Related Research Articles

The endomembrane system is composed of the different membranes (endomembranes) that are suspended in the cytoplasm within a eukaryotic cell. These membranes divide the cell into functional and structural compartments, or organelles. In eukaryotes the organelles of the endomembrane system include: the nuclear membrane, the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vesicles, endosomes, and plasma (cell) membrane among others. The system is defined more accurately as the set of membranes that forms a single functional and developmental unit, either being connected directly, or exchanging material through vesicle transport. Importantly, the endomembrane system does not include the membranes of plastids or mitochondria, but might have evolved partially from the actions of the latter.
Azotemia, also spelled azotaemia, is a medical condition characterized by abnormally high levels of nitrogen-containing compounds in the blood. It is largely related to insufficient or dysfunctional filtering of blood by the kidneys. It can lead to uremia and acute kidney injury if not controlled.
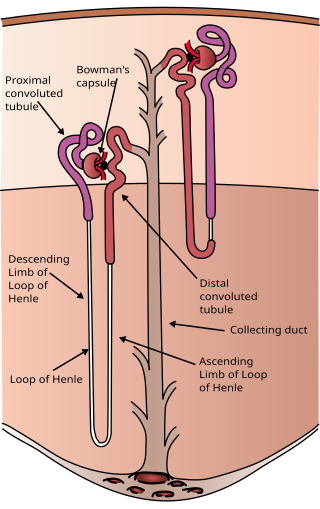
The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structure called Bowman's capsule. The renal tubule extends from the capsule. The capsule and tubule are connected and are composed of epithelial cells with a lumen. A healthy adult has 1 to 1.5 million nephrons in each kidney. Blood is filtered as it passes through three layers: the endothelial cells of the capillary wall, its basement membrane, and between the podocyte foot processes of the lining of the capsule. The tubule has adjacent peritubular capillaries that run between the descending and ascending portions of the tubule. As the fluid from the capsule flows down into the tubule, it is processed by the epithelial cells lining the tubule: water is reabsorbed and substances are exchanged ; first with the interstitial fluid outside the tubules, and then into the plasma in the adjacent peritubular capillaries through the endothelial cells lining that capillary. This process regulates the volume of body fluid as well as levels of many body substances. At the end of the tubule, the remaining fluid—urine—exits: it is composed of water, metabolic waste, and toxins.
Diuresis is the excretion of urine, especially when excessive (polyuria). The term collectively denotes the physiologic processes underpinning increased urine production by the kidneys during maintenance of fluid balance.

Renal physiology is the study of the physiology of the kidney. This encompasses all functions of the kidney, including maintenance of acid-base balance; regulation of fluid balance; regulation of sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes; clearance of toxins; absorption of glucose, amino acids, and other small molecules; regulation of blood pressure; production of various hormones, such as erythropoietin; and activation of vitamin D.

The proximal tubule is the segment of the nephron in kidneys which begins from the renal pole of the Bowman's capsule to the beginning of loop of Henle. At this location, the glomerular parietal epithelial cells (PECs) lining bowman’s capsule abruptly transition to proximal tubule epithelial cells (PTECs). The proximal tubule can be further classified into the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) and the proximal straight tubule (PST).

In the kidney, the loop of Henle is the portion of a nephron that leads from the proximal convoluted tubule to the distal convoluted tubule. Named after its discoverer, the German anatomist Friedrich Gustav Jakob Henle, the loop of Henle's main function is to create a concentration gradient in the medulla of the kidney.
The syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH), also known as the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis (SIAD), is characterized by a physiologically inappropriate release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) either from the posterior pituitary gland, or an abnormal non-pituitary source. Unsuppressed ADH causes a physiologically inappropriate increase in solute-free water being reabsorbed by the tubules of the kidney to the venous circulation leading to hypotonic hyponatremia.
An osmotic diuretic is a type of diuretic that inhibits reabsorption of water and sodium (Na). They are pharmacologically inert substances that are given intravenously. They increase the osmolarity of blood and renal filtrate. This fluid eventually becomes urine.
Acute tubular necrosis (ATN) is a medical condition involving the death of tubular epithelial cells that form the renal tubules of the kidneys. Because necrosis is often not present, the term acute tubular injury (ATI) is preferred by pathologists over the older name acute tubular necrosis (ATN). ATN presents with acute kidney injury (AKI) and is one of the most common causes of AKI. Common causes of ATN include low blood pressure and use of nephrotoxic drugs. The presence of "muddy brown casts" of epithelial cells found in the urine during urinalysis is pathognomonic for ATN. Management relies on aggressive treatment of the factors that precipitated ATN. Because the tubular cells continually replace themselves, the overall prognosis for ATN is quite good if the underlying cause is corrected, and recovery is likely within 7 to 21 days.

A contractile vacuole (CV) is a sub-cellular structure (organelle) involved in osmoregulation. It is found predominantly in protists and in unicellular algae. It was previously known as pulsatile or pulsating vacuole.

Renal tubular acidosis (RTA) is a medical condition that involves an accumulation of acid in the body due to a failure of the kidneys to appropriately acidify the urine. In renal physiology, when blood is filtered by the kidney, the filtrate passes through the tubules of the nephron, allowing for exchange of salts, acid equivalents, and other solutes before it drains into the bladder as urine. The metabolic acidosis that results from RTA may be caused either by insufficient secretion of hydrogen ions into the latter portions of the nephron or by failure to reabsorb sufficient bicarbonate ions from the filtrate in the early portion of the nephron. Although a metabolic acidosis also occurs in those with chronic kidney disease, the term RTA is reserved for individuals with poor urinary acidification in otherwise well-functioning kidneys. Several different types of RTA exist, which all have different syndromes and different causes. RTA is usually an incidental finding based on routine blood draws that show abnormal results. Clinically, patients may present with vague symptoms such as dehydration, mental status changes, or delayed growth in adolescents.
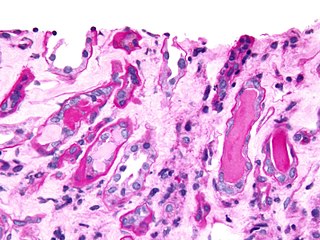
Urinary casts are microscopic cylindrical structures produced by the kidney and present in the urine in certain disease states. They form in the distal convoluted tubule and collecting ducts of nephrons, then dislodge and pass into the urine, where they can be detected by microscopy.
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, recently renamed arginine vasopressin resistance (AVP-R) and previously known as renal diabetes insipidus, is a form of diabetes insipidus primarily due to pathology of the kidney. This is in contrast to central or neurogenic diabetes insipidus, which is caused by insufficient levels of vasopressin. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is caused by an improper response of the kidney to vasopressin, leading to a decrease in the ability of the kidney to concentrate the urine by removing free water.
A countercurrent mechanism system is a mechanism that expends energy to create a concentration gradient.
Osmoregulation is the active regulation of the osmotic pressure of an organism's body fluids, detected by osmoreceptors, to maintain the homeostasis of the organism's water content; that is, it maintains the fluid balance and the concentration of electrolytes to keep the body fluids from becoming too diluted or concentrated. Osmotic pressure is a measure of the tendency of water to move into one solution from another by osmosis. The higher the osmotic pressure of a solution, the more water tends to move into it. Pressure must be exerted on the hypertonic side of a selectively permeable membrane to prevent diffusion of water by osmosis from the side containing pure water.

The organic anion transporter 1 (OAT1) also known as solute carrier family 22 member 6 (SLC22A6) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC22A6 gene. It is a member of the organic anion transporter (OAT) family of proteins. OAT1 is a transmembrane protein that is expressed in the brain, the placenta, the eyes, smooth muscles, and the basolateral membrane of proximal tubular cells of the kidneys. It plays a central role in renal organic anion transport. Along with OAT3, OAT1 mediates the uptake of a wide range of relatively small and hydrophilic organic anions from plasma into the cytoplasm of the proximal tubular cells of the kidneys. From there, these substrates are transported into the lumen of the nephrons of the kidneys for excretion. OAT1 homologs have been identified in rats, mice, rabbits, pigs, flounders, and nematodes.
Fanconi syndrome or Fanconi's syndrome is a syndrome of inadequate reabsorption in the proximal renal tubules of the kidney. The syndrome can be caused by various underlying congenital or acquired diseases, by toxicity, or by adverse drug reactions. It results in various small molecules of metabolism being passed into the urine instead of being reabsorbed from the tubular fluid. Fanconi syndrome affects the proximal tubules, namely, the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT), which is the first part of the tubule to process fluid after it is filtered through the glomerulus, and the proximal straight tubule, which leads to the descending limb of loop of Henle.

A diuretic is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from the body, through the kidneys. There exist several classes of diuretic, and each works in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin, is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine.
The rock dove, Columbia livia, has a number of special adaptations for regulating water uptake and loss.
References
- Dickenmann M, Oettl T, & Mihatsch MJ. (2008) Osmotic nephrosis: Acute kidney injury with accumulation of proximal tubular lysosomes due to administration of exogenous solutes. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 51(3), 491–503. Retrieved 9 Mar 2008 from MDConsult database.