Bromophenol blue is used as a pH indicator, a color marker, and a dye. It can be prepared by slowly adding excess bromine to a hot solution of phenolsulfonphthalein in glacial acetic acid.
Fluorosulfuric acid (IUPAC name: sulfurofluoridic acid) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula HSO3F. It is one of the strongest acids commercially available. The formula HSO3F emphasizes its relationship to sulfuric acid, H2SO4; HSO3F is a tetrahedral molecule. It is a colourless liquid, although commercial samples are often yellow.

Sigma-Aldrich Corporation is an American chemical, life science and biotechnology company owned by Merck KGaA.

Xanthene (9H-xanthene, 10H-9-oxaanthracene) is the organic compound with the formula is CH2[C6H4]2O. It is a yellow solid that is soluble in common organic solvents. Xanthene itself is an obscure compound, but many of its derivatives are useful dyes.
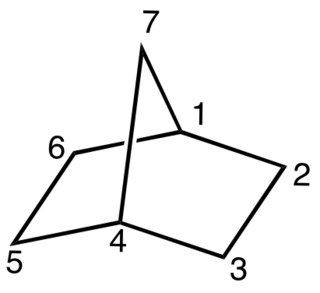
Norbornane (also known as bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane) is an organic compound and a saturated hydrocarbon with chemical formula C7H12. It is a crystalline compound with melting point 88 °C. The carbon skeleton is derived from cyclohexane ring with a methylene bridge in the 1,4- position, and is a bridged bicyclic compound. The compound is a prototype of a class of strained bicyclic hydrocarbons.
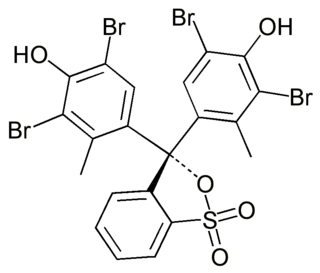
Bromocresol green (BCG) is a dye of the triphenylmethane family. It belongs to a class of dyes called sulfonephthaleins. It is used as a pH indicator in applications such as growth mediums for microorganisms and titrations. In clinical practise, it is commonly used as a diagnostic technique. The most common use of Bromocresol green is to measure serum albumin concentration within mammalian blood samples in possible cases of renal failure and liver disease.

Ethyl diazoacetate (N=N=CHC(O)OC2H5) is a diazo compound and a reagent in organic chemistry. It was discovered by Theodor Curtius in 1883. The compound can be prepared by reaction of the ethyl ester of glycine with sodium nitrite and sodium acetate in water.
Air sensitivity is a term used, particularly in chemistry, to denote the reactivity of chemical compounds with some constituent of air. Most often, reactions occur with atmospheric oxygen (O2) or water vapor (H2O), although reactions with the other constituents of air such as carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), and nitrogen (N2) are also possible.

Gallocatechol or gallocatechin (GC) is a flavan-3-ol, a type of chemical compound including catechin, with the gallate residue being in an isomeric trans position. It is one of the antioxidant chemicals found in food.

1-Pentyne, an organic compound, is a terminal alkyne. It is an isomer of 2-pentyne, an internal alkyne.

Selenium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound composed with the formula SeCl4. This compound exists as yellow to white volatile solid. It is one of two commonly available selenium chlorides, the other example being selenium monochloride, Se2Cl2. SeCl4 is used in the synthesis of other selenium compounds.

Cobalt(II,III) oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula Co3O4. It is one of two well characterized cobalt oxides. It is a black antiferromagnetic solid. As a mixed valence compound, its formula is sometimes written as CoIICoIII2O4 and sometimes as CoO•Co2O3.

2,4,6-Tribromoanisole (TBA) is a chemical compound that is a brominated derivative of anisole. It is one of the chemicals responsible for cork taint.
Iodophenol is a substitution product of phenol in which one of the hydrogen atoms is replaced by iodine.

1,3-Dioxane or m-dioxane is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C4H8O2, the CAS number 505-22-6, EC Number 208-005-1 and RTECS JG8224000.
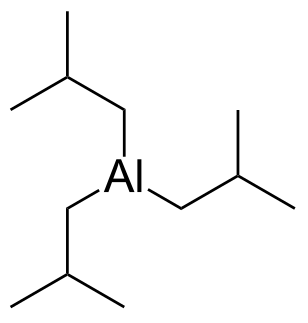
Triisobutylaluminium (TiBA) is an organoaluminium compound with the formula Al(CH2CH(CH3)2)3. This colorless pyrophoric liquid is mainly used to make linear primary alcohols and α-olefins.
Scandium sulfate is the scandium salt of sulfuric acid and has the formula Sc2(SO4)3. It is used in agriculture as a very dilute solution as a seed treatment to improve the germination of corn, peas, wheat, and other plants.
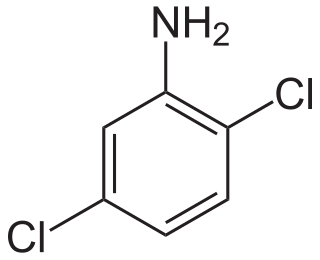
Dichloroanilines are chemical compounds which consist of an aniline ring substituted with two chlorine atoms and have the molecular formula C6H5Cl2N. There are six isomers, varying in the positions of the chlorine atoms around the ring relative to the amino group. As aniline derivatives, they are named with the amino group in position 1. They are all colorless, although commercial samples can appear colored due to the presence of impurities. Several derivatives are used in the production of dyes and herbicides.
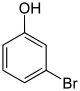
Dibromophenols form a group of aromatic chemical compounds which are both phenols and bromobenzenes. The structure consists of a benzene ring with an attached hydroxy group (-OH) and two bromine atoms (-Br) as substituents. There are six structural isomers, each with the molecular formula C6H4Br2O, which differ by arrangement of the substituents.
A bromophenol is any organobromide of phenol that contains one or more covalently bonded bromine atoms. There are five basic types of bromophenols and 19 different bromophenols in total when positional isomerism is taken into account. Bromophenols are produced by electrophilic halogenation of phenol with bromine.