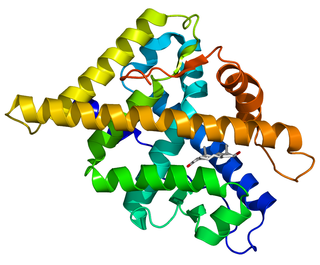
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4, is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone, in the cytoplasm and then translocating into the nucleus. The androgen receptor is most closely related to the progesterone receptor, and progestins in higher dosages can block the androgen receptor.
The Endocrine Society is a professional, international medical organization in the field of endocrinology and metabolism, founded in 1916 as The Association for the Study of Internal Secretions. The official name of the organization was changed to the Endocrine Society on January 1, 1952. It is a leading organization in the field and publishes four leading journals. It has more than 18,000 members from over 120 countries in medicine, molecular and cellular biology, biochemistry, physiology, genetics, immunology, education, industry, and allied health. The Society's mission is: "to advance excellence in endocrinology and promote its essential and integrative role in scientific discovery, medical practice, and human health."

Estrogen receptor alpha (ERα), also known as NR3A1, is one of two main types of estrogen receptor, a nuclear receptor that is activated by the sex hormone estrogen. In humans, ERα is encoded by the gene ESR1.

The follicle-stimulating hormone receptor or FSH receptor (FSHR) is a transmembrane receptor that interacts with the follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and represents a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). Its activation is necessary for the hormonal functioning of FSH. FSHRs are found in the ovary, testis, and uterus.

The luteinizing hormone/choriogonadotropin receptor (LHCGR), also lutropin/choriogonadotropin receptor (LCGR) or luteinizing hormone receptor (LHR) is a transmembrane receptor found predominantly in the ovary and testis, but also many extragonadal organs such as the uterus and breasts. The receptor interacts with both luteinizing hormone (LH) and chorionic gonadotropins and represents a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). Its activation is necessary for the hormonal functioning during reproduction.

Thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor (TRHR) is a G protein-coupled receptor which binds thyrotropin-releasing hormone.

The adrenocorticotropic hormone receptor or ACTH receptor also known as the melanocortin receptor 2 or MC2 receptor is a type of melanocortin receptor (type 2) which is specific for ACTH. A G protein–coupled receptor located on the external cell plasma membrane, it is coupled to Gαs and upregulates levels of cAMP by activating adenylyl cyclase. The ACTH receptor plays a role in immune function and glucose metabolism.
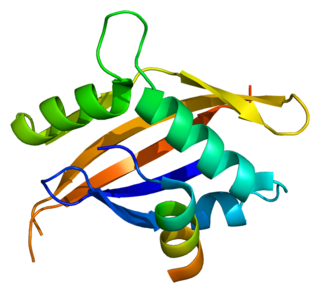
The nuclear receptor coactivator 1 (NCOA1) is a transcriptional coregulatory protein that contains several nuclear receptor interacting domains and an intrinsic histone acetyltransferase activity. NCOA1 is recruited to DNA promotion sites by ligand-activated nuclear receptors. NCOA1, in turn, acylates histones, which makes downstream DNA more accessible to transcription. Hence, NCOA1 assists nuclear receptors in the upregulation of DNA expression.

The steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1) protein is a transcription factor involved in sex determination by controlling the activity of genes related to the reproductive glands or gonads and adrenal glands. This protein is encoded by the NR5A1 gene, a member of the nuclear receptor subfamily, located on the long arm of chromosome 9 at position 33.3. It was originally identified as a regulator of genes encoding cytochrome P450 steroid hydroxylases, however, further roles in endocrine function have since been discovered.

The liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1) also known as totipotency pioneer factor NR5A2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR5A2 gene. LRH-1 is a member of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular transcription factors.

The small heterodimer partner (SHP) also known as NR0B2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR0B2 gene. SHP is a member of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular transcription factors. SHP is unusual for a nuclear receptor in that it lacks a DNA binding domain. Therefore, it is technically neither a transcription factor nor nuclear receptor but nevertheless it is still classified as such due to relatively high sequence homology with other nuclear receptor family members.

DAX1 is a nuclear receptor protein that in humans is encoded by the NR0B1 gene. The NR0B1 gene is located on the short (p) arm of the X chromosome between bands Xp21.3 and Xp21.2, from base pair 30,082,120 to base pair 30,087,136.

CAMP responsive element binding protein 1, also known as CREB-1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CREB1 gene. This protein binds the cAMP response element, a DNA nucleotide sequence present in many viral and cellular promoters. The binding of CREB1 stimulates transcription.

Liver X receptor alpha (LXR-alpha) is a nuclear receptor protein that in humans is encoded by the NR1H3 gene.

The testicular receptor 2 (TR2) also known as NR2C1 is protein that in humans is encoded by the NR2C1 gene. TR2 is a member of the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors.

Thyroid hormone receptor alpha (TR-alpha) also known as nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group A, member 1 (NR1A1), is a nuclear receptor protein that in humans is encoded by the THRA gene.

Melatonin receptor type 1A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MTNR1A gene.

Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3 (AKR1C3), also known as 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 5 is a key steroidogenic enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKR1C3 gene.
The American Journal of Physiology is a peer-reviewed scientific journal on physiology published by the American Physiological Society.
The Journal of Molecular Endocrinology is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published eight times per year. Its focus is on molecular and cellular mechanisms in endocrinology, including gene regulation, cell biology, signalling, mutations and transgenesis.
















