Related Research Articles

The inch is a unit of length in the British Imperial and the United States customary systems of measurement. It is equal to 1/36 yard or 1/12 of a foot. Derived from the Roman uncia ("twelfth"), the word inch is also sometimes used to translate similar units in other measurement systems, usually understood as deriving from the width of the human thumb.

The kilogram is the base unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI), having the unit symbol kg. 'Kilogram' means 'one thousand grams' and is colloquially abbreviated to kilo.
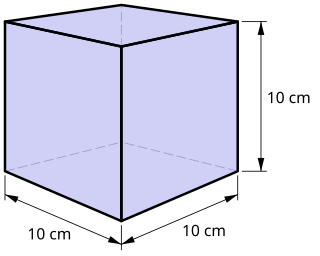
The litre or liter is a metric unit of volume. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm3), 1000 cubic centimetres (cm3) or 0.001 cubic metres (m3). A cubic decimetre occupies a volume of 10 cm × 10 cm × 10 cm and is thus equal to one-thousandth of a cubic metre.

Metrication or metrification is the act or process of converting to the metric system of measurement. All over the world, countries have transitioned from local and traditional units of measurement to the metric system. This process began in France during the 1790s, and has persistently advanced over two centuries, accumulating into 95% of the world officially only using the modern metric system. Nonetheless, this also highlights that certain countries and sectors are either still transitioning or have chosen not to fully adopt the metric system.

The pound or pound-mass is a unit of mass used in both the British imperial and United States customary systems of measurement. Various definitions have been used; the most common today is the international avoirdupois pound, which is legally defined as exactly 0.45359237 kilograms, and which is divided into 16 avoirdupois ounces. The international standard symbol for the avoirdupois pound is lb; an alternative symbol is lbm, #, and ℔ or ″̶.

The International System of Units, internationally known by the abbreviation SI, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. Coordinated by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures it is the only system of measurement with official status in nearly every country in the world, employed in science, technology, industry, and everyday commerce.
A metric prefix is a unit prefix that precedes a basic unit of measure to indicate a multiple or submultiple of the unit. All metric prefixes used today are decadic. Each prefix has a unique symbol that is prepended to any unit symbol. The prefix kilo-, for example, may be added to gram to indicate multiplication by one thousand: one kilogram is equal to one thousand grams. The prefix milli-, likewise, may be added to metre to indicate division by one thousand; one millimetre is equal to one thousandth of a metre.

Ton is any of several units of measure of mass, volume or force. It has a long history and has acquired several meanings and uses.

The tonne is a unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton in the United States to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton and the long ton. It is equivalent to approximately 2,204.6 pounds, 1.102 short tons, and 0.984 long tons. The official SI unit is the megagram (Mg), a less common way to express the same amount.

United States customary units form a system of measurement units commonly used in the United States and most U.S. territories, since being standardized and adopted in 1832. The United States customary system developed from English units that were in use in the British Empire before the U.S. became an independent country. The United Kingdom's system of measures evolved by 1824 to create the imperial system, which was officially adopted in 1826, changing the definitions of some of its units. Consequently, while many U.S. units are essentially similar to their imperial counterparts, there are noticeable differences between the systems.

The metric system is a decimal-based system of measurement. The current international standard for the metric system is the International System of Units, in which all units can be expressed in terms of seven base units: the metre (m), kilogram (kg), second (s), ampere (A), kelvin (K), mole (mol), and candela (cd). These can be made into larger or smaller units with the use of metric prefixes.

Troy weight is a system of units of mass that originated in the Kingdom of England in the 15th century and is primarily used in the precious metals industry. The troy weight units are the grain, the pennyweight, the troy ounce, and the troy pound. The troy grain is equal to the grain unit of the avoirdupois system, but the troy ounce is heavier than the avoirdupois ounce, and the troy pound is lighter than the avoirdupois pound. One troy ounce equals exactly 31.1034768 grams.
The gray is the unit of ionizing radiation dose in the International System of Units (SI), defined as the absorption of one joule of radiation energy per kilogram of matter.
The Mendenhall Order marked a decision to change the fundamental standards of length and mass of the United States from the customary standards based on those of England to metric standards. It was issued on April 5, 1893, by Thomas Corwin Mendenhall, superintendent of the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey, with the approval of the United States Secretary of the Treasury, John Griffin Carlisle. The order was issued as the Survey's Bulletin No. 26 – Fundamental Standards of Length and Mass.

Myria- (symbol my) is a now obsolete decimal metric prefix denoting a factor of 104 (ten thousand). It originates from the Greek μύριοι (mýrioi) (myriad). The prefix was part of the original metric system adopted by France in 1795, but was not adopted when the SI prefixes were internationally adopted by the 11th CGPM conference in 1960.

The grave, abbreviated gv, is the unit of mass used in the first metric system which was implemented in France in 1793. In 1795, the grave was renamed as the kilogram.

The Metric Act of 1866, also known as the Kasson Act, is a piece of United States legislation that legally protected use of the metric system in commerce from lawsuit, and provided an official conversion table from U.S. customary units.
The international yard and pound are two units of measurement that were the subject of an agreement among representatives of six nations signed on 1 July 1959: Australia, Canada, New Zealand, South Africa, the United Kingdom and the United States. The agreement defined the yard as exactly 0.9144 meters and the avoirdupois pound as exactly 0.45359237 kilograms.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the metric system:

The imperial and US customary measurement systems are both derived from an earlier English system of measurement which in turn can be traced back to Ancient Roman units of measurement, and Carolingian and Saxon units of measure.
References
- ↑ Roberts, Richard W. (1975-06-01). Metric System of Weights and Measures - Guidelines for Use. USA: Director of the National Bureau of Standards. Federal Register FR Doc.75-15798 (1975-06-18).
Accordingly, the following units and terms listed in the table of metric units in section 2 of the act of July 28, 1866, that legalized the metric system of weights and measures in the United States, are no longer accepted for use in the United States: myriameter, stere, millier or tonneau, quintal, myriagram, kilo (for kilogram).
- ↑ Judson, Lewis V. (1976-10-01) [1963]. "Appendix 7". In Barbrow, Louis E. (ed.). Weights and Measures Standards of the United States, a brief history (PDF). Derived from a prior work by Louis A. Fisher (1905). USA: US Department of Commerce, National Bureau of Standards. p. 33. LCCN 76-600055. NBS Special Publication 447; NIST SP 447; 003-003-01654-3. Retrieved 2015-10-12.