
Ascaris lumbricoides is a large parasitic roundworm of the genus Ascaris. It is the most common parasitic worm in humans. An estimated 807 million–1.2 billion people are infected with A. lumbricoides worldwide. People living in tropical and subtropical countries are at greater risk of infection. Infection by Ascaris lumbricoides is known as ascariasis.

Ascariasis is a disease caused by the parasitic roundworm Ascaris lumbricoides. Infections have no symptoms in more than 85% of cases, especially if the number of worms is small. Symptoms increase with the number of worms present and may include shortness of breath and fever in the beginning of the disease. These may be followed by symptoms of abdominal swelling, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Children are most commonly affected, and in this age group the infection may also cause poor weight gain, malnutrition, and learning problems.
Toxocariasis is an illness of humans caused by the dog roundworm and, less frequently, the cat roundworm. These are the most common intestinal roundworms of dogs, coyotes, wolves and foxes and domestic cats, respectively. Humans are among the many "accidental" or paratenic hosts of these roundworms.

Gnathostomiasis, also known as larva migrans profundus, is the human infection caused by the nematode Gnathostoma spinigerum and/or Gnathostoma hispidum, which infects vertebrates.

Baylisascaris is a genus of roundworms that infect more than fifty animal species.

The Toxocaridae are a zoonotic family of parasitic nematodes that infect canids and felids and which cause toxocariasis in humans. The worms are unable to reproduce in humans.

Cutaneous larva migrans is a skin disease in humans, caused by the larvae of various nematode parasites of the hookworm family (Ancylostomatidae). The parasites live in the intestines of dogs, cats, and wild animals; they should not be confused with other members of the hookworm family for which humans are definitive hosts, namely Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus.

Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are a polyphyletic group of large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other parasitic worms such as schistosomes reside in blood vessels.
Visceral larva migrans (VLM) is a condition in humans caused by the migratory larvae of certain nematodes, humans being a dead-end host, and was first reported in 1952. Nematodes causing such zoonotic infections are Baylisascaris procyonis, Toxocara canis, Toxocara cati, and Ascaris suum. These nematodes can infect but not mature in humans and after migrating through the intestinal wall, travel with the blood stream to various organs where they cause inflammation and damage. Affected organs can include the liver, heart and the CNS. A special variant is ocular larva migrans where usually T. canis larvae travel to the eye.
Larva migrans generally refers to disease caused by the migration of the larvae of a helminth to various tissues. Some variants of larva migrans include:

Ancylostomiasis is a hookworm disease caused by infection with Ancylostoma hookworms. The name is derived from Greek ancylos αγκύλος "crooked, bent" and stoma στόμα "mouth".

Toxocara canis is a worldwide-distributed helminth parasite that primarily infects dogs and other canids, but can also infect other animals including humans. The name is derived from the Greek word "toxon," meaning bow or quiver, and the Latin word "caro," meaning flesh. T. canis live in the small intestine of the definitive host. This parasite is very common in puppies and somewhat less common in adult dogs. In adult dogs, infection is usually asymptomatic but may be characterized by diarrhea. By contrast, untreated infection with Toxocara canis can be fatal in puppies, causing diarrhea, vomiting, pneumonia, enlarged abdomen, flatulence, poor growth rate, and other complications.
Angiostrongyliasis is an infection by a roundworm of the Angiostrongylus type. Symptoms may vary from none, to mild, to meningitis.

Toxocara cati, also known as the feline roundworm, is a parasite of cats and other felids. It is one of the most common nematodes of cats, infecting both wild and domestic felids worldwide. Adult worms are localised in the gut of the host. In adult cats, the infection – which is called toxocariasis – is usually asymptomatic. However, massive infection in juvenile cats can be fatal.

Toxascaris leonina is a common parasitic roundworm found in dogs, cats, foxes, and related host species. T. leonina is an ascarid nematode, a worldwide distributed helminth parasite which is in a division of eukaryotic parasites that, unlike external parasites such as lice and fleas, live inside their host. The definitive hosts of T. leonina include canids and felines (cats), while the intermediate hosts are usually rodents, such as mice or rats. Infection occurs in the definitive host when the animal eats an infected rodent. While T. leonina can occur in either dogs or cats, it is far more frequent in cats.

Baylisascaris procyonis, also known by the common name raccoon roundworm, is a roundworm nematode, found ubiquitously in raccoons, the definitive hosts. It is named after H. A. Baylis, who studied them in the 1920s–30s, and Greek askaris. Baylisascaris larvae in paratenic hosts can migrate, causing larva migrans. Baylisascariasis as the zoonotic infection of humans is rare, though extremely dangerous due to the ability of the parasite's larvae to migrate into brain tissue and cause damage. Concern for human infection has been increasing over the years due to the urbanization of rural areas, resulting in the increase in proximity and potential human interaction with raccoons.
Gnathostoma hispidum is a nematode (roundworm) that infects many vertebrate animals including humans. Infection of Gnathostoma hispidum, like many species of Gnathostoma causes the disease gnathostomiasis due to the migration of immature worms in the tissues.

Retinal vasculitis is inflammation of the vascular branches of the retinal artery, caused either by primary ocular disease processes, or as a specific presentation of any systemic form of vasculitis such as Behçet's disease, sarcoidosis, multiple sclerosis, or any form of systemic necrotizing vasculitis such as temporal arteritis, polyarteritis nodosa, and granulomatosis with polyangiitis, or due to lupus erythematosus, or rheumatoid arthritis. Eales disease, pars planitis, birdshot retinochoroidopathy, and Fuchs heterochromic iridocyclitis (FHI) can also cause retinal vasculitis. Infectious pathogens such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, visceral larva migrans can also cause retinal vasculitis. Drug-induced vasculitis may involve retina as well, as seen in methamphetamine induced vasculitis.
Toxocara malayasiensis is a species of feline roundworm, a parasite which infects the intestine of cats. Feline roundworms are passed in the fecal matter of cats, and can be transmitted to humans, causing toxocariasis, a potentially serious disease.
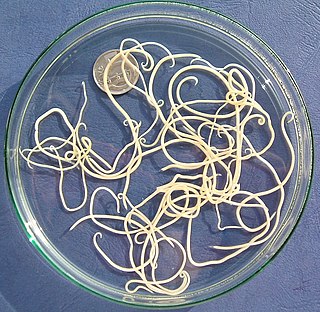
Nematode infection in dogs - the infection of dogs with parasitic nemamotodes - are, along with tapeworm infections and infections with protozoa, frequent parasitoses in veterinary practice. Nematodes, as so-called endoparasites, colonize various internal organs - most of them the digestive tract - and the skin. To date, about 30 different species of nematode have been identified in domestic dogs; they are essentially also found in wild dog species. However, the majority of them often cause no or only minor symptoms of disease in adult animals. The infection therefore does not necessarily have to manifest itself in a worm disease (helminthosis). For most nematodes, an infection can be detected by examining the feces for eggs or larvae. Roundworm infection in dogs and the hookworm in dogs is of particular health significance in Central Europe, as they can also be transmitted to humans (zoonosis). Regular deworming can significantly reduce the frequency of infection and thus the risk of infection for humans and dogs.













