
The statute of frauds is the requirement that certain kinds of contracts be memorialized in writing, signed by the party against whom they are to be enforced, with sufficient content to evidence the contract.

Sales are activities related to selling or the number of goods sold in a given targeted time period. The delivery of a service for a cost is also considered a sale.

The Uniform Commercial Code (UCC), first published in 1952, is one of a number of Uniform Acts that have been established as law with the goal of harmonizing the laws of sales and other commercial transactions across the United States through UCC adoption by all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and the Territories of the United States.
The Incoterms or International Commercial Terms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) relating to international commercial law. They are widely used in international commercial transactions or procurement processes and their use is encouraged by trade councils, courts and international lawyers. A series of three-letter trade terms related to common contractual sales practices, the Incoterms rules are intended primarily to clearly communicate the tasks, costs, and risks associated with the global or international transportation and delivery of goods. Incoterms inform sales contracts defining respective obligations, costs, and risks involved in the delivery of goods from the seller to the buyer, but they do not themselves conclude a contract, determine the price payable, currency or credit terms, govern contract law or define where title to goods transfers.
Caveat emptor is Latin for "Let the buyer beware". It has become a proverb in English. Generally, caveat emptor is the contract law principle that controls the sale of real property after the date of closing, but may also apply to sales of other goods. The phrase caveat emptor and its use as a disclaimer of warranties arises from the fact that buyers typically have less information than the seller about the good or service they are purchasing. This quality of the situation is known as 'information asymmetry'. Defects in the good or service may be hidden from the buyer, and only known to the seller.
In business or commerce, an order is a stated intention, either spoken or written, to engage in a commercial transaction for specific products or services. From a buyer's point of view it expresses the intention to buy and is called a purchase order. From a seller's point of view it expresses the intention to sell and is referred to as a sales order. When the purchase order of the buyer and the sales order of the seller agree, the orders become a contract between the buyer and seller.
The law of agency is an area of commercial law dealing with a set of contractual, quasi-contractual and non-contractual fiduciary relationships that involve a person, called the agent, that is authorized to act on behalf of another to create legal relations with a third party. Succinctly, it may be referred to as the equal relationship between a principal and an agent whereby the principal, expressly or implicitly, authorizes the agent to work under their control and on their behalf. The agent is, thus, required to negotiate on behalf of the principal or bring them and third parties into contractual relationship. This branch of law separates and regulates the relationships between:
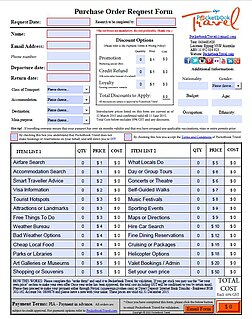
A purchase order (PO) is a commercial document and first official offer issued by a buyer to a seller, indicating types, quantities, and agreed prices for products or services. It is used to control the purchasing of products and services from external suppliers. Purchase orders can be an essential part of enterprise resource planning system orders.

A letter of credit (LC), also known as a documentary credit or bankers commercial credit, or letter of undertaking (LoU), is a payment mechanism used in international trade to provide an economic guarantee from a creditworthy bank to an exporter of goods. Letters of credit are used extensively in the financing of international trade, when the reliability of contracting parties cannot be readily and easily determined. Its economic effect is to introduce a bank as an underwriter that assumes the counterparty risk of the buyer paying the seller for goods.
In contract law, a warranty is a promise which is not a condition of the contract or an innominate term: (1) it is a term "not going to the root of the contract", and (2) which only entitles the innocent party to damages if it is breached: i.e. the warranty is not true or the defaulting party does not perform the contract in accordance with the terms of the warranty. A warranty is not a guarantee. It is a mere promise. It may be enforced if it is breached by an award for the legal remedy of damages.
A bulk sale, sometimes called a bulk transfer, is when a business sells all or nearly all of its inventory to a single buyer and such a sale is not part of the ordinary course of business. This type of action is often used in an attempt to dodge creditors who intend to seize such business's inventory; in order to protect the purchaser from claims made by creditors of the seller, the seller must usually complete an affidavit outlining its secured and unsecured creditors, which must usually be filed with a government department, such as a court office. Such procedures are outlined in the bulk sales act of most jurisdictions. If the buyer does not complete the registration process for a bulk sale, creditors of the seller may obtain a declaration that the sale was invalid against the creditors and the creditors may take possession of the goods or obtain judgment for any proceeds the buyer received from a subsequent sale.

In common law jurisdictions, an implied warranty is a contract law term for certain assurances that are presumed to be made in the sale of products or real property, due to the circumstances of the sale. These assurances are characterized as warranties regardless of whether the seller has expressly promised them orally or in writing. They include an implied warranty of fitness for a particular purpose, an implied warranty of merchantability for products, implied warranty of workmanlike quality for services, and an implied warranty of habitability for a home.

Lost volume seller is a legal term in the law of contracts. Such a seller is a special case in contract law. Ordinarily, a seller whose buyer breaches a contract and refuses to purchase the goods can recover from the breaching buyer only the difference between the contract price and the price for which the seller ultimately sells the goods to another buyer.

The United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (CISG), sometimes known as the Vienna Convention, is a multilateral treaty that establishes a uniform framework for international commerce. As of 2022, it has been ratified by 95 countries, representing two-thirds of world trade.
A retention of title clause is a provision in a contract for the sale of goods that the title to the goods remains vested in the seller until the buyer fulfils certain obligations.

Canadian contract law is composed of two parallel systems: a common law framework outside Québec and a civil law framework within Québec. Outside Québec, Canadian contract law is derived from English contract law, though it has developed distinctly since Canadian Confederation in 1867. While Québecois contract law was originally derived from that which existed in France at the time of Québec's annexation into the British Empire, it was overhauled and codified first in the Civil Code of Lower Canada and later in the current Civil Code of Quebec, which codifies most elements of contract law as part of its provisions on the broader law of obligations. Individual common law provinces have codified certain contractual rules in a Sale of Goods Act, resembling equivalent statutes elsewhere in the Commonwealth. As most aspects of contract law in Canada are the subject of provincial jurisdiction under the Canadian Constitution, contract law may differ even between the country's common law provinces and territories. Conversely; as the law regarding bills of exchange and promissory notes, trade and commerce, maritime law, and banking among other related areas is governed by federal law under Section 91 of the Constitution Act, 1867; aspects of contract law pertaining to these topics are harmonised between Québec and the common law provinces.

The Sale of Goods Act 1979 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which regulated English contract law and UK commercial law in respect of goods that are sold and bought. The Act consolidated the original Sale of Goods Act 1893 and subsequent legislation, which in turn had codified and consolidated the law. Since 1979, there have been numerous minor statutory amendments and additions to the 1979 Act. It was replaced for some aspects of consumer contracts from 1 October 2015 by the Consumer Rights Act 2015 but remains the primary legislation underpinning business-to-business transactions involving selling or buying goods.
International Commercial Law is a body of legal rules, conventions, treaties, domestic legislation and commercial customs or usages, that governs international commercial or business transactions. A transaction will qualify to be international if elements of more than one country are involved.

A contract is a legally enforceable agreement that creates, defines, and governs mutual rights and obligations among its parties. A contract typically involves the transfer of goods, services, money, or a promise to transfer any of those at a future date. In the event of a breach of contract, the injured party may seek judicial remedies such as damages or rescission. Contract law, the field of the law of obligations concerned with contracts, is based on the principle that agreements must be honoured.

The Indian Sale of Goods Act, 1930 is a mercantile law which came into existence on 1 July 1930, during the British Raj, borrowing heavily from the United Kingdom's Sale of Goods Act 1893. It provides for the setting up of contracts where the seller transfers or agrees to transfer the title (ownership) in the goods to the buyer for consideration. It is applicable all over India. Under the act, goods sold from owner to buyer must be sold for a certain price and at a given period of time. The act was amended on 23 September 1963, and was renamed to the Sale of Goods Act, 1930. It is still in force in India, after being amended in 1963, and in Bangladesh, as the Sale of Goods Act, 1930 (Bangladesh).








