
The first indigenous peoples of Costa Rica were hunters and gatherers, and when the Spanish conquerors arrived, Costa Rica was divided in two distinct cultural areas due to its geographical location in the Intermediate Area, between Mesoamerican and the Andean cultures, with influences of both cultures.

A colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, the rule remains separate to the original country of the colonizers, the metropolitan state, within the shared imperialist administration. This colonial administrative separation, though often blurred, makes colonies neither annexed or incorporated territories nor client states. Colonies contemporarily are identified and organized as not sufficiently self-governed dependent territories. Other past colonies have become either sufficiently incorporated and self-governed, or independent, with some to a varying degree dominated by remaining colonial settler societies or neocolonialism.
Leon, Léon (French) or León (Spanish) may refer to:

The second millennium of the Anno Domini or Common Era was a millennium spanning the years 1001 to 2000.
Iberia, in its most common meaning, refers to the Iberian Peninsula in southwestern Europe. In history, it was also used to refer to anything pertaining to the former Kingdom of Iberia, an exonym for the Georgian kingdom of Kartli.
Rome is the English name of the capital of Italy. The city, called Roma in Latin and Italian, was also the capital of the Roman Empire and the seat of the papacy.

British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestown, Virginia, and more substantially with the founding of the Thirteen Colonies along the Atlantic coast of North America.
Egypt is a country mainly in North Africa.
The phrase "the empire on which the sun never sets" was used to describe certain global empires that were so extensive that it seemed as though it was always daytime in at least one part of its territory.
West is a cardinal direction or compass point.

The Captaincy General of Guatemala, also known as the Kingdom of Guatemala, was an administrative division of the Spanish Empire, under the viceroyalty of New Spain in Central America, including the present-day nations of Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Honduras, El Salvador, and Guatemala, and the Mexican state of Chiapas. The governor-captain general was also president of the Royal Audiencia of Guatemala, the superior court.
A colonial empire is a collective of territories, either contiguous with the imperial center or located overseas, settled by the population of a certain state and governed by that state.

The decolonization of the Americas occurred over several centuries as most of the countries in the Americas gained their independence from European rule. The American Revolution was the first in the Americas, and the British defeat in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783) was a victory against a great power, aided by France and Spain, Britain's enemies. The French Revolution in Europe followed, and collectively these events had profound effects on the Spanish, Portuguese, and French colonies in the Americas. A revolutionary wave followed, resulting in the creation of several independent countries in Latin America. The Haitian Revolution lasted from 1791 to 1804 and resulted in the independence of the French slave colony. The Peninsular War with France, which resulted from the Napoleonic occupation of Spain, caused Spanish Creoles in Spanish America to question their allegiance to Spain, stoking independence movements that culminated in various Spanish American wars of independence (1808–33), which were primarily fought between opposing groups of colonists and only secondarily against Spanish forces. At the same time, the Portuguese monarchy fled to Brazil during the French invasion of Portugal. After the royal court returned to Lisbon, the prince regent, Pedro, remained in Brazil and in 1822 successfully declared himself emperor of a newly independent Brazilian Empire.

British America comprised the colonial territories of the English Empire, and the successor British Empire, in the Americas from 1607 to 1783. These colonies were formally known as British America and the British West Indies just before the thirteen of the colonies declared their independence in the American Revolution (1765–1783) and formed the United States of America.
Angola is a country in Southern Africa.
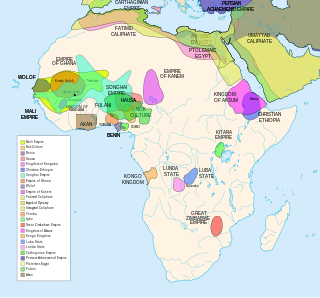
African empires is an umbrella term used in African studies to refer to a number of pre-colonial African kingdoms in Africa with multinational structures incorporating various populations and polities into a single entity, usually through conquest.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.







