
Vitiligo is a long-term skin condition characterized by patches of the skin losing their pigment. The patches of skin affected become white and usually have sharp margins. The hair from the skin may also become white. The inside of the mouth and nose may also be involved. Typically both sides of the body are affected. Often the patches begin on areas of skin that are exposed to the sun. It is more noticeable in people with dark skin. Vitiligo may result in psychological stress and those affected may be stigmatized.

Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta (PLEVA) is a disease of the immune system. It is the more severe version of pityriasis lichenoides chronica. The disease is characterized by rashes and small lesions on the skin. The disease is more common in males and usually occurs in young adulthood, although it has been seen in every age group and every race. It is possible for the disease to go into remission for short periods of time or forever.
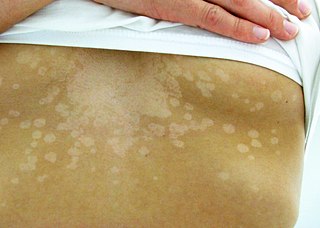
Tinea versicolor is a condition characterized by a skin eruption on the trunk and proximal extremities. The majority of tinea versicolor is caused by the fungus Malassezia globosa, although Malassezia furfur is responsible for a small number of cases. These yeasts are normally found on the human skin and become troublesome only under certain circumstances, such as a warm and humid environment, although the exact conditions that cause initiation of the disease process are poorly understood.

Darier's disease (DAR), also known as Darier disease, Darier–White disease, Dyskeratosis follicularis, and Keratosis follicularis, is an autosomal dominant disorder discovered by French dermatologist Ferdinand-Jean Darier. Darier's is characterized by dark crusty patches on the skin, sometimes containing pus. The crusty patches are also known as keratotic papules, keratosis follicularis, or dyskeratosis follicularis.
A dermatofibroma, or benign fibrous histiocytomas, is a benign skin growth.

Palmoplantar keratodermas are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by abnormal thickening of the palms and soles.
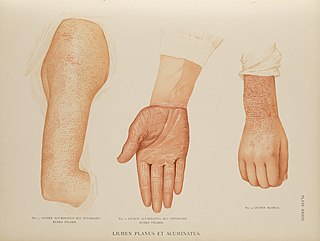
Pityriasis rubra pilaris refers to a group of chronic disorders characterized by reddish orange, scaling plaques and keratotic follicular papules. Symptoms may include reddish-orange patches on the skin, severe flaking, uncomfortable itching, thickening of the skin on the feet and hands, and thickened bumps around hair follicles. For some, early symptoms may also include generalized swelling of the legs, feet and other parts of the body. PRP has a varied clinical progression and a varied rate of improvement. There is currently no known cause or cure for PRP.
Parapsoriasis refers to one of a group of skin disorders that are characterized primarily by their resemblance to psoriasis, rather than by their underlying cause.

Degos disease, also known as Köhlmeier-Degos disease ormalignant atrophic papulosis(MAP), is an extremely rare condition caused by blockage of arteries and veins. Individuals with this condition will develop papules. Those diagnosed with this disease may also develop complications due to impairment of internal organs. The exact underlying mechanism is still unknown, and an effective treatment is still being developed. There are fewer than 50 living patients presently known worldwide, and fewer than 200 reported in medical literature. However, it is important to note that many individuals may go undiagnosed due to rarity of the disease. Most individuals develop symptoms between the ages of 20-50; however, cases outside of this age range have been reported as well.
Lichen spinulosus is a rare skin disorder characterized by follicular keratotic papules that are grouped into large patches. It is a variant of keratosis pilaris named for its resemblance to a patch of lichen.
Pityriasis alba is a common skin condition mostly occurring in children and young adults usually seen as dry, fine-scaled, pale patches on the face. It is self-limiting and usually only requires use of moisturizer creams.
Dermatoses of pregnancy are the inflammatory skin diseases that are specific to women while they are pregnant. While some use the term 'polymorphic eruption of pregnancy' to cover these, this term is a synonym used in the UK for Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy, which is the commonest of these skin conditions.

Marie-Guillaume-Alphonse Devergie was a French dermatologist born in Paris.

Camille-Melchior Gibert was a French dermatologist who was a native of Paris.
Gianotti–Crosti syndrome, also known as infantile papular acrodermatitis, papular acrodermatitis of childhood, and papulovesicular acrolocated syndrome, is a reaction of the skin to a viral infection. Hepatitis B virus and Epstein–Barr virus are the most frequently reported pathogens. Other incriminated viruses are hepatitis A virus, hepatitis C virus, cytomegalovirus, coxsackievirus, adenovirus, enterovirus, rotavirus, rubella virus, HIV, and parainfluenza virus.
Acrokeratosis verruciformis (also known as "Acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf" is a rare autosomal dominant disorder appearing at birth or in early childhood, characterized by skin lesions that are small, verrucous, flat papules resembling warts along with palmoplantar punctate keratoses and pits. However sporadic forms, whose less than 10 cases have been reported, presents at a later age, usually after the first decade and generally lack palmoplantar keratoses. Whether acrokeratosis verruciformis and Darier disease are related or distinct entities has been controversial, like Darier's disease, it is associated with defects in the ATP2A2 gene. however the specific mutations found in the ATP2A2 gene in acrokeratosis verruciformis have never been found in Darier's disease.

Porokeratosis is a specific disorder of keratinization that is characterized histologically by the presence of a cornoid lamella, a thin column of closely stacked, parakeratotic cells extending through the stratum corneum with a thin or absent granular layer.
Malassezia sympodialis is a species in the genus Malassezia. It is characterized by a pronounced lipophily, unilateral, percurrent or sympodial budding and an irregular, corrugated cell wall ultrastructure. It is one of the most common species found on the skin of healthy and diseased individuals. It is considered to be part of the skin's normal human microbiota and begins to colonize the skin of humans shortly after birth. Malassezia sympodialis, often has a symbiotic or commensal relationship with its host, but it can act as a pathogen causing a number of different skin diseases, such as atopic dermatitis.














