
Wilmington is the largest city in the U.S. state of Delaware. The city was built on the site of Fort Christina, the first Swedish settlement in North America. It lies at the confluence of the Christina River and Brandywine Creek, near where the Christina flows into the Delaware River. It is the county seat of New Castle County and one of the major cities in the Delaware Valley metropolitan area. Wilmington was named by Proprietor Thomas Penn after his friend Spencer Compton, Earl of Wilmington, who was prime minister during the reign of George II of Great Britain.
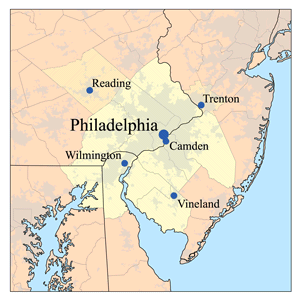
The Delaware Valley, sometimes referred to as Greater Philadelphia or the Philadelphia metropolitan area, is a metropolitan region in the Northeast United States that centers around Philadelphia, the nation's sixth-most populous city, and spans parts of four U.S. states: southeastern Pennsylvania, southern New Jersey, northern Delaware, and the northern Eastern Shore of Maryland. With a core Metropolitan Statistical Area population of 6.288 million residents and a Combined Statistical Area population of 7.366 million as of the 2020 census, the Delaware Valley is the seventh-largest metropolitan region in the nation, the eighth-largest metropolitan region in North America, and the 35th-largest metropolitan region in the world.

John Wanamaker Department Store was one of the first department stores in the United States. Founded by John Wanamaker in Philadelphia, it was influential in the development of the retail industry including as the first store to use price tags. At its zenith in the early 20th century, Wanamaker's also had a store in New York City at Broadway and Ninth Street. Both employed extremely large staffs. By the end of the 20th century, there were 16 Wanamaker's outlets, but after years of change, the chain was bought by A. Alfred Taubman in late 1986, and added to his previous purchase of Woodward & Lothrop, the Washington, D.C., department store. In 1994, Woodies, as it was known, filed for bankruptcy. The assets of Woodies were purchased by the May Company Department Stores and JCPenney. In 1995, Wanamaker's transitioned to Hecht's, one of the May Company brands. In 2006, Macy's opened in the former Philadelphia Wanamaker's Department Store, now called Macy's Center City. The building is a National Historic Landmark. One if its expansions was designed by master architect Daniel Burnham. It contains the Wanamaker Organ, the largest functional organ in the world.

Gimbel Brothers was an American department store corporation that operated for over a century, from 1842 until 1987. Gimbel patriarch Adam Gimbel opened his first store in Vincennes, Indiana, in 1842. In 1887, the company moved its operations to the Gimbel Brothers Department Store in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. It became a chain when it opened a second, larger store in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in 1894, moving its headquarters there. At the urging of future company president Bernard Gimbel, grandson of the founder, the company expanded to New York City in 1910.

Fishtown is a neighborhood in the River Wards section of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. Located northeast of Center City Philadelphia, its borders are somewhat disputed today due to many factors, but are roughly defined by the triangle created by the Delaware River, Front Street, and York Street. Some newer residents expand the area to Lehigh Avenue to the northeast, while some older residents shrink the area to Norris Street. It is served by the Market–Frankford Line rapid transit subway/elevated line of the SEPTA system. Fishtown is a largely working class Irish Catholic neighborhood, but has recently seen a large influx of young urban professionals and gentrification.
Hecht's, also known as Hecht Brothers, Hecht Bros. and The Hecht Company, was a large chain of department stores that operated mainly in the mid-Atlantic and southern region of the United States. The firm originated in Baltimore, Maryland.
Strawbridge's, formerly Strawbridge & Clothier, was a department store in the northeastern United States, with stores in Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and Delaware. The Center City Philadelphia flagship store was, in its day, a gracious urban emporium. The retailer started adding branch stores starting in the 1930s and, by their zenith in the 1980s, enjoyed annual sales of over a billion dollars By the 1990s, Strawbridge's became part of the May Department Stores conglomerate until May's acquisition by Federated Department Stores on August 30, 2005.
The Baltimore and Philadelphia Railroad was a railroad line built by the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O) from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, to the Maryland-Delaware state line, where it connected with the B&O's Philadelphia Branch to reach Baltimore, Maryland. It was built in the 1880s after the B&O lost access to its previous route to Philadelphia, the Philadelphia, Wilmington and Baltimore Railroad (PW&B). The cost of building the new route, especially the Howard Street Tunnel on the connecting Baltimore Belt Line, led to the B&O's first bankruptcy. Today, the line is used by CSX Transportation for freight trains.

Center City East is part of the downtown district known as Center City, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. The area is generally bounded by Arch Street to the north, Chestnut Street to the south, Juniper Street to the west, and 6th Street to the east. The area serves as one of the major retail centers in the city as well as the home of the Pennsylvania Convention Center.

Samuel Sloan was a Philadelphia-based architect and best-selling author of architecture books in the mid-19th century. He specialized in Italianate villas and country houses, churches, and institutional buildings. His most famous building—the octagonal mansion "Longwood" in Natchez, Mississippi—is unfinished; construction was abandoned during the American Civil War.
Best & Co. was a department store founded in 1879 by Albert Best in New York City. The company initially sold clothing for infants and children, but later expanded to women's clothing and accessories. It was known for its "tastefully styled and proper women's clothes and its sturdy children's wear." Philip Le Boutillier served as president during the late 1930s. The store had expanded to 20 branches by 1966, when the company was acquired by McCrory's, who also operated Lerner Shops and S. Klein. In late-1970, McCrory's liquidated the company. At the time of its closing, the store had 1,200 employees.

Theophilus Parsons Chandler Jr. was an American architect of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. He spent his career at Philadelphia, and is best remembered for his churches and country houses. He founded the Department of Architecture at the University of Pennsylvania (1890), and served as its first head.

Delaware Route 52 (DE 52) is a state highway in New Castle County, Delaware. The route runs from U.S. Route 13 Business in downtown Wilmington north to Pennsylvania Route 52 (PA 52) at the Pennsylvania border near Centerville. DE 52 runs through the city of Wilmington and passes through areas of the Brandywine Valley north of Wilmington. DE 52 intersects Interstate 95 (I-95)/US 202 and DE 2 in Wilmington and DE 100/DE 141 and DE 82 in Greenville. The entire route is designated as part of the Brandywine Valley National Scenic Byway, a National Scenic Byway and Delaware Byway, while most of the route is also designated as part of the Harriet Tubman Underground Railroad Byway of the Delaware Byways system. The road was built as the Kennett Pike, a turnpike, between 1811 and 1813. The Kennett Pike was bought by Pierre S. du Pont in 1919 and was widened and paved before being sold to the State of Delaware for $1. The road received the DE 52 designation by 1936.

Lit Brothers was a moderately-priced department store based in Philadelphia. Samuel and Jacob Lit opened the first store at Market and N. 8th streets in 1891. Lits positioned itself well as a more affordable alternate to its upscale competitors Strawbridge and Clothier, John Wanamaker, and Gimbels. The store's slogan was "A Great Store in A Great City," and it was noted for its millinery department.

Loveman's of Alabama was a Birmingham, Alabama-based chain of department stores with locations across Alabama. It adopted this name to distinguish it from Loveman's department stores operating in Chattanooga, Tennessee, and in Nashville, Tennessee.
Foxwoods Casino Philadelphia was a proposed casino to be located first along the Delaware River, then under pressure from local residents attempted to move to The Gallery at Market East in Center City in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was one of five stand-alone casinos awarded a gaming license on December 20, 2006, by the Pennsylvania Gaming Control Board. The Board revoked the license in December 2010.

Philadelphia is the center of economic activity in both Pennsylvania and the four-state Delaware Valley metropolitan region of the United States. Philadelphia's close geographical and transportation connections to other large metropolitan economies along the Eastern Seaboard of the United States have been cited as offering a significant competitive advantage for business creation and entrepreneurship. Five Fortune 500 companies are headquartered in the city. As of 2021, the Philadelphia metropolitan area was estimated to produce a gross metropolitan product (GMP) of US$479 billion, an increase from the $445 billion calculated by the Bureau of Economic Analysis for 2017, representing the ninth largest U.S. metropolitan economy. Philadelphia was rated by the GaWC as a 'Beta' city in its 2016 ranking of world cities.

The Delaware Railroad was the major railroad in the US state of Delaware, traversing almost the entire state north to south. It was planned in 1836 and built in the 1850s. It began in Porter and was extended south through Dover, Seaford and finally reached Delmar on the border of Maryland in 1859. Although operated independently, in 1857 it was leased by and under the financial control of the Philadelphia, Wilmington, and Baltimore Railroad. In 1891, it was extended north approximately 14 miles (23 km) with the purchase of existing track to New Castle and Wilmington. With this additional track, the total length was 95.2 miles (153.2 km).
The William Steele & Sons Company was an architectural firm that was located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.

E. William Martin was a Scottish-born American architect in practice in Wilmington, Delaware from 1926 to 1965. In part through personal and political connections to members of the wealthy du Pont family Martin was architect of many important public works in Delaware, including public schools, the Zwaanendael Museum and the Delaware Legislative Hall.














