
Phenytoin (PHT), sold under the brand name Dilantin among others, is an anti-seizure medication. It is useful for the prevention of tonic-clonic seizures and focal seizures, but not absence seizures. The intravenous form, fosphenytoin, is used for status epilepticus that does not improve with benzodiazepines. It may also be used for certain heart arrhythmias or neuropathic pain. It can be taken intravenously or by mouth. The intravenous form generally begins working within 30 minutes and is effective for roughly 24 hours. Blood levels can be measured to determine the proper dose.
Anticonvulsants are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Anticonvulsants suppress the excessive rapid firing of neurons during seizures. Anticonvulsants also prevent the spread of the seizure within the brain.
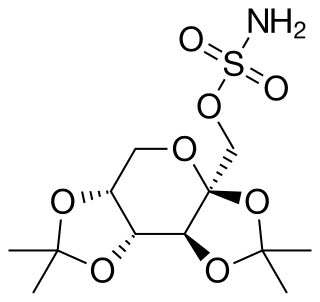
Topiramate, sold under the brand name Topamax among others, is a medication used to treat epilepsy and prevent migraines. It has also been used in alcohol dependence and essential tremor. For epilepsy this includes treatment for generalized or focal seizures. It is taken orally.

Duloxetine, sold under the brand name Cymbalta among others, is a medication used to treat major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, fibromyalgia, neuropathic pain and central sensitization. It is taken by mouth.

Fenfluramine, sold under the brand name Fintepla, is a serotonergic medication used for the treatment of seizures associated with Dravet syndrome and Lennox–Gastaut syndrome. It was formerly used as an appetite suppressant in the treatment of obesity, but was discontinued for this use due to cardiovascular toxicity before being repurposed for new indications. Fenfluramine was used for weight loss both alone under the brand name Pondimin and in combination with phentermine commonly known as fen-phen.
Anti-obesity medication or weight loss medications are pharmacological agents that reduce or control excess body fat. These medications alter one of the fundamental processes of the human body, weight regulation, by: reducing appetite and consequently energy intake, increasing energy expenditure, redirecting nutrients from adipose to lean tissue, or interfering with the absorption of calories.

Budesonide/formoterol, sold under the brand name Symbicort among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication used in the management of asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It contains budesonide, a steroid and formoterol, a long-acting β2-agonist (LABA). The product monograph does not support its use for sudden worsening or treatment of active bronchospasm. However, a 2020 review of the literature does support such use. It is used by breathing in the medication.

Phentermine, sold under the brand name Ionamin among others, is a medication used together with diet and exercise to treat obesity. It is taken by mouth for up to a few weeks at a time, after which the benefits subside. It is also available as the combination phentermine/topiramate.

Desvenlafaxine, sold under the brand name Pristiq among others, is a medication used to treat depression. It is an antidepressant of the serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) class and is taken by mouth. It is recommended that the need for further treatment be occasionally reassessed. It may be less effective than its parent compound venlafaxine, although some studies have found comparable efficacy.
Dexatrim is an over-the-counter (OTC) dietary supplement meant to assist with weight loss. Dexatrim claims it "gives you the power to lose weight, curb binges, and keep you in control of your diet." Current Dexatrim products available are in capsule form and include Dexatrim Max Complex 7, Dexatrim Max Daytime Appetite Control, Dexatrim Natural Green Tea, and Dexatrim Natural Extra Energy. The major active ingredients found in current Dexatrim products include caffeine, green tea extract, Asian (Panax) ginseng root extract, and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA).

Lorcaserin, marketed under the brand name Belviq, was a weight-loss drug developed by Arena Pharmaceuticals. It reduces appetite by activating a type of serotonin receptor known as the 5-HT2C receptor in a region of the brain called the hypothalamus, which is known to control appetite. It was approved in 2012, and in 2020, it was removed from the market in the United States due to an increased risk of cancer detected in users of Belviq.

Naltrexone/bupropion, sold under the brand name Contrave among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication for the management of chronic obesity in adults in combination with a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity. It contains naltrexone, an opioid antagonist, and bupropion, an aminoketone atypical antidepressant. It is taken by mouth. Both medications have individually shown some evidence of effectiveness in weight loss, and the combination has been shown to have some synergistic effects on weight.

Olaparib, sold under the brand name Lynparza, is a medication for the maintenance treatment of BRCA-mutated advanced ovarian cancer in adults. It is a PARP inhibitor, inhibiting poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP), an enzyme involved in DNA repair. It acts against cancers in people with hereditary BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations, which include some ovarian, breast, and prostate cancers.
Vivus is a small pharmaceutical company headquartered in Campbell, California, working in obesity, sleep, and sexual health. Vivus is developing an erectile dysfunction drug, Avanafil, that has completed Phase 3 clinical trials. The drug has been approved for use by the FDA, and will be sold under the trademark name Stendra. Stendra is the first and only oral ED treatment approved to be taken approximately 15 minutes before sexual activity.

Hydrocodone/ibuprofen (INNs), sold under the brand name Vicoprofen, is a fixed-dose combination analgesic medication used in short-term therapy to relieve severe pain. Vicoprofen combines the analgesic and antitussive properties of hydrocodone with the analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties of ibuprofen. In contrast to hydrocodone/acetaminophen combination analgesics such as Vicodin, this hydrocodone/ibuprofen avoids some of the liver toxicity which may occur from acetaminophen, but still presents significant dangers in hydrocodone overdose, namely respiratory depression. Vicoprofen is supplied in a fixed dose combination tablet which contains hydrocodone bitartrate, USP 7.5 mg with ibuprofen, USP 200 mg. Additional strengths of generic Vicoprofen are now available, in combinations of 5 mg/200 mg and 10 mg/200 mg respectively.
Nintedanib, sold under the brand names Ofev and Vargatef, is an oral medication used for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and along with other medications for some types of non-small-cell lung cancer.

Naldemedine is a medication that is used for the treatment of opioid-induced constipation in adults with chronic non-cancer pain. It is a peripherally acting μ-opioid receptor antagonist and was developed by Shionogi. Clinical studies have found it to possess statistically significant effectiveness for these indications and to be generally well tolerated, with predominantly mild to moderate gastrointestinal side effects. Effects indicative of central opioid withdrawal or impact on the analgesic or miotic effects of co-administered opioids have only been observed in a small number of patients.
Dextromethorphan/quinidine, sold under the brand name Nuedexta, is a fixed-dose combination medication for the treatment of pseudobulbar affect (PBA). It contains dextromethorphan (DXM) and the class I antiarrhythmic agent quinidine.

Oliceridine, sold under the brand name Olinvyk, is an opioid medication that is used for the treatment of moderate to severe acute pain in adults. It is given by intravenous (IV) injection.
Netupitant/palonosetron, sold under the brand name Akynzeo, is a fixed-dose combination medication used for the prevention of acute and delayed chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. It is marketed and distributed by Helsinn Therapeutics. Netupitant is an NK1 receptor antagonist and palonosetron is a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist.















