
Venice is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 126 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are linked by 472 bridges. The islands are in the shallow Venetian Lagoon, an enclosed bay lying between the mouths of the Po and the Piave rivers. In 2020, around 258,685 people resided in greater Venice or the Comune di Venezia, of whom around 51,000 live in the historical island city of Venice and the rest on the mainland (terraferma). Together with the cities of Padua and Treviso, Venice is included in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area (PATREVE), which is considered a statistical metropolitan area, with a total population of 2.6 million.

The Doge of Venice was the highest role of authority within the Republic of Venice. The word "Doge" originates from the Latin word "Dux," which translates to "leader" or "Duke."

Catherine Cornaro was the last monarch of the Kingdom of Cyprus, also holding the titles of Queen of Jerusalem and Queen of Armenia. She became queen consort of Cyprus by marriage to James II of Cyprus, and then regent of Cyprus during the minority of her son James III of Cyprus in 1473–1474, and finally queen regnant of Cyprus upon his death. She reigned from 26 August 1474 to 26 February 1489 and was declared a "Daughter of Saint Mark" in order that the Republic of Venice could claim control of Cyprus after the death of her husband.
Venetian, wider Venetian or Venetan is a Romance language spoken natively in the northeast of Italy, mostly in Veneto, where most of the five million inhabitants can understand it. It is sometimes spoken and often well understood outside Veneto: in Trentino, Friuli, the Julian March, Istria, and some towns of Slovenia, Dalmatia (Croatia) and Bay of Kotor (Montenegro) by a surviving autochthonous Venetian population, and in Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, Mexico, the United States and the United Kingdom by Venetians in the diaspora.

The Republic of Venice or Venetian Republic, traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and maritime republic in parts of the present-day Italian Republic that existed for 1,100 years from 697 until 1797. Centered on the lagoon communities of the prosperous city of Venice, it incorporated numerous overseas possessions in modern Croatia, Slovenia, Montenegro, Greece, Albania and Cyprus. The republic grew into a trading power during the Middle Ages and strengthened this position during the Renaissance. Most citizens spoke the Venetian language, although publishing in Italian became the norm during the Renaissance, alongside Latin and Medieval Greek.

The War of the League of Cambrai, sometimes known as the War of the Holy League and several other names, was fought from February 1508 to December 1516 as part of the Italian Wars of 1494–1559. The main participants of the war, who fought for its entire duration, were France, the Papal States, and the Republic of Venice; they were joined at various times by nearly every significant power in Western Europe, including Spain, the Holy Roman Empire, England, the Duchy of Milan, the Republic of Florence, the Duchy of Ferrara, and the Swiss.

The Julian March, also called Julian Venetia, is an area of southeastern Europe which is currently divided among Croatia, Italy, and Slovenia. The term was coined in 1863 by the Italian linguist Graziadio Isaia Ascoli, a native of the area, to demonstrate that the Austrian Littoral, Veneto, Friuli, and Trentino shared a common Italian linguistic identity. Ascoli emphasized the Augustan partition of Roman Italy at the beginning of the Empire, when Venetia et Histria was Regio X.
The city of Venice in Italy has played an important role in the development of the music of Italy. The Venetian state—i.e. the medieval Maritime Republic of Venice—was often popularly called the "Republic of Music", and an anonymous Frenchman of the 17th century is said to have remarked that "In every home, someone is playing a musical instrument or singing. There is music everywhere."

Liga Veneta, whose complete name is Liga Veneta per Salvini Premier, is a regionalist political party active in Veneto.

Venetian nationalism is a nationalist, but primarily regionalist, political movement active mostly in Veneto, Italy, as well as in other parts of the former Republic of Venice.
The Florentine calendar, also referred to as the stylus Florentinus, was the calendar used in the Republic of Florence in Italy during the Middle Ages. Unusually, both the beginning of the day and the beginning of the year differed from the traditional Julian calendar.
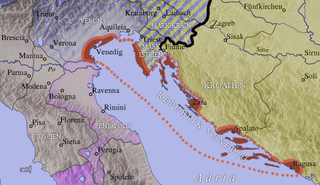
The Republic of Venice was a sovereign state and maritime republic in Northeast Italy, which existed for a millennium between the 8th century and 1797.

The Republic of China calendar, often shortened to the ROC calendar or the Minguo calendar, is a calendar used in Taiwan, Penghu, Kinmen, and Matsu. The calendar uses 1912, the year of the establishment of the Republic of China (ROC) in Nanjing, as the first year.

Venetian Albania was the official term for several possessions of the Republic of Venice in the southeastern Adriatic, encompassing coastal territories primarily in present-day southern Montenegro and partially in northern Albania.
The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It went into effect in October 1582 following the papal bull Inter gravissimas issued by Pope Gregory XIII, which introduced it as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian calendar. The principal change was to space leap years differently so as to make the average calendar year 365.2425 days long, more closely approximating the 365.2422-day 'tropical' or 'solar' year that is determined by the Earth's revolution around the Sun.

The Statute of the Region of Veneto is the constitution of Veneto, a Region of Italy.
The Pisan calendar, also referred to as the stile pisano or the calculus Pisanus, was the calendar used in the Republic of Pisa in Italy during the Middle Ages, which differed from the traditional Julian calendar.

The Lion of Saint Mark, representing Mark the Evangelist, pictured in the form of a winged lion, is an aspect of the Tetramorph. On the pinnacle of St Mark's Cathedral he is depicted as holding a Bible, and surmounting a golden lion which is the symbol of the city of Venice and formerly of the Venetian Republic.

The Flag of the Republic of Venice, commonly known as the Banner or Standard of Saint Mark, was the symbol of the Republic of Venice, until its dissolution in 1797.
This is the list of operas performed at the Teatro San Cassiano in Venice.













