
Streaming media is multimedia that is constantly received by and presented to an end-user while being delivered by a provider. The verb to stream refers to the process of delivering or obtaining media in this manner. Streaming refers to the delivery method of the medium, rather than the medium itself. Distinguishing delivery method from the media distributed applies specifically to telecommunications networks, as most of the delivery systems are either inherently streaming or inherently non-streaming. There are challenges with streaming content on the Internet. For example, users whose Internet connection lacks sufficient bandwidth may experience stops, lags, or slow buffering of the content. And users lacking compatible hardware or software systems may be unable to stream certain content.

Video on Demand (VoD) is a media distribution system that allows users to access videos without a traditional video playback device and the constraints of a typical static broadcasting schedule. In the 20th century, broadcasting in the form of over-the-air programming was the most common form of media distribution. As Internet and IPTV technologies continued to develop in the 1990s, consumers began to gravitate towards non-traditional modes of content consumption, which culminated in the arrival of VoD on televisions and personal computers.

Interactive television is a form of media convergence, adding data services to traditional television technology. Throughout its history, these have included on-demand delivery of content, as well as new uses such as online shopping, banking, and so forth. Interactive TV is a concrete example of how new information technology can be integrated vertically rather than laterally.

Streaming television is the digital distribution of television content, such as TV shows, as streaming media delivered over the Internet. Streaming TV stands in contrast to dedicated terrestrial television delivered by over-the-air aerial systems, cable television, and/or satellite television systems. The use of streaming online video and web television by consumers has seen a dramatic increase ever since the launch of online video platforms such as YouTube and Netflix.

Internet Protocol television (IPTV) is the delivery of television content over Internet Protocol (IP) networks. This is in contrast to delivery through traditional terrestrial, satellite, and cable television formats. Unlike downloaded media, IPTV offers the ability to stream the source media continuously. As a result, a client media player can begin playing the content almost immediately. This is known as streaming media.
Mobile content is any type of electronic media which is viewed or used on mobile phones, like ringtones, graphics, discount offers, games, movies, and GPS navigation. As mobile phone use has grown since the mid-1990s, the significance of the devices in everyday life has grown accordingly. Owners of mobile phones can now use their devices to make calendar appointments, send and receive text messages (SMS), listen to music, watch videos, shoot videos, redeem coupons for purchases, view office documents, get driving instructions on a map, and so forth. The use of mobile content has grown accordingly.
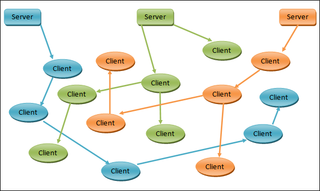
P2PTV refers to peer-to-peer (P2P) software applications designed to redistribute video streams in real time on a P2P network; the distributed video streams are typically TV channels from all over the world but may also come from other sources. The draw to these applications is significant because they have the potential to make any TV channel globally available by any individual feeding the stream into the network where each peer joining to watch the video is a relay to other peer viewers, allowing a scalable distribution among a large audience with no incremental cost for the source.

TVU Networks Corporation is a technology company that provides IP-based live video solutions. The company, which was founded in 2005, is headquartered in Mountain View, California and also has offices in Raleigh, North Carolina, Shanghai and Beijing, China, Uttar Pradesh, India and Barcelona, Spain.

Mobile television is television watched on a small handheld or mobile device. It includes service delivered via mobile phone networks, received free-to-air via terrestrial television stations, or via satellite broadcast. Regular broadcast standards or special mobile TV transmission formats can be used. Additional features include downloading TV programs and podcasts from the Internet and storing programming for later viewing.
Live streaming refers to online streaming media simultaneously recorded and broadcast in real-time. It is often referred to simply as streaming, but this abbreviated term is ambiguous because "streaming" may refer to any media delivered and played back simultaneously without requiring a completely downloaded file. Non-live media such as video-on-demand, vlogs, and YouTube videos are technically streamed, but not live-streamed.
Social media marketing is the use of social media platforms and websites to promote a product or service. Although the terms e-marketing and digital marketing are still dominant in academia, social media marketing is becoming more popular for both practitioners and researchers. Most social media platforms have built-in data analytics tools, enabling companies to track the progress, success, and engagement of ad campaigns. Companies address a range of stakeholders through social media marketing, including current and potential customers, current and potential employees, journalists, bloggers, and the general public. On a strategic level, social media marketing includes the management of a marketing campaign, governance, setting the scope and the establishment of a firm's desired social media "culture" and "tone."

A smart TV, also known as a connected TV (CTV), is a traditional television set with integrated Internet and interactive Web 2.0 features, which allows users to stream music and videos, browse the internet, and view photos. Smart TV is a technological convergence of computers, television sets, and set-top boxes. Besides the traditional functions of television sets and set-top boxes provided through traditional broadcasting media, these devices can provide Internet TV, online interactive media, over-the-top content (OTT) as well as on-demand streaming media, and home networking access.
A second screen involves the use of a computing device to provide an enhanced viewing experience for content on another device, such as a television. In particular, the term commonly refers to the use of such devices to provide interactive features during broadcast content, such as a television program, especially social media postings on social networking platforms, such as Facebook and Twitter. This type of technology is designed to keep an audience engaged in whatever they are involved in. The use of a second screen supports social television and generates an online conversation around the specific content.

Social media and television broadcasting have a number of connections and interrelationships. In the 2010s, social media technologies and websites allow for television shows to be accessed online on a range of desktop and mobile computer devices, smartphones and smart TVs. As well, online users can use social media websites to share digital video clips or excerpts from TV shows with fellow fans or even share an entire show online. Many social media websites enable users to post online comments on the programs—both negative and positive—in a variety of ways. Viewers can actively participate while watching a TV program by posting comments online, and have their interactions viewed and responded to in real time by other viewers. Technologies such as smartphones, tablets, and laptop computers allow viewers to watch downloaded digital files of TV shows or "stream" digital files of TV shows on a range of devices, both in the home and while on the go. In the 2010s, some television producers and broadcasters are encouraging active social media participation by viewers by posting "hashtags" on the TV screen during shows; these hashtags enable viewers to post online comments about the show, which may either be read by other social media users, or even, in some cases, displayed on the screen.
An online video platform (OVP), provided by a video hosting service, enables users to upload, convert, store and play back video content on the Internet, often via a structured, large-scale system that may generate revenue. Users generally will upload video content via the hosting service's website, mobile or desktop application, or other interface (API). The type of video content uploaded might be anything from shorts to full-length TV shows and movies. The video host stores the video on its server and offers users the ability to enable different types of embed codes or links that allow others to view the video content. The website, mainly used as the video hosting website, is usually called the video sharing website.

A mukbang, also spelled meokbang and also known as eating show, is an online audiovisual broadcast in which a host consumes large quantities of food while interacting with the audience. It became popular in South Korea in 2010, and since then it has become a worldwide trend. Varieties of foods, ranging from pizza to noodles, are consumed in front of a camera.
Non-linear media is a form of media that can be interacted with by the consumer, such as by selecting television shows to watch through a video on demand type service, by playing a video game, by clicking through a website, or by interacting through social media. Non-linear media is a move away from traditional linear media, in which content is selected by the publisher to be consumed and is then done so passively. There is no single specific form of non-linear media; rather, what might be considered non-linear changes as technology changes.
Mobibase is a France-based company., publishing and distributing ethnic and thematic TV channels and VOD content to mobile publishers, operators, cable and satellite TV and IPTV/OTT services in Europe, the Americas, Middle East, and Africa
An online streamer, also known as a live streamer, internet streamer, or streamer, is a person who broadcasts themselves online through a live stream or prerecorded video. The scope of online streamers has grown to include different genres ranging from playing video games, tutorials, or even solo chats.
Live streaming world news refers to live videos streams of world television news which are provided via streaming television or via streaming media by various television networks and television news outlets, from various countries. These are provided through Smart TV, or else through the networks' own websites, or also possibly via internet television, especially YouTube, or via video on demand services, subscription video on demand websites such as e.g. Hulu, mobile apps, or digital media players that are designed to play streaming television, such as e.g. the Roku media player.