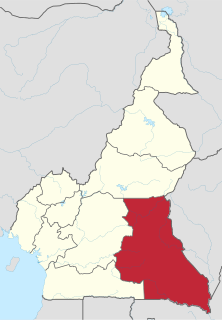
The East Region occupies the southeastern portion of the Republic of Cameroon. It is bordered to the east by the Central African Republic, to the south by Congo, to the north by the Adamawa Region, and to the west by the Centre and South Regions. With 109,002 km² of territory, it is the largest region in the nation as well as the most sparsely populated. Historically, the peoples of the East have been settled in Cameroonian territory for longer than any other of the country's many ethnic groups, the first inhabitants being the Baka pygmies.

The South Region is located in the southwestern and south-central portion of the Republic of Cameroon. It is bordered to the east by the East Region, to the north by the Centre Region, to the northwest by the Littoral Region, to the west by the Gulf of Guinea, and to the south by the countries of Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and Congo. The South occupies 47,720 km2 of territory, making it the fourth largest region in the nation. The major ethnic groups are the various Beti-Pahuin peoples, such as the Ewondo, Fang, and Bulu.

There is no official language in Gabon, however 32% of the people speak Fang as a mother tongue. French is the medium of instruction. Before World War II very few Gabonese learned French, nearly all of them working in either business or government administration. After the war, France worked for universal primary education in Gabon, and by the 1960-61 census, 47% of the Gabonese over the age of 14 spoke some French, while 13% were literate in the language. By the 1990s, the literacy rate had risen to about 60%.

The Maka or Makaa are an ethnic group inhabiting the southern rain forest zone of Cameroon. They live primarily in the northern portions of the Upper Nyong division of Cameroon's East Province. Major Maka settlements include Abong-Mbang, Doumé, and Nguélémendouka. Some Maka villages lie over the border into the Centre Province, as well.
The Badwe'e are an ethnic group inhabiting the rain forest zone of southeastern Cameroon. They recognize themselves as the descendants of Edwe'e, the youngest son of Koo and the brother of Njeme and Nzime. The Badwe'e live south of Messaména in the East Province in a region south of the Bekol and both north and west of the Nzime. Their territory includes much of the northern and western border of the Dja Biosphere Reserve. They speak a dialect of Koozime, together with the Nzime.
The Beti-Pahuin are a Bantu ethnic group located in rain forest regions of Cameroon, Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and São Tomé and Príncipe. Though they separate themselves into several individual clans, they all share a common origin, history and culture.

The Bamileke is the native group which is now dominant in Cameroon's West and Northwest Regions. It is part of the Semi-Bantu ethnic group. The Bamileke are regrouped under several groups, each under the guidance of a chief or fon. They speak a number of related languages from the Bantoid branch of the Niger–Congo language family. These languages are closely related, however, and some classifications identify a Bamileke dialect continuum with seventeen or more dialects.
Lolodorf is a small town-centred region in the south province of the Republic of Cameroon, near the western coast of Africa. It is between Ngoumou and Bipindi, in a zone of the Atlantic Littoral Evergreen Forest.

Lomié is a town in the Lomié District in the Upper Nyong division of the East Province of Cameroon. An article in the Mail & Guardian Online describes it as having "no telephone connection to the outside world, and a single access road that is little more than a forest trail". In fact Lomié has been connected to the cellular phone network since 2006 and the town has had several 'boom' periods. While previous employment came from the logging industry currently the town is near an important cobalt and zinc mining project. The GEOVIC mining company uses Lomié as a base. Lomié has a number of interesting historical buildings, dating from the German and French era. Among these building are the house of the senior civil administrator, a jail, a courthouse and a post-office. The town used to be center of the Upper Nyong Division until it was replaced by Abong-Mbang. Roads from Lomié lead north to Abong-Mbang via Mindourou, east to Messok and Yokadouma and south to Ngoila.

The Bamboko are a Bantu ethnic group of the Republic of Cameroon. They are part of the Sawa ethnic groups, those who live on the coast.

The Makaa–Njem languages are a group of Bantu languages spoken in Cameroon, the Central African Republic, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon and the Republic of the Congo. They are coded Zone A.80 in Guthrie's classification.
The Nzime are an ethnic group inhabiting the rain forest zone of southeastern Cameroon. The Nzime live along the road running south of Abong-Mbang, through Mindourou and Lomié, and forking to Zoulabot and Zwadiba. Their territory lies south of the Koonzime in Djaposten, east of the Badwe'e, north of the Njyem, and west of the Konabembe people, all related groups. The Nzime speak the Nzime dialect of Koonzime ("OZM"), one of the Makaa–Njyem Bantu languages.
Semi-Bantu or Semibantu is a non-linguistic term that refers to those African languages spoken by the inhabitants of the Western grassfields of Cameroon which are Bantoid languages, but don't belong to the Bantu languages.
Aka, also known as Yaka or Beka, is a Bantu language spoken in the Central African Republic and Republic of Congo, along the Ubangi River dividing the two countries.
The Kwasio language, also known as Ngumba / Mvumbo, Bujeba, and Gyele / Kola, is a language of Cameroon, spoken in the south along the coast and at the border with Equatorial Guinea by some 70 000 members of the Ngumba, Kwasio, Gyele and Mabi peoples. Many authors view Kwasio and the Gyele/Kola language as distinct. In the Ethnologue, the languages therefore receive different codes: Kwasio has the ISO 639-3 code nmg, while Gyele has the code gyi. The Kwasio, Ngumba, and Mabi are village farmers; the Gyele are nomadic Pygmy hunter-gatherers living in the rain forest.
Baka is a dialect cluster of Ubangian languages spoken by the Baka Pygmies of Cameroon and Gabon. The people are ethnically close to the Aka, the two together called the Mbenga (Bambenga), but the languages are not related, apart from some vocabulary dealing with the forest economy, which suggests the Aka may have shifted to Bantu from a language like Baka about 1500 CE.
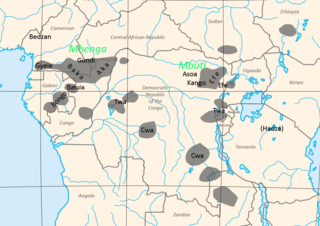
The Congo Pygmies are those "forest people" who have, or recently had, a deep-forest hunter-gather economy and a simple, non-hierarchical societal structure based on bands, are of short stature, and have a deep cultural and religious affinity with the Congo forest and live in a generally subservient relationship with agricultural "patrons".
Njem (Njyem) is a Bantu language of Congo and Cameroon. Speakers are mostly (85%) monolingual, and many Baka Pygmies speak Njema as a second language.
Bekwel (Bekwil) is a Bantu language of the Republic of the Congo. There are some 10,000 speakers there, with a quarter that number across the border in Gabon, and perhaps a similar on the opposite side in Cameroon. It is rather close to Nzime (Koonzime).






















