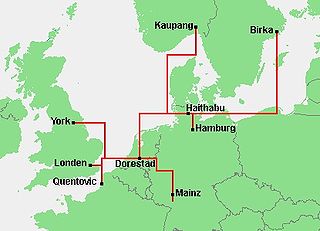
Dorestad was an early medieval emporium, located in the southeast of the province of Utrecht in the Netherlands, close to the modern-day town of Wijk bij Duurstede. It flourished during the 8th to early 9th centuries, as an important port on the northeastern shipping routes due to its proximity to the fork in the Rhine, with access to Germany via the Nederrijn, to the southern Netherlands, northern France, and England, and to the northern Netherlands, northern Germany, and Scandinavia.

Quimperlé is a commune in the Finistère department, region of Brittany, northwestern France.

Ahr is a river in Germany, a left tributary of the Rhine. Its source is at an elevation of approximately 470 metres (1,540 ft) above sea level in Blankenheim in the Eifel, in the cellar of a timber-frame house near the castle of Blankenheim. After 18 kilometres (11 mi) it crosses from North Rhine-Westphalia into Rhineland-Palatinate.

The Longshanculture, also sometimes referred to as the Black Pottery Culture, was a late Neolithic culture in the middle and lower Yellow River valley areas of northern China from about 3000 to 1900 BC. The first archaeological find of this culture took place at the Chengziya Archaeological Site in 1928, with the first excavations in 1930 and 1931. The culture is named after the nearby modern town of Longshan in Zhangqiu, Shandong. The culture was noted for its highly polished black pottery. The population expanded dramatically during the 3rd millennium BC, with many settlements having rammed earth walls. It decreased in most areas around 2000 BC until the central area evolved into the Bronze Age Erlitou culture. The Longshan culture has been linked to the early Sinitic . According to the area and cultural type, the Longshan culture can be divided into two types: Shandong Longshan and Henan Longshan. Among them, Shandong Longshan Cultural Site includes Chengziya Site; Henan Longshan Cultural Site includes Dengfeng Wangchenggang Site in Wangwan, Taosi Site and Mengzhuang Site in Hougang.

Ollantaytambo is a town and an Inca archaeological site in southern Peru some 72 km (45 mi) by road northwest of the city of Cusco. It is located at an altitude of 2,792 m (9,160 ft) above sea level in the district of Ollantaytambo, province of Urubamba, Cusco region. During the Inca Empire, Ollantaytambo was the royal estate of Emperor Pachacuti, who conquered the region, and built the town and a ceremonial center. At the time of the Spanish conquest of Peru, it served as a stronghold for Manco Inca Yupanqui, leader of the Inca resistance. Located in the Sacred Valley of the Incas, it is now an important tourist attraction on account of its Inca ruins and its location en route to one of the most common starting points for the four-day, three-night hike known as the Inca Trail.

Polabian Slavs, also known as Elbe Slavs and more broadly as Wends, is a collective term applied to a number of Lechitic tribes who lived scattered along the Elbe river in what is today eastern Germany. The approximate territory stretched from the Baltic Sea in the north, the Saale and the Limes Saxoniae in the west, the Ore Mountains and the Western Sudetes in the south, and Poland in the east.
The Cherokee Path was the primary route of English and Scots traders from Charleston to Columbia, South Carolina in Colonial America. It was the way they reached Cherokee towns and territories along the upper Keowee River and its tributaries. In its lower section it was known as the Savannah River. They referred to these towns along the Keowee and Tugaloo rivers as the Lower Towns, in contrast to the Middle Towns in Western North Carolina and the Overhill Towns in present-day southeastern Tennessee west of the Appalachian Mountains.

The Anglo-Cherokee War, was also known from the Anglo-European perspective as the Cherokee War, the Cherokee Uprising, or the Cherokee Rebellion. The war was a conflict between British forces in North America and Cherokee bands during the French and Indian War.

The Cherokee–American wars, also known as the Chickamauga Wars, were a series of raids, campaigns, ambushes, minor skirmishes, and several full-scale frontier battles in the Old Southwest from 1776 to 1794 between the Cherokee and American settlers on the frontier. Most of the events took place in the Upper South region. While the fighting stretched across the entire period, there were extended periods with little or no action.

Great Tellico was a Cherokee town at the site of present-day Tellico Plains, Tennessee, where the Tellico River emerges from the Appalachian Mountains. Great Tellico was one of the largest Cherokee towns in the region, and had a sister town nearby named Chatuga. Its name in Cherokee is more properly written Talikwa, but more commonly known as Diligwa. It is sometimes spelled Telliquo, Telliquah or, in Oklahoma, Tahlequah. There were several Cherokee settlements named Tellico, the largest of which is distinguished from the others by calling it "Great". The meaning of the word "Talikwa" is thought to be lost by the Cherokees. However, in an article authored by reporter Tesina Jackson of the Cherokee Phoenix the meaning of the word is stated as "the open place where the grass grows".

Lower Town is the westernmost settlement on the island of St Martin's in the Isles of Scilly, England.
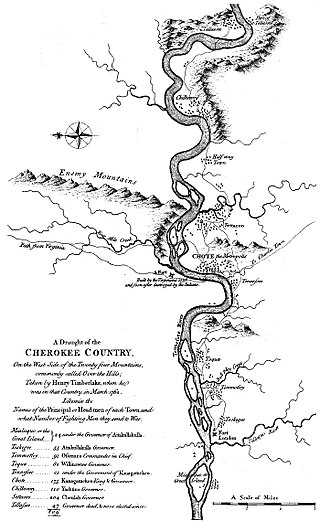
Overhill Cherokee was the term for the Cherokee people located in their historic settlements in what is now the U.S. state of Tennessee in the Southeastern United States, on the western side of the Appalachian Mountains. This name was used by 18th-century European traders and explorers from British colonies along the Atlantic coast, as they had to cross the mountains to reach these settlements.

Silesian Przesieka, literally Silesian Cutting was a densely forested, uninhabited and unpassable strip of land in the middle of Silesia, spreading from Golden Mountains in the south, along the Nysa Kłodzka to the Odra, and then along the Stobrawa, reaching the towns of Namysłów and Byczyna in northern Silesia. Originally, the Silesian Cutting was a boundary, separating territories of two Western Slavic tribes, the Slezanie and the Opolanie. In the 12th century, along the Cutting a border of Lower Silesia and Upper Silesia was established.
The Cherokee people of the southeastern United States, and later Oklahoma and surrounding areas, have a long military history. Since European contact, Cherokee military activity has been documented in European records. Cherokee tribes and bands had a number of conflicts during the 18th century with Europeans, primarily British colonists from the Southern Colonies. The Eastern Band and Cherokees from the Indian Territory fought in the American Civil War, with bands allying with the Union or the Confederacy. Because many Cherokees allied with the Confederacy, the United States government required a new treaty with the nation after the war. Cherokees have also served in the United States military during the 20th and 21st centuries.

The Battle of Echoee, or Etchoe Pass, was a battle on June 27, 1760 during the French and Indian War, between the British and colonial force under Archibald Montgomerie and a force of Cherokee warriors under Seroweh. It took place near the present-day municipality of Otto, in Macon County, North Carolina.

The siege of Fort Loudoun was an engagement during the Anglo-Cherokee War fought from February 1760 to August 1760 between the warriors of the Cherokee led by Ostenaco and the garrison of Fort Loudoun composed of British and colonial soldiers commanded by Captain Paul Demeré.
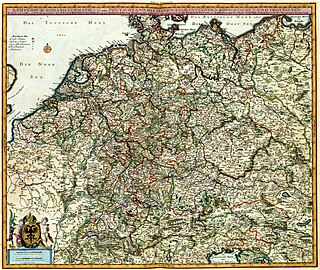
Ostsiedlung is the term for the Early Medieval and High Medieval migration of ethnic Germans and Germanization of the areas populated by Slavic, Baltic and Finnic peoples, the most settled area was known as Germania Slavica. Germanization efforts included eastern parts of Francia, East Francia, and the Holy Roman Empire and beyond; and the consequences for settlement development and social structures in the areas of settlement. Other regions were also settled, though not as heavily. The Ostsiedlung encompassed multiple modern and historical regions such as Germany east of the Saale and Elbe rivers, the states of Lower Austria and Styria in Austria, Livonia, Poland, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Slovenia, Hungary, and Transylvania in Romania.
The Pira-tapuya, or variations like Pira-Tapuia, Piratapuyo, etc., or Tapuya for short, are an indigenous people of the Amazon regions. They live along the Vaupés River in Colombia and in the state of Amazonas, Brazil.

The historic Cherokee settlements were Cherokee settlements established in Southeastern North America up to the removals of the early 19th century. Several settlements had existed prior to and were initially contacted by explorers and colonists of the colonial powers as they made inroads into frontier areas. Others were established later.